Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 28, 2022; 28(12): 1239-1256
Published online Mar 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i12.1239
Published online Mar 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i12.1239
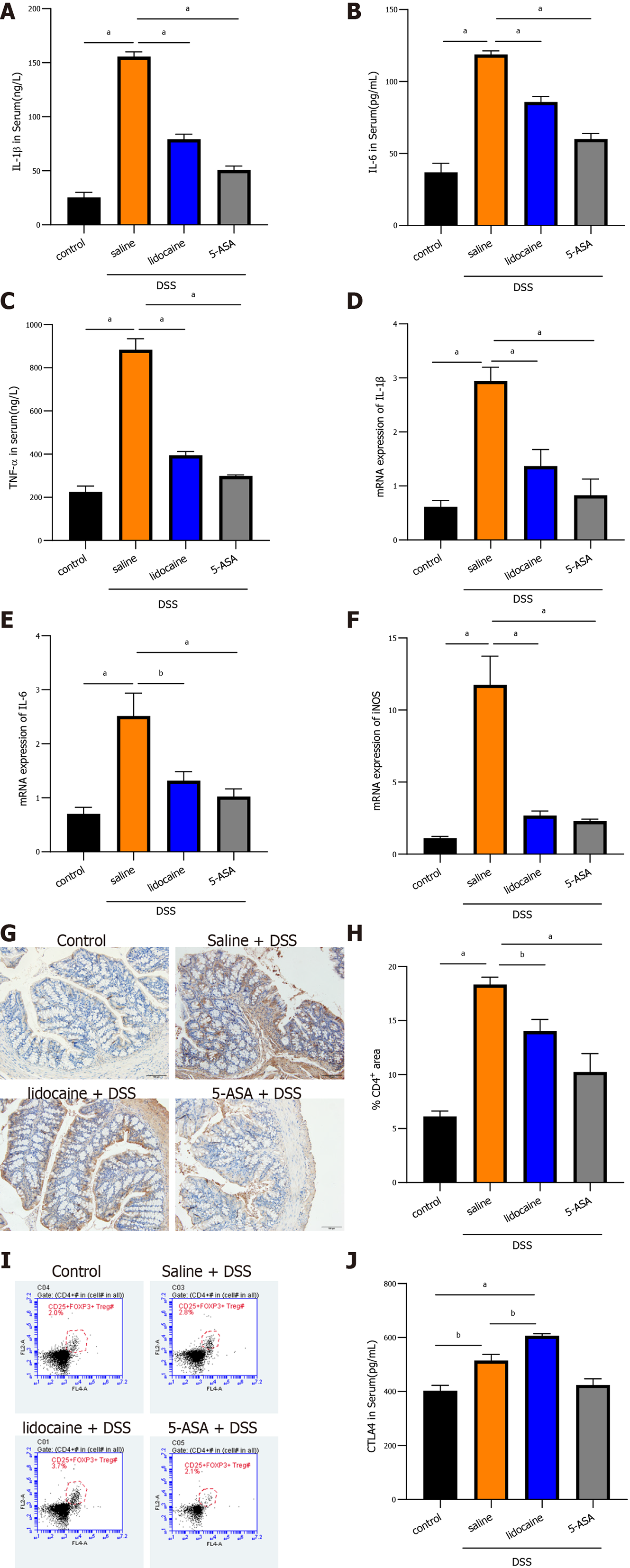
Figure 2 Spinal anesthesia relieves intestinal inflammation activated by dextran sodium sulfate.
A-C: Serum levels of interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA); D-F: The mRNA expression of IL-1β, IL-6, and inducible nitric oxide synthase detected by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction; G: Expression of CD4 detected using immunohistochemistry; H: Quantitation of the immunohistochemistry result; I: Proportion of CD4+/CD25+/Foxp3+ Tregs analyzed by flow cytometry; J: Serum level of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein determined by ELISA; Data are presented as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. P-values were calculated using one-way ANOVA between different groups. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. 5-ASA: 5-aminosalicylic acid; DSS: Dextran sodium sulfate; IL: Interleukin; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase.
- Citation: Hong Y, Zhao J, Chen YR, Huang ZH, Hou LD, Shen B, Xin Y. Spinal anesthesia alleviates dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis by modulating the gut microbiota. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(12): 1239-1256
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i12/1239.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i12.1239