Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2022; 28(11): 1139-1158
Published online Mar 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i11.1139
Published online Mar 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i11.1139
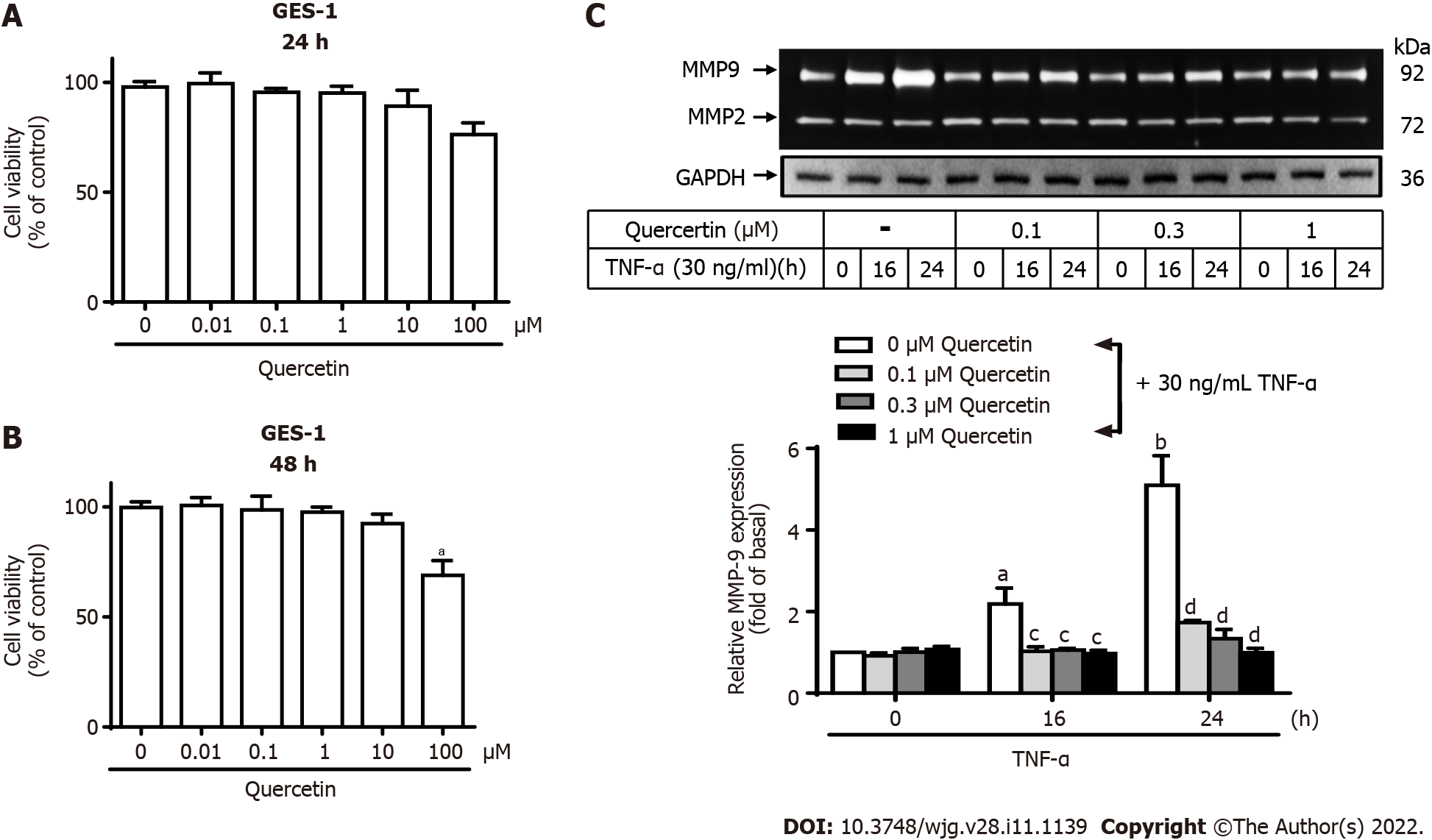
Figure 3 Quercetin suppresses tumor necrosis factor-α-induced matrix metallopeptidase-9 expression in normal human gastric mucosa epithelial cells.
A and B: Effects of quercetin on the viability of normal human gastric mucosa epithelial cells (GES-1). GES-1 cells were treated with different concentrations of quercetin (0, 0.01, 0.1, 1, 10, or 100 mM) for 24 h (A) or 48 h (B), and cell viability was measured using the cell counting Kit-8 assay; C: Cells were either untreated or treated with quercetin (0, 0.1, 0.3, or 1 mM) for 1 h before the addition of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) (30 ng/mL) and then incubated for 0, 16, or 24 h as described in the Materials and Methods section. Matrix metallopeptidase-9 zymogen activity was analyzed by gelatin zymography. One-way ANOVA was used for comparisons among different treatment time points (aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs control cells in 0 h). One-way ANOVA was used for comparisons among different treatments (cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01 vs TNF-α-stimulated cells). Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. CCK-8: Cell Counting Kit-8; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; GES-1: Normal human gastric mucosa epithelial cell line; MMP-9: Matrix metallopeptidase-9; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α.
- Citation: Hsieh HL, Yu MC, Cheng LC, Chu MY, Huang TH, Yeh TS, Tsai MM. Quercetin exerts anti-inflammatory effects via inhibiting tumor necrosis factor-α-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in normal human gastric epithelial cells. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(11): 1139-1158
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i11/1139.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i11.1139