Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2021; 27(9): 794-814
Published online Mar 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i9.794
Published online Mar 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i9.794
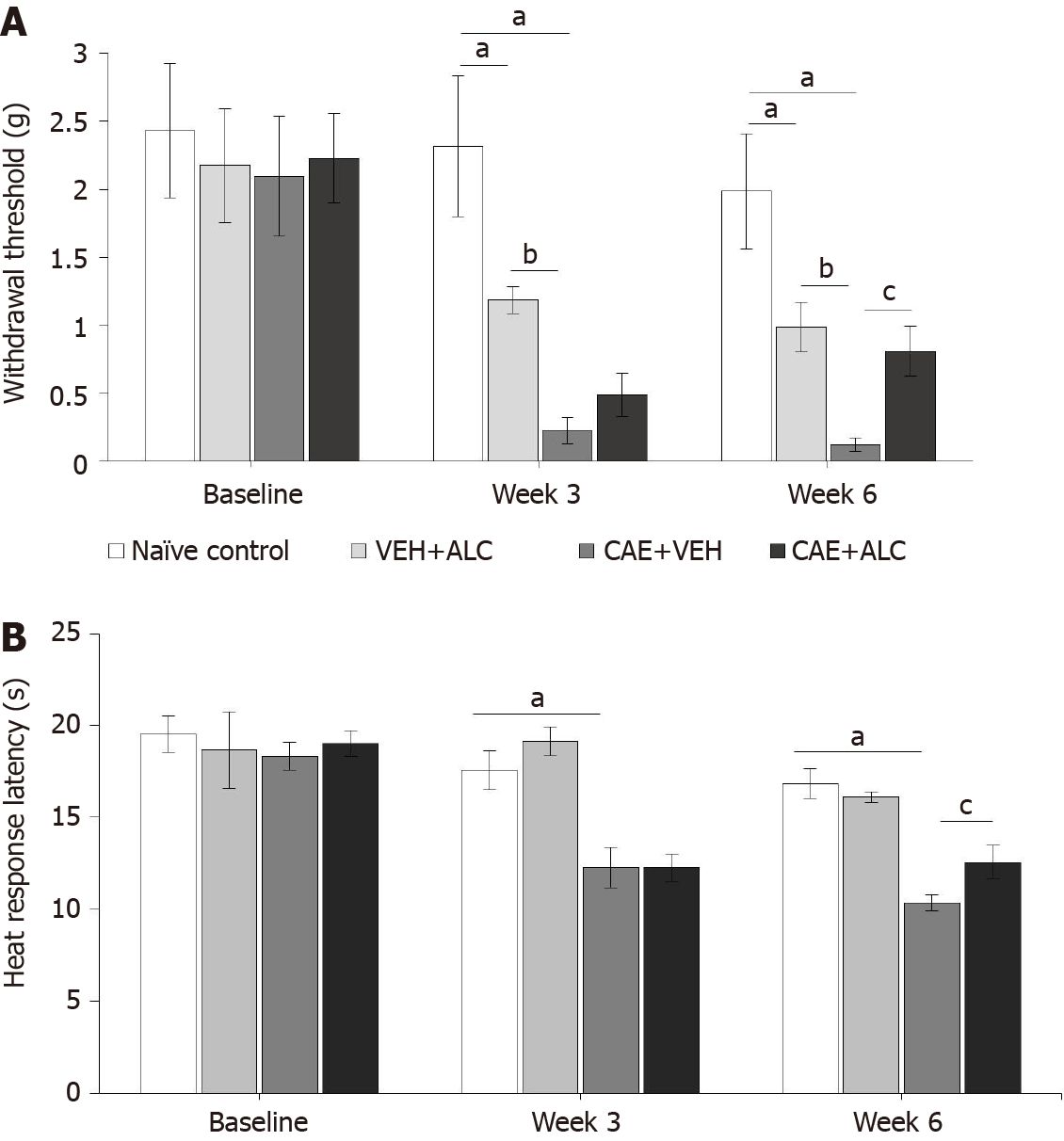
Figure 1 Caerulein-induced pancreatitis produced secondary hypersensitivity of the hindpaws that was attenuated by treatment with acetyl-L-carnitine.
A: Mechanical withdrawal thresholds were significantly reduced after 3 wk of caerulein (CAE) injections indicating hypersensitivity and remained reduced after 6 wk of CAE injections; B: Response latencies to heat stimulation in the hotplate test were significantly reduced after 3 and 6 wk of CAE injections. Concurrent treatment with acetyl-L-carnitine (ALC) during the last 3 wk attenuated mechanical and heat hypersensitivity. n = 6/group; aP < 0.05 compared to naïve control; bP < 0.05 compared to VEH + ALC; cP < 0.05 compared to CAE + ALC; two-way ANOVA with Newman-Keuls post hoc test. ALC: Acetyl-L-carnitine; CAE: Caerulein; VEH: Vehicle.
- Citation: McIlwrath SL, Starr ME, High AE, Saito H, Westlund KN. Effect of acetyl-L-carnitine on hypersensitivity in acute recurrent caerulein-induced pancreatitis and microglial activation along the brain’s pain circuitry. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(9): 794-814
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i9/794.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i9.794