Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2022; 28(21): 2302-2319
Published online Jun 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i21.2302
Published online Jun 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i21.2302
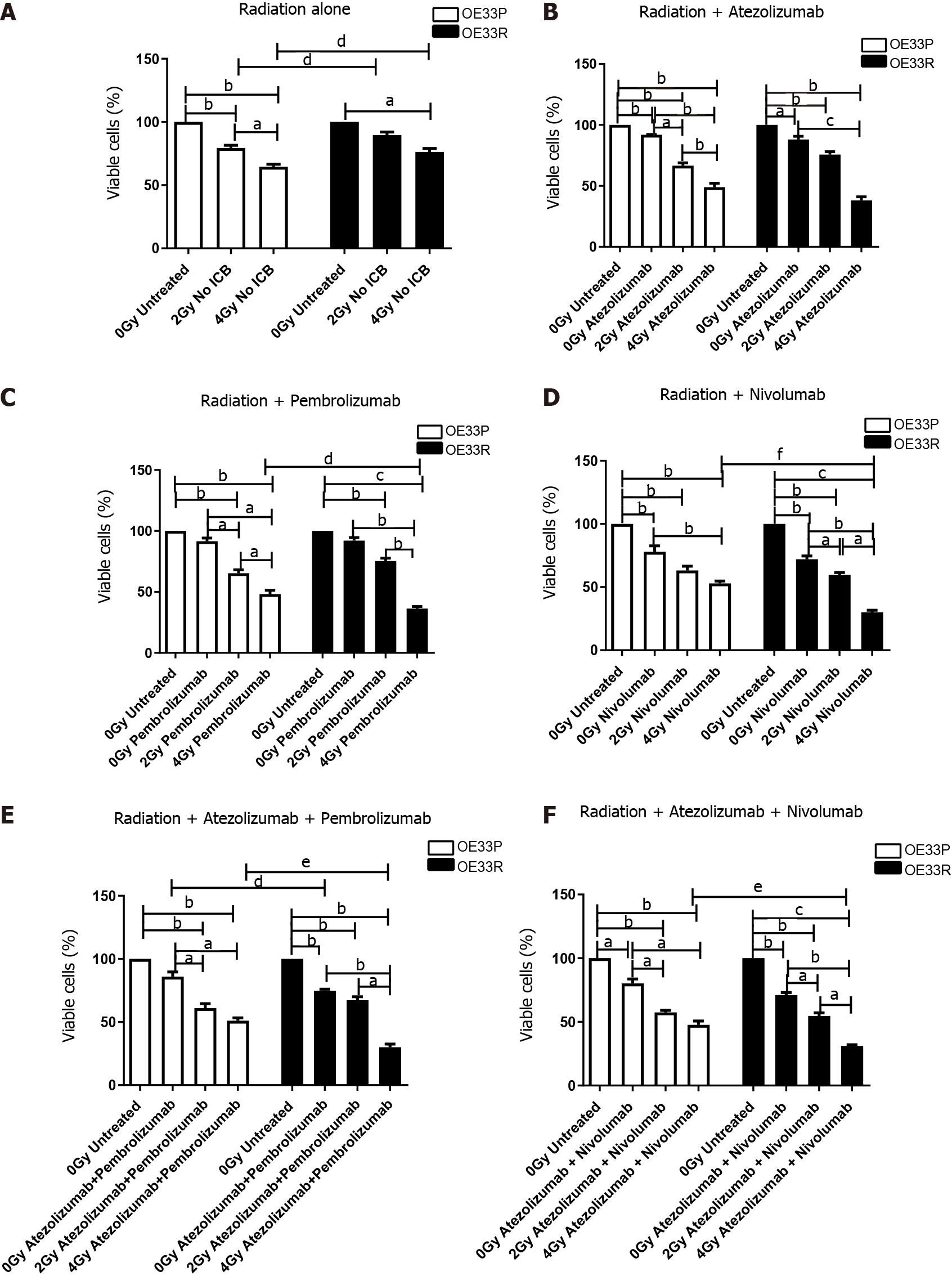
Figure 2 Viability (± SE) of OE33P and OE33R cells were assessed using a cell counting kit-8 assay with or without radiation (n = 3).
Ionising radiation with immune checkpoint blockade results in a greater reduction in cell viability when compared to either modality alone. Graph shows % expression (± SE). A: Treatment with radiation dosing only; B: Treatment with radiation and single agent immunotherapy Atezolizumab; C: Treatment with radiation and single agent immunotherapy Pembrolizumab; D: Treatment with radiation and single agent immunotherapy Nivolumab; E: Treatment with radiation and dual immunotherapy agents Atezolizumab & Pembrolizumab; F: Treatment with radiation and dual immunotherapy agents Atezolizumab & Nivolumab. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 paired t-test; dP < 0.05, eP < 0.01, fP < 0.001 unpaired t-test.
- Citation: Donlon NE, Davern M, O’Connell F, Sheppard A, Heeran A, Bhardwaj A, Butler C, Narayanasamy R, Donohoe C, Phelan JJ, Lynam-Lennon N, Dunne MR, Maher S, O’Sullivan J, Reynolds JV, Lysaght J. Impact of radiotherapy on the immune landscape in oesophageal adenocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(21): 2302-2319
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i21/2302.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i21.2302