Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2022; 28(24): 2705-2732
Published online Jun 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i24.2705
Published online Jun 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i24.2705
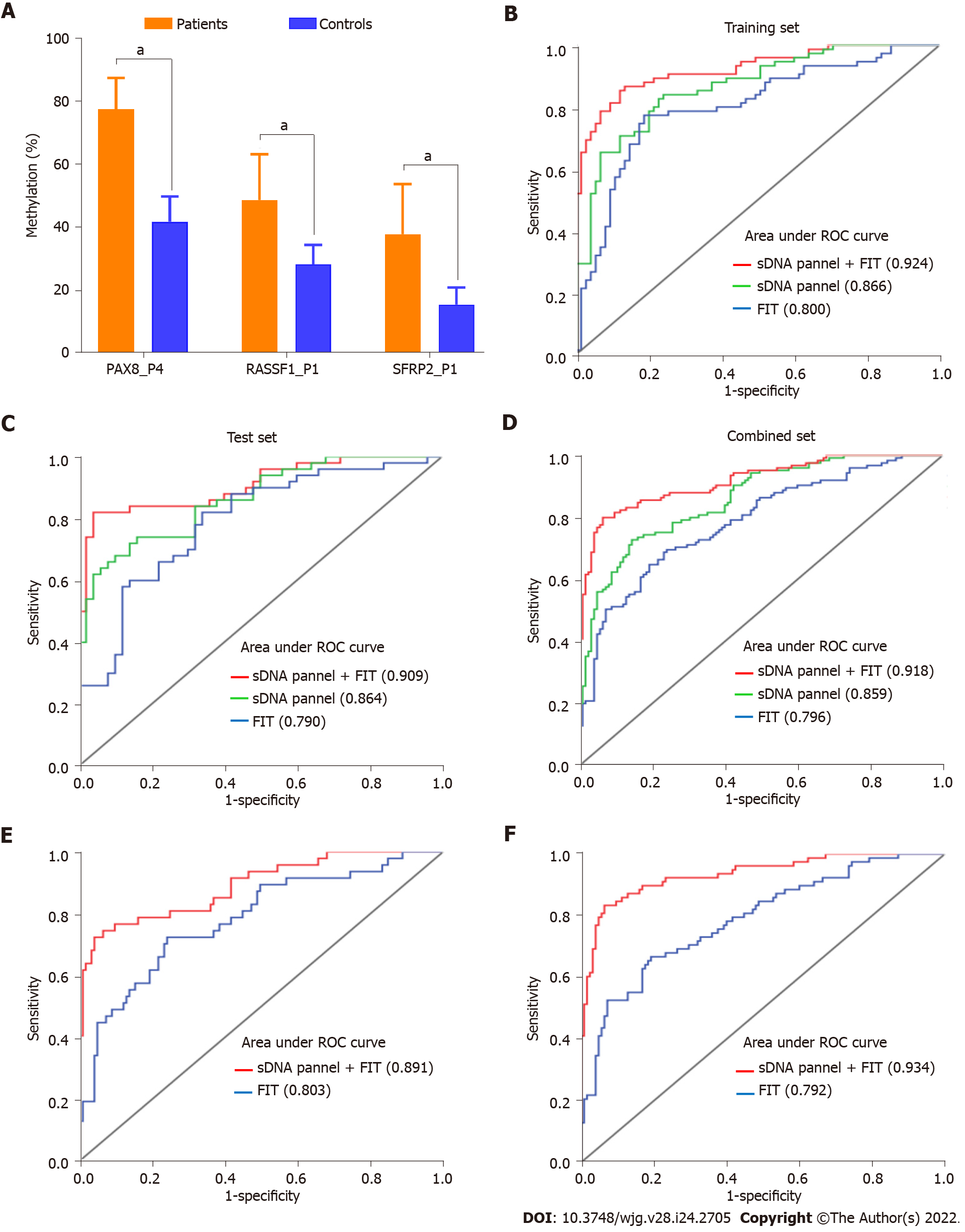
Figure 4 The evaluation of diagnostic model based on pyrosequencing.
A: Comparison of methylation percentage of the three target biomarkers between the patients and controls in training set; B: Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves comparing fecal immunochemical test (FIT), stool DNA (sDNA) panel and sDNA panel + FIT for the detection of early-stage colon cancer (ECC) in training set; C: ROC curves comparing FIT, sDNA panel and sDNA panel + FIT for the detection of ECC in test set; D: ROC curves comparing FIT, sDNA panel and sDNA panel + FIT for the detection of ECC in combined set; E: ROC curves comparing FIT and sDNA panel + FIT for the detection of stage I ECC in combined set; F: ROC curves comparing FIT and sDNA panel + FIT for the detection of stage II ECC in combined set. aP < 0.05. sDNA: Stool DNA; FIT: Fecal immunochemical test; ROC: Receiver operating characteristic; PAX8: Paired box 8; RASSF1: Ras-association domain family 1; SFRP2: Secreted frizzled-related protein 2.
- Citation: Jiang HH, Xing SW, Tang X, Chen Y, Lin K, He LW, Lin MB, Tang EJ. Novel multiplex stool-based assay for the detection of early-stage colon cancer in a Chinese population. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(24): 2705-2732
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i24/2705.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i24.2705