Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2022; 28(16): 1608-1624
Published online Apr 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i16.1608
Published online Apr 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i16.1608
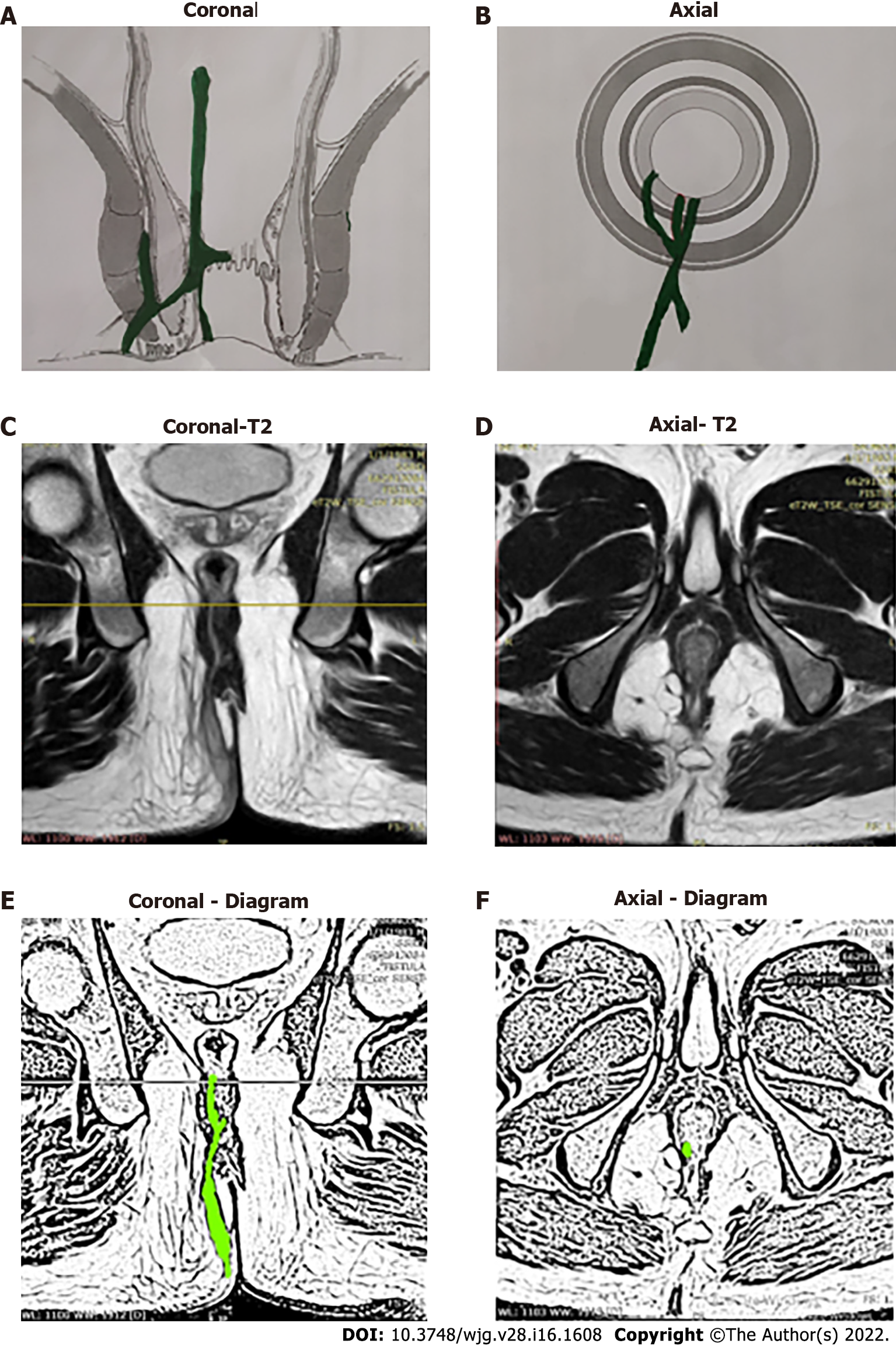
Figure 9 A 36-year-old male patient with a high intrarectal fistula at 7 o’clock.
A: Coronal section (schematic diagram); B: Axial section (schematic diagram); C: T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) Coronal section showing high intrarectal fistula tract; D: T2-weighted MRI Axial section; E: Sketch of MRI Coronal section highlighting high intrarectal fistula tract (light green color); F: Sketch of MRI Axial section highlighting fistula tract (light green color).
- Citation: Garg P, Yagnik VD, Dawka S, Kaur B, Menon GR. Guidelines to diagnose and treat peri-levator high-5 anal fistulas: Supralevator, suprasphincteric, extrasphincteric, high outersphincteric, and high intrarectal fistulas. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(16): 1608-1624
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i16/1608.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i16.1608