Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2022; 28(1): 140-153
Published online Jan 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i1.140
Published online Jan 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i1.140
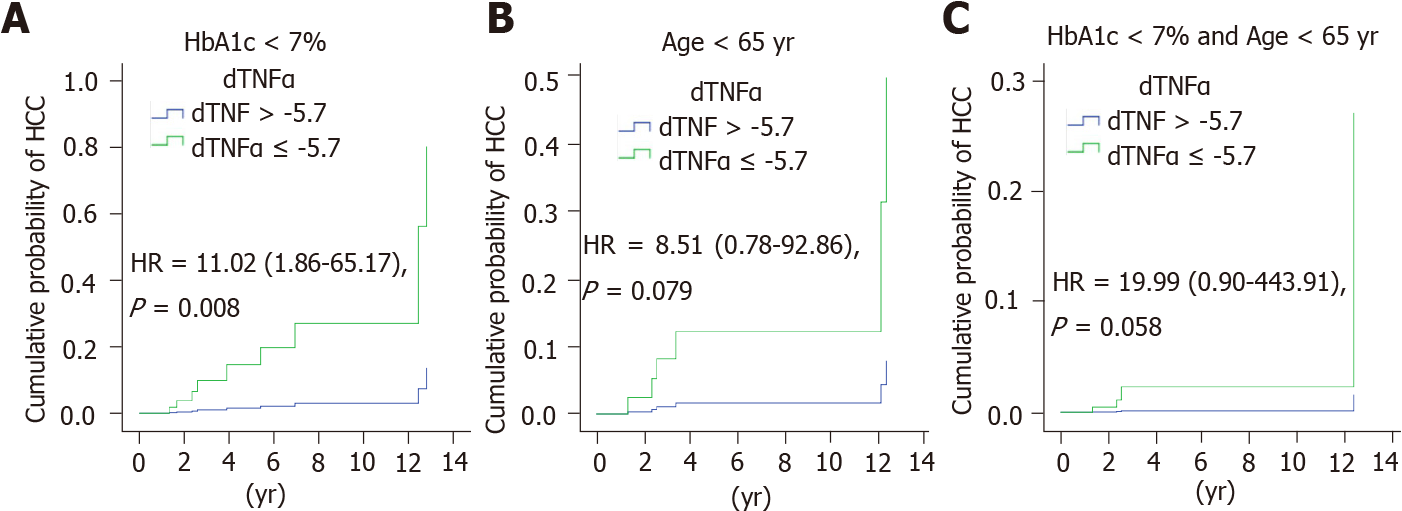
Figure 3 Multivariate Cox regression analysis of tumor necrosis factor-α associated with hepatocellular carcinoma in subgroups.
Comparison of the cumulative probability of hepatocellular carcinoma development divided by Δtumor necrosis factor-α with a cutoff value of -5.7 pg/mL in patients with (A) hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) < 7%, (B) age < 65 years old and (C) HbA1c < 7% and age < 65 years old. The P value was adjusted by age, sex, Fibrosis-4 index, and HbA1c. HR: Hazard ratio; CI: Confidence interval; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; HbA1c: Hemoglobin A1c.
- Citation: Lu MY, Yeh ML, Huang CI, Wang SC, Tsai YS, Tsai PC, Ko YM, Lin CC, Chen KY, Wei YJ, Hsu PY, Hsu CT, Jang TY, Liu TW, Liang PC, Hsieh MY, Lin ZY, Chen SC, Huang CF, Huang JF, Dai CY, Chuang WL, Yu ML. Dynamics of cytokines predicts risk of hepatocellular carcinoma among chronic hepatitis C patients after viral eradication. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(1): 140-153
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i1/140.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i1.140