Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2022; 28(21): 2251-2281
Published online Jun 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i21.2251
Published online Jun 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i21.2251
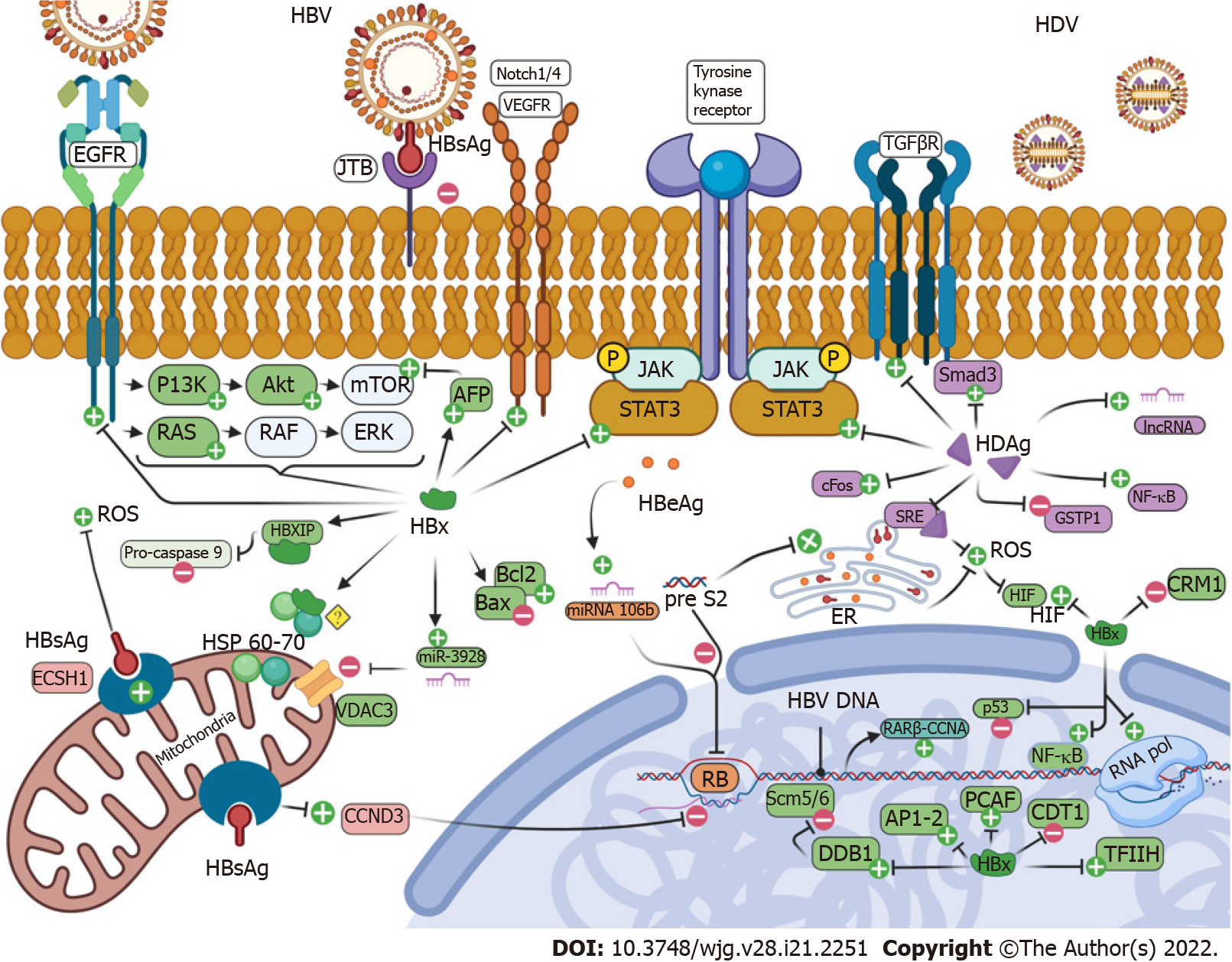
Figure 1 Molecular pathways in hepatitis B virus and hepatitis D virus carcinogenesis.
Created with BioRender.com. HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HDV: Hepatitis D virus; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; JTB: Jumping translocation breakpoint; HBsAg: Hepatitis B virus surface antigen; VEGFR: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor; TGF: Transforming growth factor; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; Akt: AKT serine/threonine kinase; RAS: Rat sarcoma virus gene; RAF: Rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma; mTOR: Mechanistic target of rapamycin kinase; JAK: Janus kinase; STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; Smad3: Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3; lncRNA: Long non coding RNA; NF-kB: Nuclear factor-kappa B; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; HSP: Heat shock protein; ECSH1: Enoyl-CoA hydratase short chain 1; VDAC: Voltage dependent anion channel; CCND3: Cytoplasmatic Cyclin D3; RB: Retinoblastoma; Bcl2: B-cell lymphoma 2; Bax: Bcl2 associated X; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; HIF: Hypoxia-inducible factor; AP: Activator protein; DDB: Damage specific DNA binding protein; Scm5/6: Structural maintenance of chromosomes 5/6; PCAF: P300/CBP-associated factor; TFIIH: Transcription factor II H.
- Citation: Stella L, Santopaolo F, Gasbarrini A, Pompili M, Ponziani FR. Viral hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma: From molecular pathways to the role of clinical surveillance and antiviral treatment. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(21): 2251-2281
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i21/2251.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i21.2251