Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2022; 28(22): 2482-2493
Published online Jun 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i22.2482
Published online Jun 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i22.2482
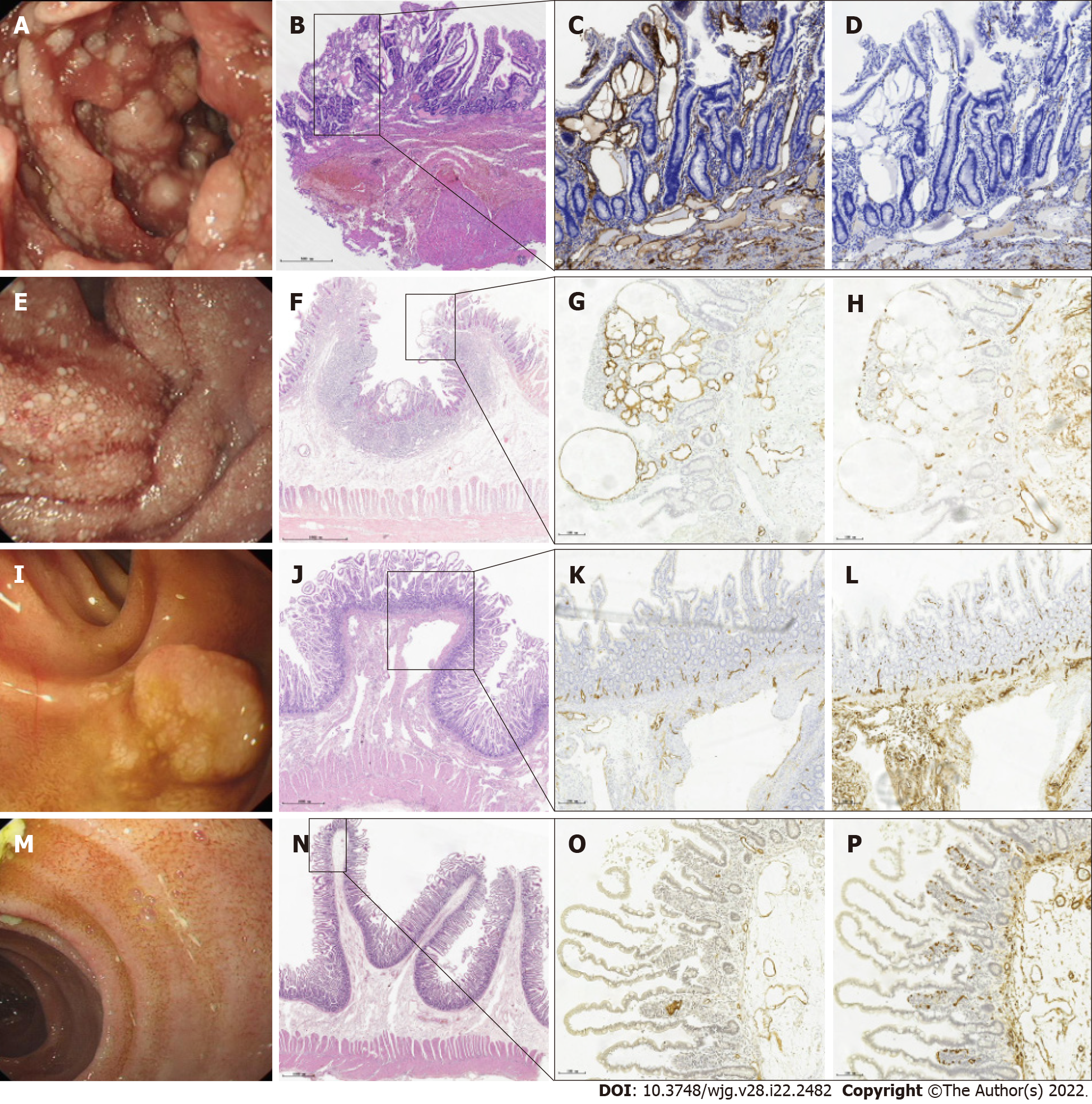
Figure 4 Endoscopic images and corresponding histological findings of primary intestinal lymphangiectasia.
A, E, I, and M: Four types of endoscopic images in patients with primary intestinal lymphangiectasia; B, F, J, and N: Hematoxylin and eosin stain showing the full mucosa of the small intestine; C, G, K, and O: Immunohistochemical stain shows that D2-40 positive cells are located in the cytoplasm and envelope of lymphatic epithelial cells and are brownish yellow (magnification: × 10), indicating dilated lymphatics; D, H, L, and P: CD34 stain showing normal vascular endothelial cells (magnification: × 10).
- Citation: Meng MM, Liu KL, Xue XY, Hao K, Dong J, Yu CK, Liu H, Wang CH, Su H, Lin W, Jiang GJ, Wei N, Wang RG, Shen WB, Wu J. Endoscopic classification and pathological features of primary intestinal lymphangiectasia. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(22): 2482-2493
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i22/2482.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i22.2482