Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2021; 27(7): 624-640
Published online Feb 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i7.624
Published online Feb 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i7.624
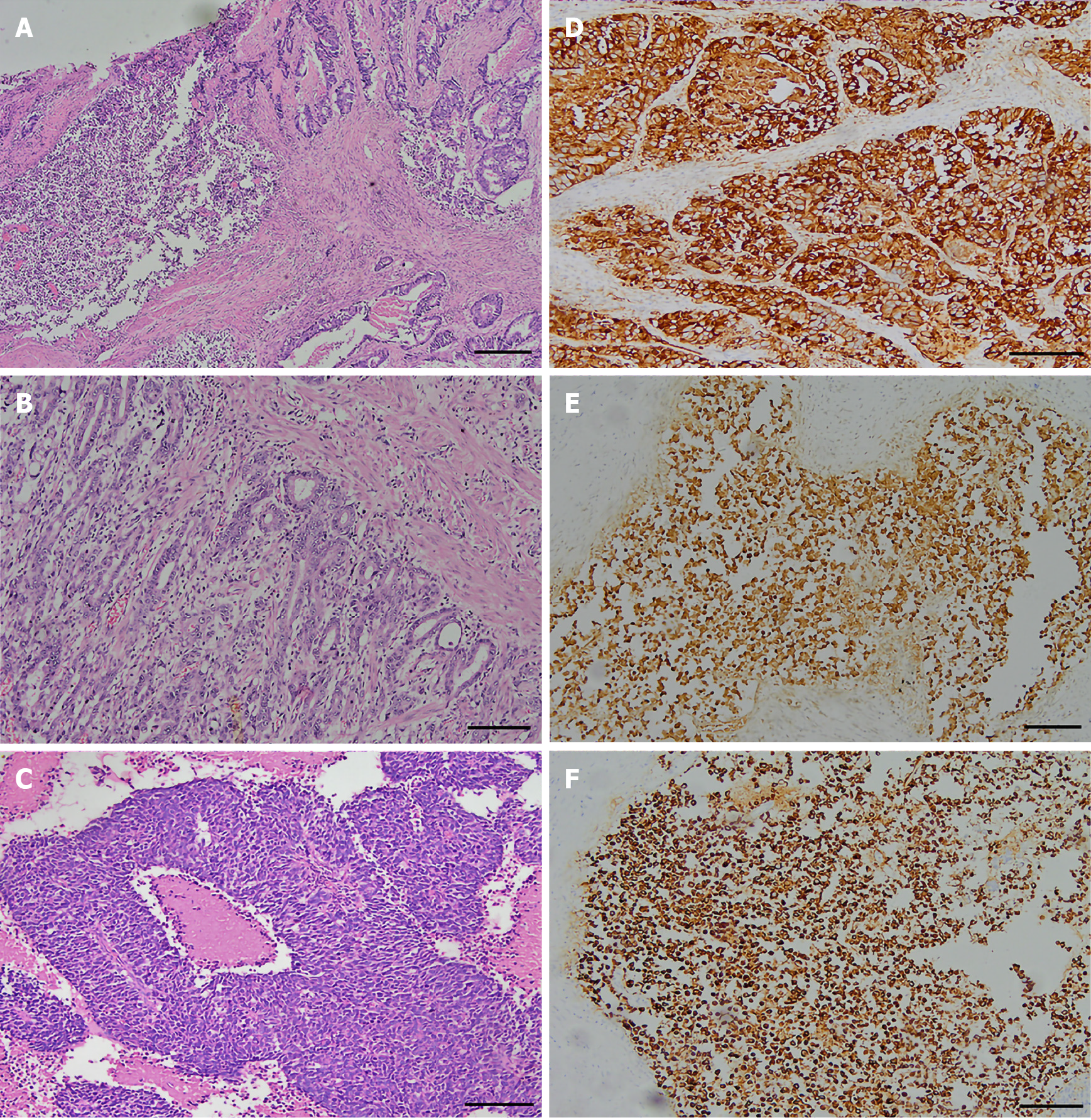
Figure 1 Histopathological and immunohistochemical findings of gastroenteropancreatic mixed neuroendocrine-non-neuroendocrine neoplasms.
A: Neuroendocrine carcinoma (left) and adenocarcinoma (right) (Hematoxylin-eosin staining, scale bar 200 µm); B: Adenocarcinoma component (Hematoxylin-eosin staining, scale bar 200 μm); C: Neuroendocrine component (Hematoxylin-eosin staining, scale bar 100 μm); D: Cytokeratin-positive adenocarcinoma (EnVision, scale bar 100 μm); E: CgA-positive neuroendocrine (EnVision, scale bar 100 μm); F: Syn-positive neuroendocrine (EnVision, scale bar 100 μm).
- Citation: Huang YC, Yang NN, Chen HC, Huang YL, Yan WT, Yang RX, Li N, Zhang S, Yang PP, Feng ZZ. Clinicopathological features and prognostic factors associated with gastroenteropancreatic mixed neuroendocrine non-neuroendocrine neoplasms in Chinese patients. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(7): 624-640
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i7/624.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i7.624