Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2022; 28(17): 1798-1813
Published online May 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i17.1798
Published online May 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i17.1798
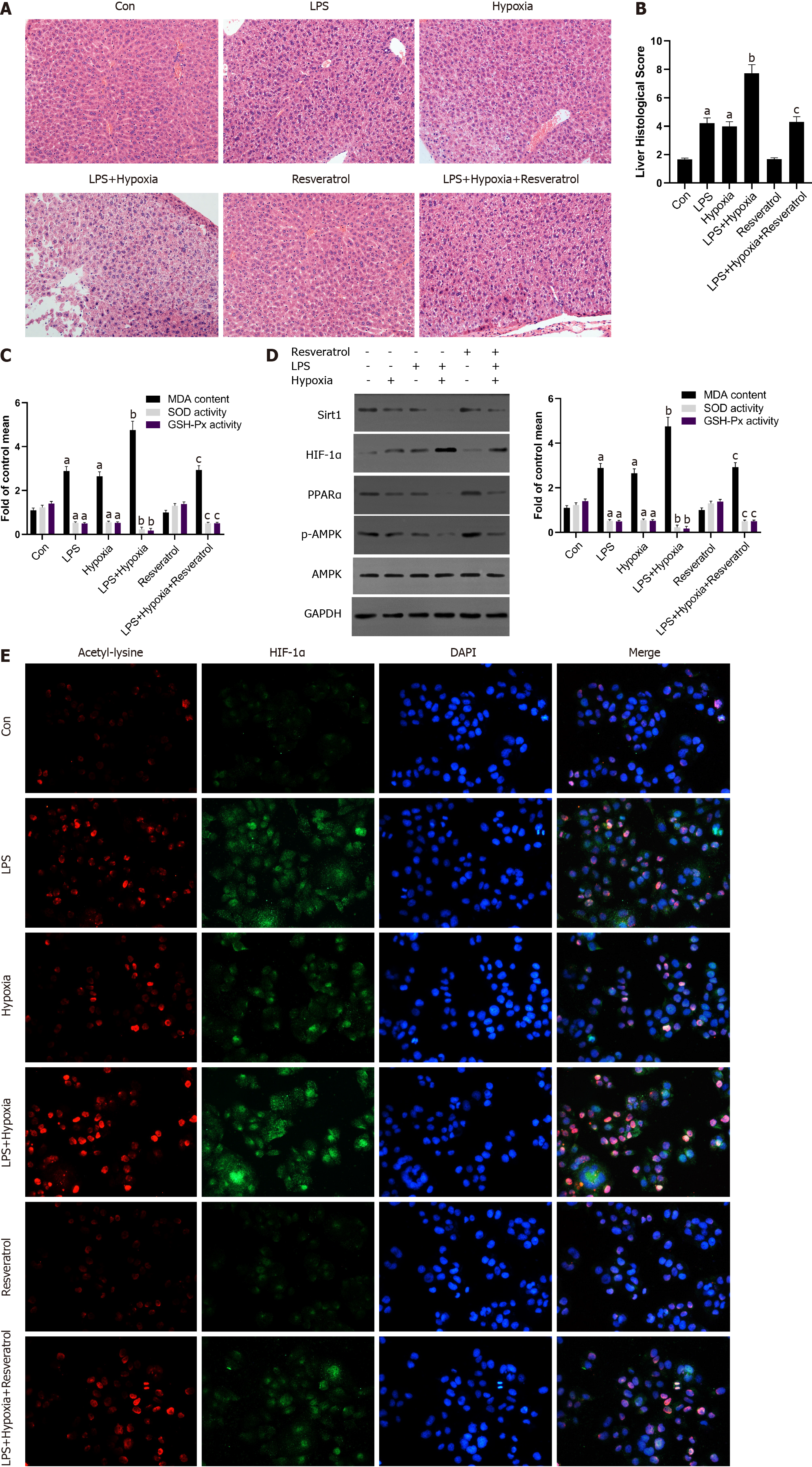
Figure 6 The activation of Sirtuin1 induced the deacetylation and inactivation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α, and subsequently rescued the progressive aggravation of acute liver failure induced by hypoxia.
A: Mice were pretreated with resveratrol or exposed to hypoxia and then stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS). The representative images of hematoxylin and eosin staining of liver in each group; B: The liver histological score of liver in each group; C: The levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) of mice in each group; D: Western blotting was performed to measure the levels of Sirtuin1 (Sirt1), hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)-1α, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα) and p-AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) in liver tissues and the protein expression were quantified; E: The representative images of immunofluorescence staining for Acetyl-lysine and HIF-1α. Data shown are means ± standard deviations (SDs) of three separate experiments. aP < 0.05 vs Control group; bP < 0.05 vs LPS-treated group; cP < 0.05 vs LPS + Hypoxia-treated group; one-way analysis of variance combined with Bonferroni's post hoc test; the error bars indicate the SDs.
- Citation: Cao P, Chen Q, Shi CX, Wang LW, Gong ZJ. Sirtuin1 attenuates acute liver failure by reducing reactive oxygen species via hypoxia inducible factor 1α. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(17): 1798-1813
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i17/1798.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i17.1798