Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2022; 28(21): 2302-2319
Published online Jun 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i21.2302
Published online Jun 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i21.2302
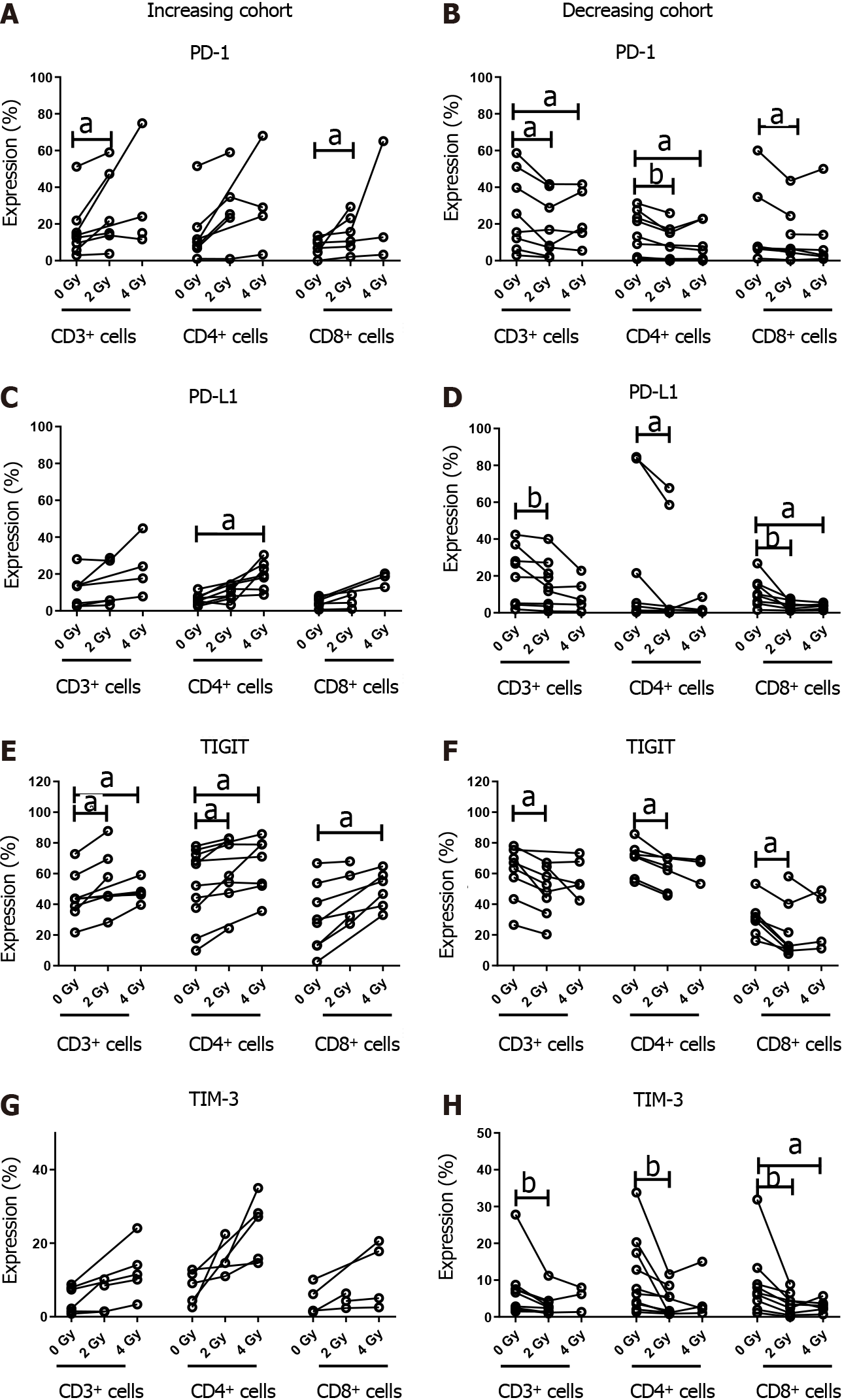
Figure 3 Oesophageal adenocarcinoma patients were screened for the surface expression of immune checkpoints ex vivo by flow cytometric analysis.
Subcohorts where ionising radiation induced upregulation and downregulation of immune checkpoints (ICs). Inhibitory ICs are expressed at a higher level with conventional and hypofractionated dosing regimens in one cohort (n = 8). Inhibitory ICs are expressed at a lower level with conventional and hypofractionated dosing regimens in a separate cohort (n = 9). A and B: Increasing and decreasing cohort of PD-1; C and D: Increasing and decreasing cohort of PD-L1; E and F: Increasing and decreasing cohort of TIGIT; G and H: Increasing and decreasing cohort of TIM-3. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01 by Wilcoxon signed rank test.
- Citation: Donlon NE, Davern M, O’Connell F, Sheppard A, Heeran A, Bhardwaj A, Butler C, Narayanasamy R, Donohoe C, Phelan JJ, Lynam-Lennon N, Dunne MR, Maher S, O’Sullivan J, Reynolds JV, Lysaght J. Impact of radiotherapy on the immune landscape in oesophageal adenocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(21): 2302-2319
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i21/2302.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i21.2302