Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2022; 28(19): 2057-2075
Published online May 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i19.2057
Published online May 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i19.2057
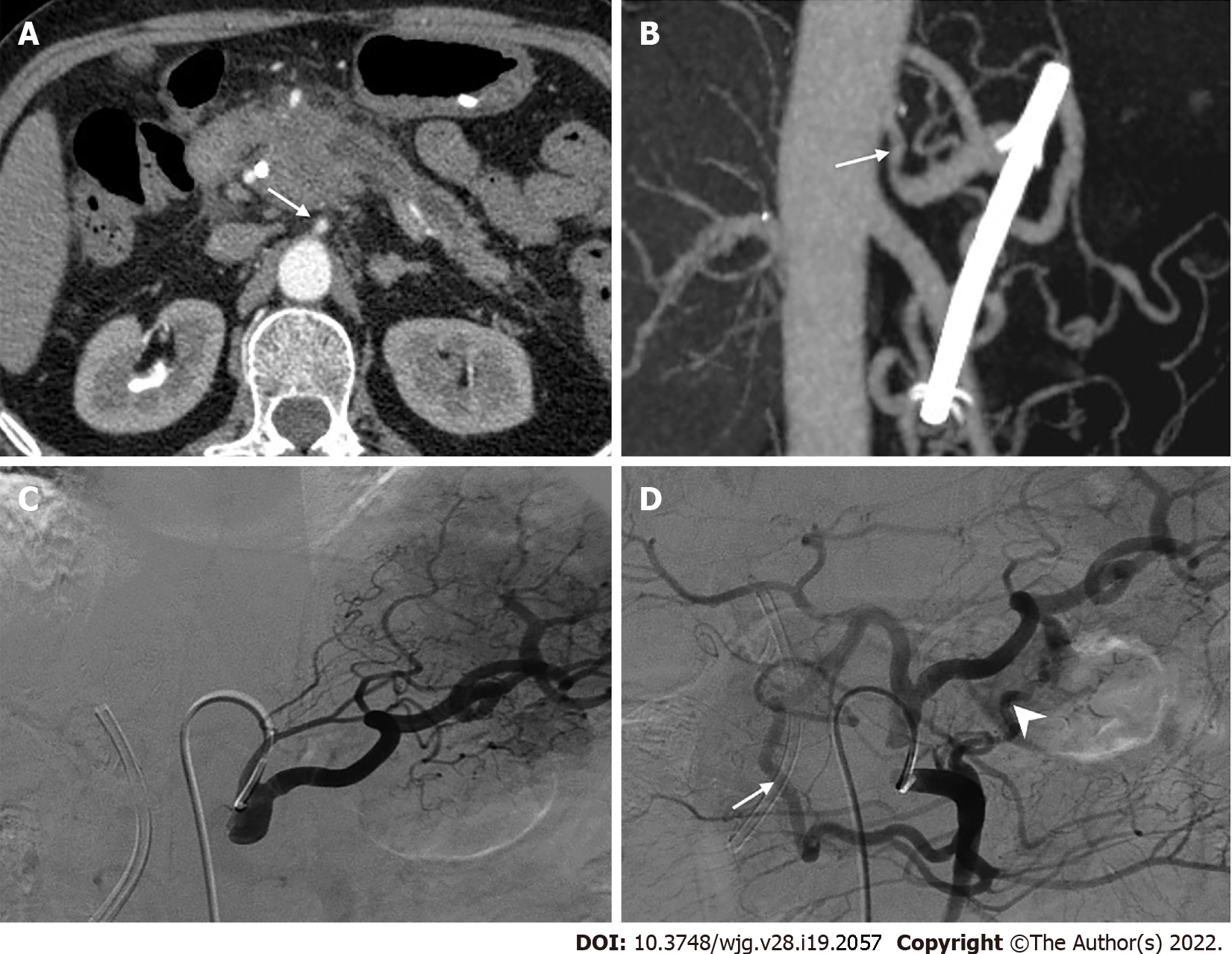
Figure 6 Collateral pathways due to celiac axis stenosis.
A: Computed tomography scan showed a mass in the pancreatic head with dilated biliary-pancreatic duct, and celiac axis stenosis (CAS, arrow); B: Sagittal maximum intensity projection image demonstrated CAS (arrow); C: Selective celiac angiographic examination revealed the left gastric artery and splenic artery, with no hepatic arteries depicted, which is compatible with occlusion of the common hepatic artery; D: Superior mesenteric arteriogram demonstrated retrograde filling of the celiac branches via the pancreaticoduodenal arcades (arrow) by way of the gastroduodenal artery and anomalous blood vessels traversing the pancreas (arrowhead).
- Citation: Xu YC, Yang F, Fu DL. Clinical significance of variant hepatic artery in pancreatic resection: A comprehensive review. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(19): 2057-2075
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i19/2057.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i19.2057