Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2022; 28(19): 2076-2087
Published online May 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i19.2076
Published online May 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i19.2076
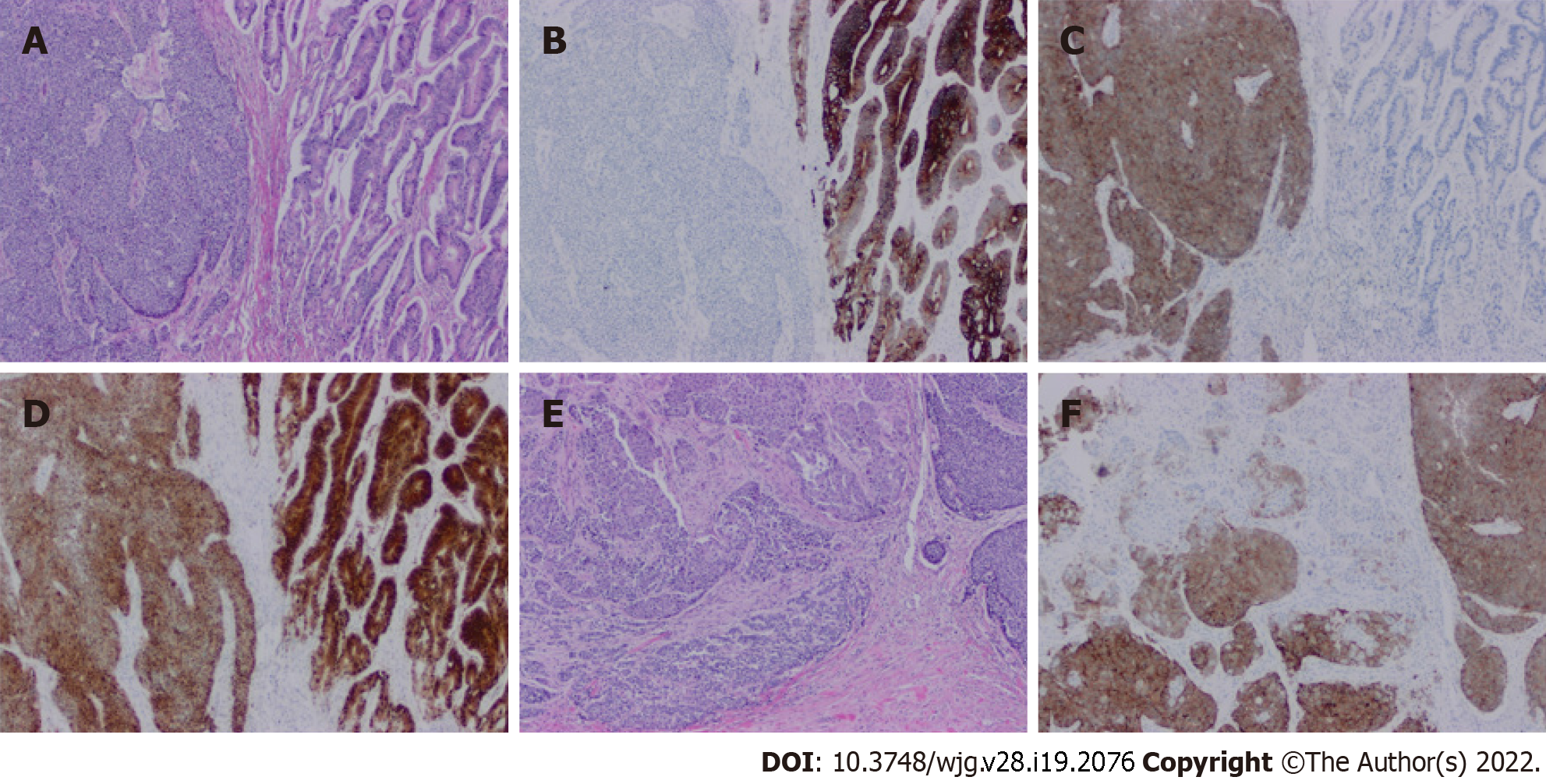
Figure 4 Histopathology of a mixed neuroendocrine-non-neuroendocrine neoplasm of colon.
A: Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stain of mixed neuroendocrine-non-neuroendocrine neoplasm. On the right side is a well-differentiated invasive adenocarcinoma. On the left side is a poorly differentiated neuroendocrine carcinoma (20 ×, H&E); B: The adenocarcinoma component is positive for cytokeratin 20, but the neuroendocrine component is negative (20 ×); C: Positive synaptophysin staining in the neuroendocrine component but negative staining in the adenocarcinoma component (20 ×); D: Positive CDX2 staining in both adenocarcinoma and neuroendocrine carcinoma components (20 ×); E: Merging area of adenocarcinoma and neuroendocrine carcinoma components (20 ×); F: Positive synaptophysin staining of neuroendocrine cells in the merged area (20 ×).
- Citation: Toor D, Loree JM, Gao ZH, Wang G, Zhou C. Mixed neuroendocrine-non-neuroendocrine neoplasms of the digestive system: A mini-review. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(19): 2076-2087
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i19/2076.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i19.2076