Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2022; 28(14): 1444-1454
Published online Apr 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i14.1444
Published online Apr 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i14.1444
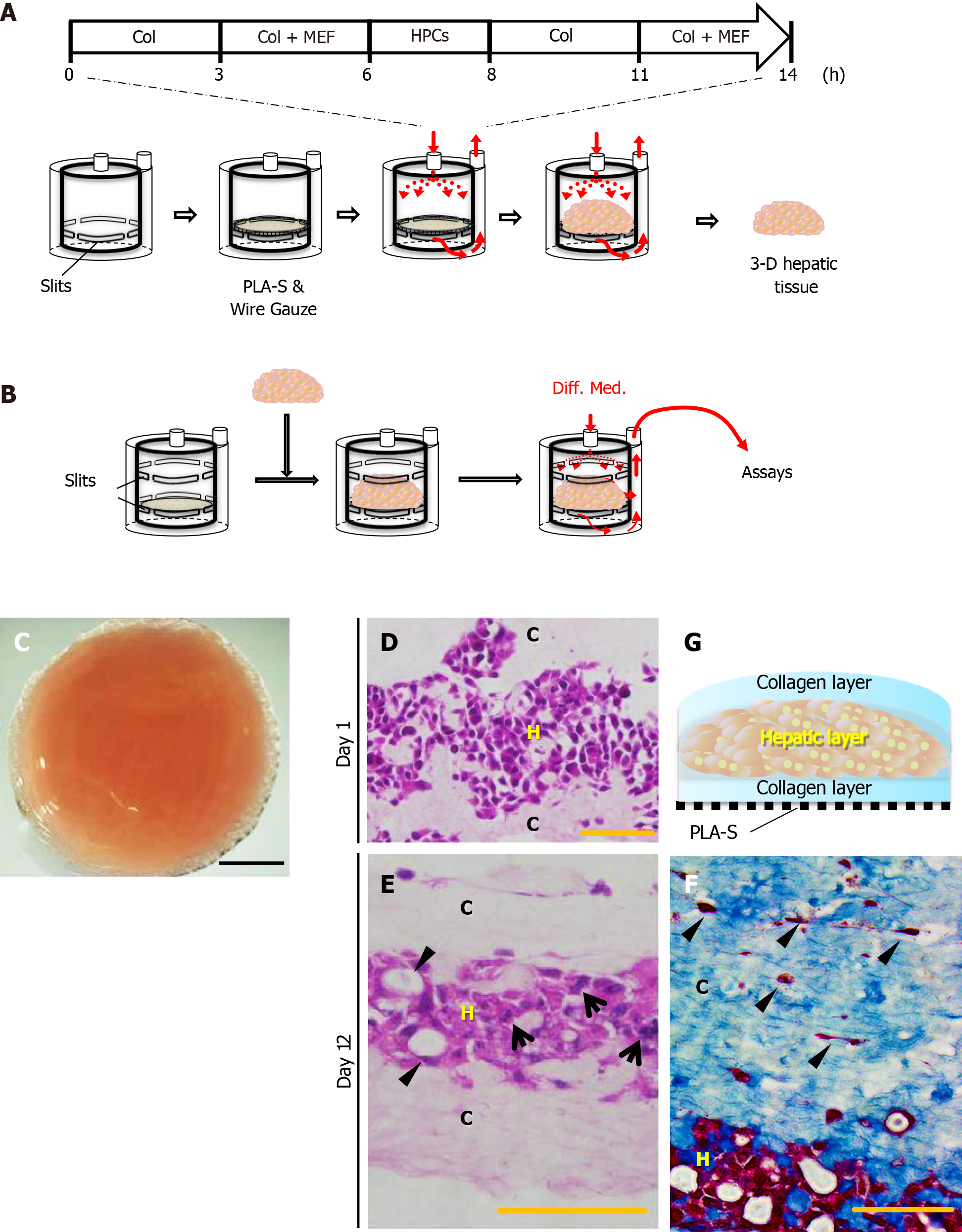
Figure 1 Reconstruction of the three-dimensional liver tissue culture model using hepatic progenitor cells.
A and B: A schematic illustration showing reconstruction of the liver tissue culture model using a bioreactor; preparation steps (A), and culture steps (B); C: Micrographs of a reconstructed three-dimensional (3-D) liver tissue culture model with dense collagen fibrils; D and E: Histological analyses: hematoxylin-eosin staining of a section of the 3-D liver tissue culture model on day 1 (D) and day 12 (E). Arrows indicate binuclear populations, like hepatocytes. Arrowheads indicate a bile duct–like structure; F: Histological analyses: AZAN staining of a section of the 3-D liver tissue culture model on day 12. Arrowheads indicate fibroblasts at condensed collagen fibril matrices. Bar corresponds to (C) 5 mm, (D) 50 μm, and (E) and (F) 100 μm. Col: Collagen; HPCs: Portal branch-ligated-hepatic progenitor cells; PLA-S: Polylactic acid sheet; C: Collagen layer; H: Hepatic layer.
- Citation: Tamai M, Adachi E, Kawase M, Tagawa YI. Syngeneic implantation of mouse hepatic progenitor cell-derived three-dimensional liver tissue with dense collagen fibrils. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(14): 1444-1454
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i14/1444.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i14.1444