Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2021; 27(9): 835-853
Published online Mar 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i9.835
Published online Mar 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i9.835
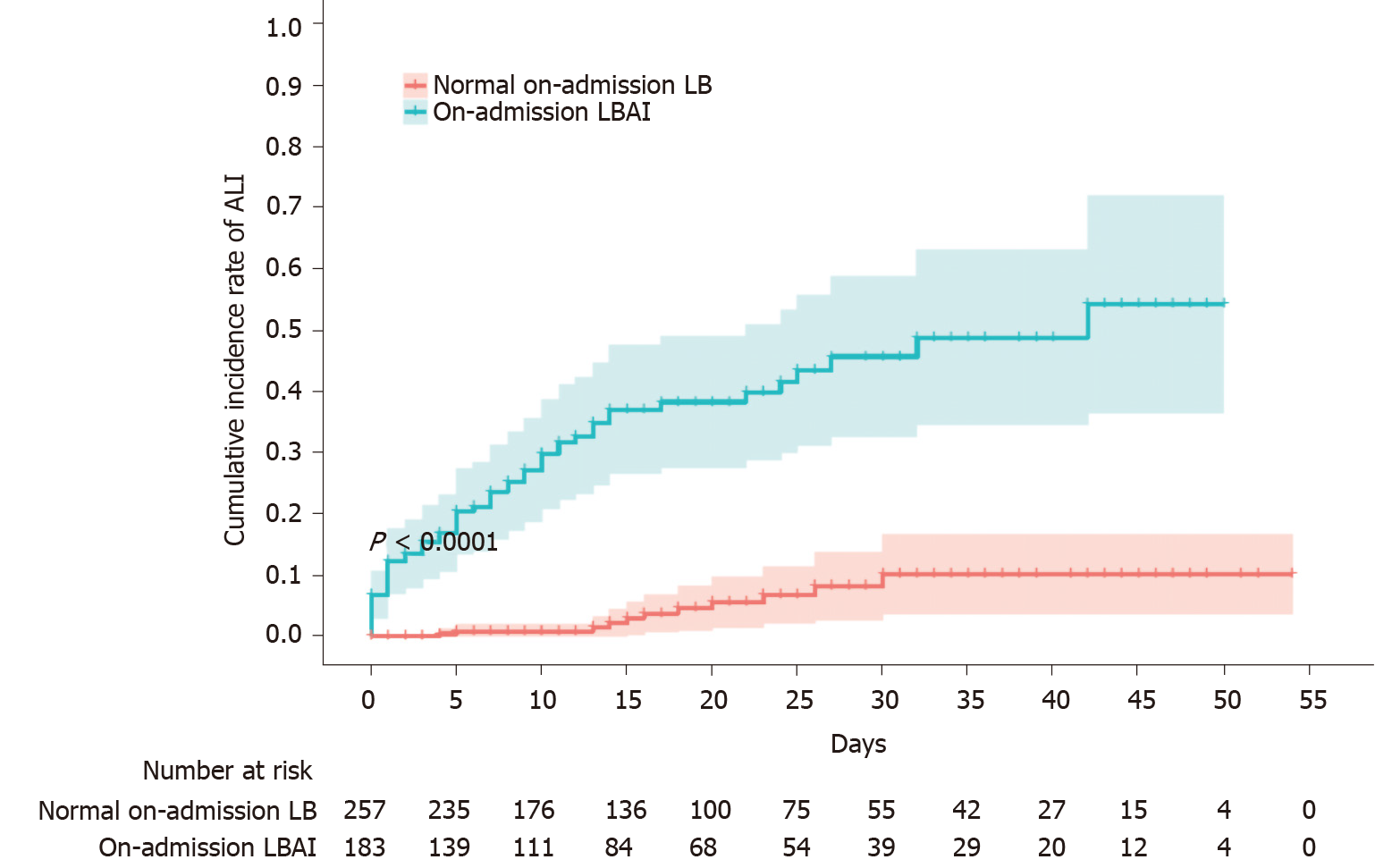
Figure 1 Cumulative incidence rate of acute liver injury stratified by on-admission liver biochemistry.
Shadows indicate the 95% confidence intervals of the corresponding estimates cumulative incidence rate. ALI: Acute liver injury; LB: Liver biochemistry; LBAI: Liver biochemical abnormality or injury.
- Citation: Zhang SS, Dong L, Wang GM, Tian Y, Ye XF, Zhao Y, Liu ZY, Zhai JY, Zhao ZL, Wang JH, Zhang HM, Li XL, Wu CX, Yang CT, Yang LJ, Du HX, Wang H, Ge QG, Xiu DR, Shen N. Progressive liver injury and increased mortality risk in COVID-19 patients: A retrospective cohort study in China. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(9): 835-853
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i9/835.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i9.835