Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 28, 2022; 28(12): 1257-1271
Published online Mar 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i12.1257
Published online Mar 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i12.1257
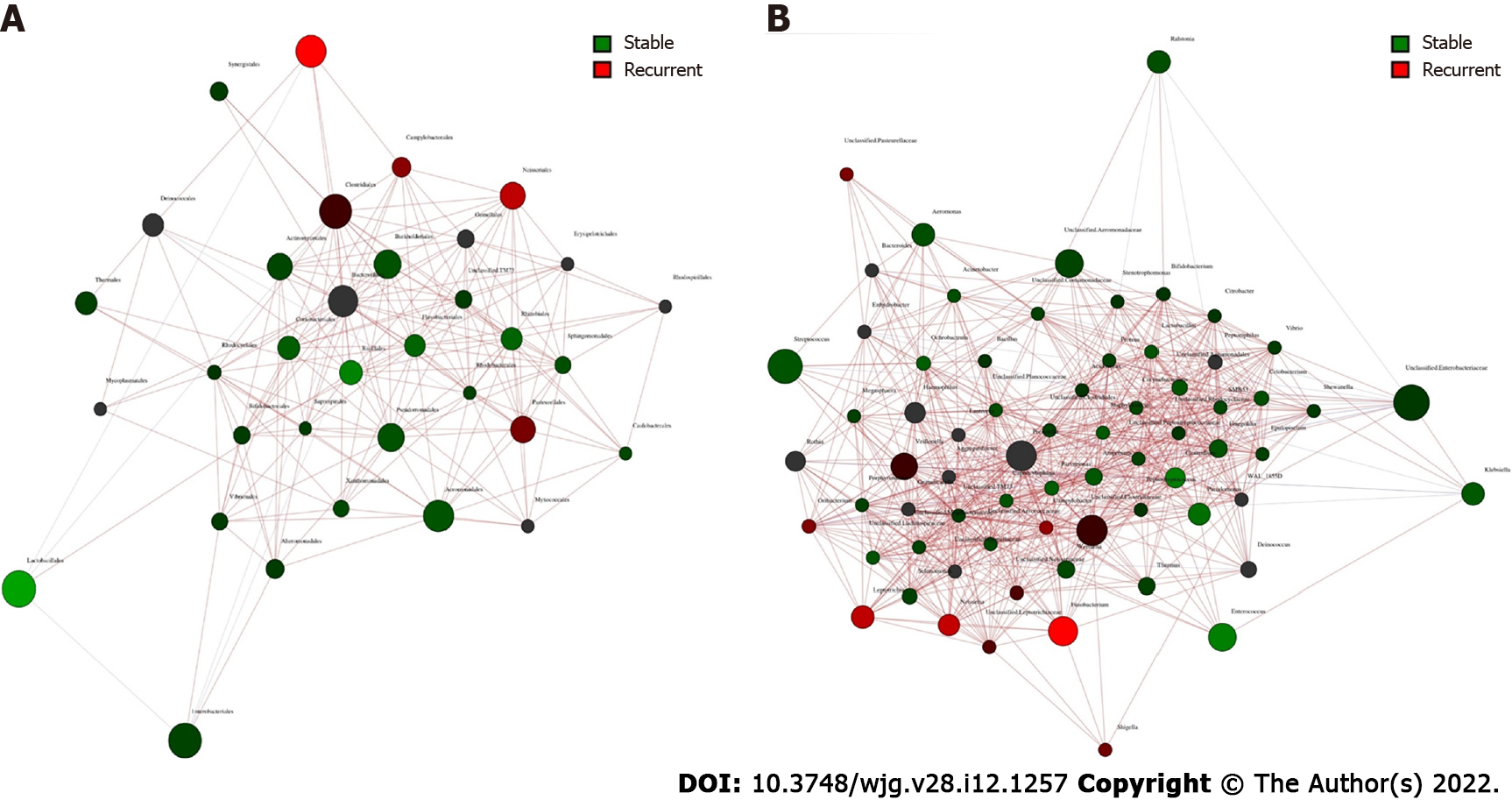
Figure 4 Co-occurrence network analysis of bile microbiome of choledocholithiasis patients with different prognosis post endoscopic sphincterotomy.
A: Co-occurrence and disease-specific bacterial interactions at the order level. Order was presented as nodes (stable group specific order in green and recurrent group specific order in red), order abundance was presented as node size, and edges were represented based on their association tested using Pearson’s correlation (positive inter-node correlations in blue, negative inter-node correlations in red); B: Co-occurrence and disease-specific bacterial interactions at the genus level. Genus was presented as nodes (stable group specific genus in green and recurrent group specific genus in red), genus abundance was presented as node size, and edges were represented based on their association tested using Pearson’s correlation (positive inter-node correlations in blue, negative inter-node correlations in red).
- Citation: Li Y, Tan WH, Wu JC, Huang ZX, Shang YY, Liang B, Chen JH, Pang R, Xie XQ, Zhang JM, Ding Y, Xue L, Chen MT, Wang J, Wu QP. Microbiologic risk factors of recurrent choledocholithiasis post-endoscopic sphincterotomy. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(12): 1257-1271
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i12/1257.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i12.1257