Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2021; 27(8): 677-691
Published online Feb 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i8.677
Published online Feb 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i8.677
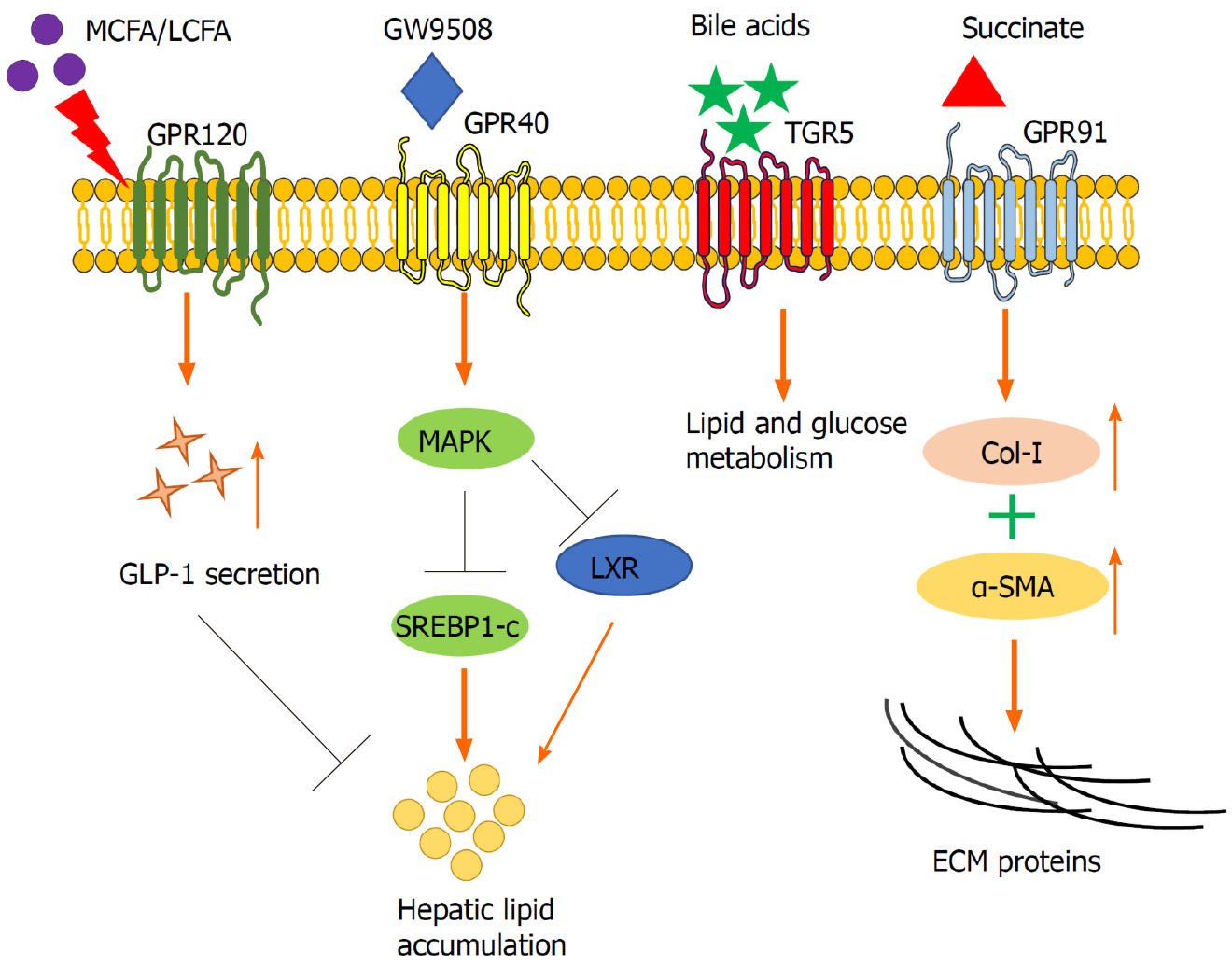
Figure 1 The role of G protein-coupled receptors in liver metabolism and the generation of extracellular matrix proteins.
G protein-coupled receptors are receptors of diverse molecules, such as fatty acids, bile acids, and other agonists (e.g., GW9508). They can regulate hepatic lipid and glucose metabolism and extracellular matrix (ECM) production via directly modulating hepatic cells (hepatocytes and hepatic stellate cells), and indirectly regulating gut hormones (e.g., glucagon-like peptide-1, GLP-1). α-SMA: α-smooth muscle actin; Col-I: Collagen type I; LCFA: Long-chain fatty acid; LXR: Liver X receptor; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; MCFA: Medium-chain fatty acid; SREBP1-c: Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1.
- Citation: Yang M, Zhang CY. G protein-coupled receptors as potential targets for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease treatment. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(8): 677-691
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i8/677.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i8.677