Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2022; 28(19): 2034-2056
Published online May 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i19.2034
Published online May 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i19.2034
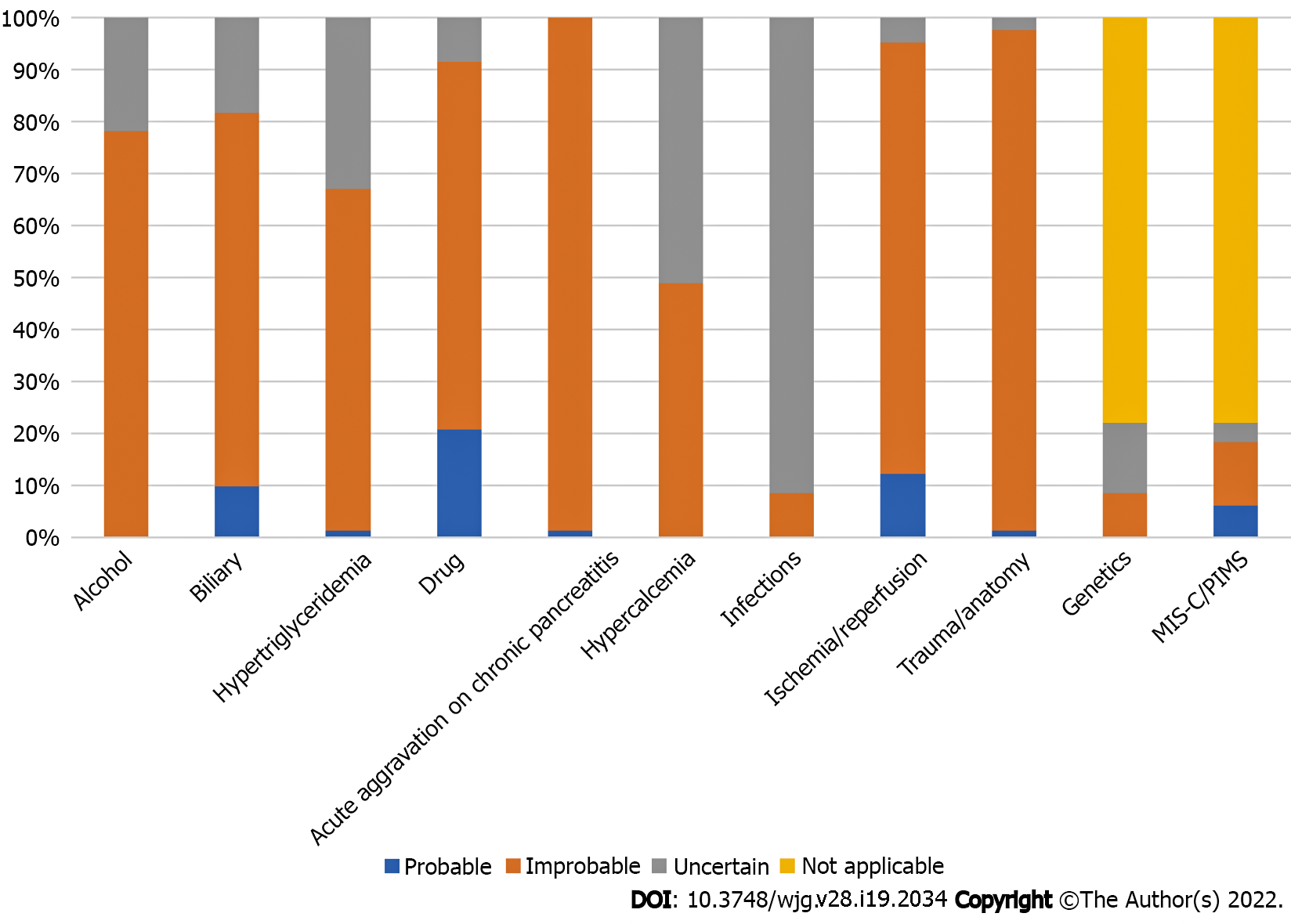
Figure 2 The probability of other etiologies of acute pancreatitis in cases with concurrent coronavirus disease 2019 and acute pancreatitis.
The potential of other etiologies, including alcoholism, biliary, hypertriglyceridemia, hypercalcemia, drug-induced, acute aggravation on chronic pancreatitis, ischemia/reperfusion, and trauma/anatomy. In children, the potential of genetic and multisystemic inflammatory syndrome in children/pediatric inflammatory multisystem syndrome-induced acute pancreatitis (AP) are also evaluated. Moreover, these causes are regarded as inapplicable etiologies of AP in adults. The probability of AP is disregarded in cases with insufficient information on the etiologies of AP. Some etiologies of AP, such as alcohol, acute aggravation on chronic pancreatitis, and trauma/anatomy are well verified. Furthermore, the etiological workup for infections and hypercalcemia is insufficient. Moreover, some cases of AP may have been caused by drug and biliary disease as it may be difficult to exclude them from the etiology of AP. MIS-C: Multisystemic inflammatory syndrome in children; PIMS: Pediatrics inflammatory multisystem syndrome; AP: Acute pancreatitis.
- Citation: Onoyama T, Koda H, Hamamoto W, Kawahara S, Sakamoto Y, Yamashita T, Kurumi H, Kawata S, Takeda Y, Matsumoto K, Isomoto H. Review on acute pancreatitis attributed to COVID-19 infection. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(19): 2034-2056
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i19/2034.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i19.2034