Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2021; 27(9): 866-885
Published online Mar 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i9.866
Published online Mar 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i9.866
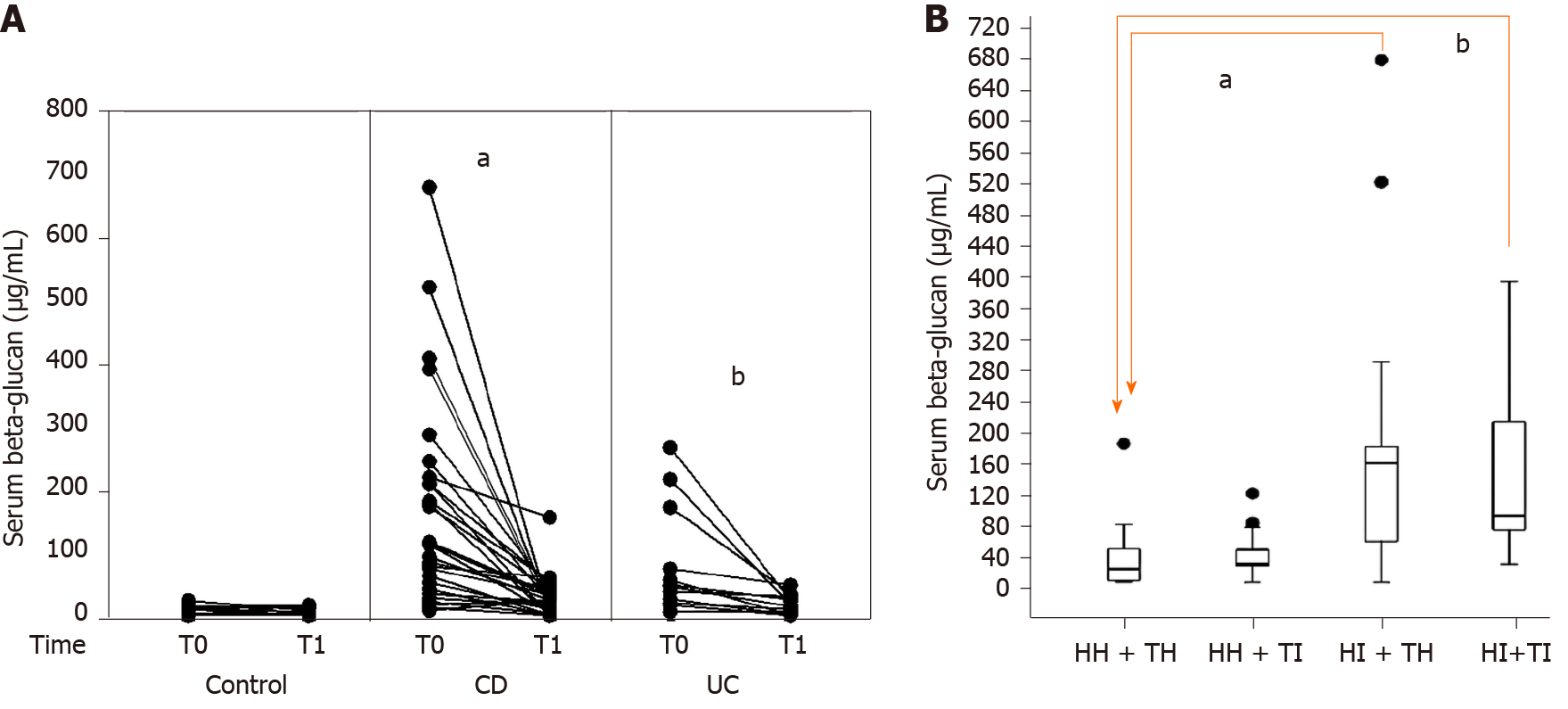
Figure 5 Analysis of serum beta-glucan in response to therapeutic intervention in inflammatory bowel diseases, and in relation to histologic and transmural inflammation in Crohn’s disease.
A: Serial concentrations of serum beta-glucan are shown at week 0 (T0) and between weeks 12 and 16 (T1) in controls and after therapeutic interventions in patients with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. The analysis was performed by the pairwise Wilcoxon rank-sum test. Significant results are depicted (aP < 0.0001; bP = 0.003); B: Serum beta-glucan concentrations of patients with Crohn’s disease are stratified according to histologic healing or inflammation, and transmural healing or inflammation, based on magnetic resonance enterography. The analysis was performed by the Kruskal-Wallis on ranks test, in which multiple comparisons were performed using Dunn’s test. The horizontal bars represent medians, and the boxes represent the 25th and 75th percentiles. Significant results are depicted (aP = 0.0018; bP = 0.011).
- Citation: Farias e Silva K, Nanini HF, Cascabulho CM, Rosas SLB, Santana PT, Carneiro AJV, Anaissie E, Nucci M, de Souza HSP. Serum 1,3-beta-D-glucan as a noninvasive test to predict histologic activity in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(9): 866-885
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i9/866.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i9.866