Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2021; 27(48): 8323-8342
Published online Dec 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i48.8323
Published online Dec 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i48.8323
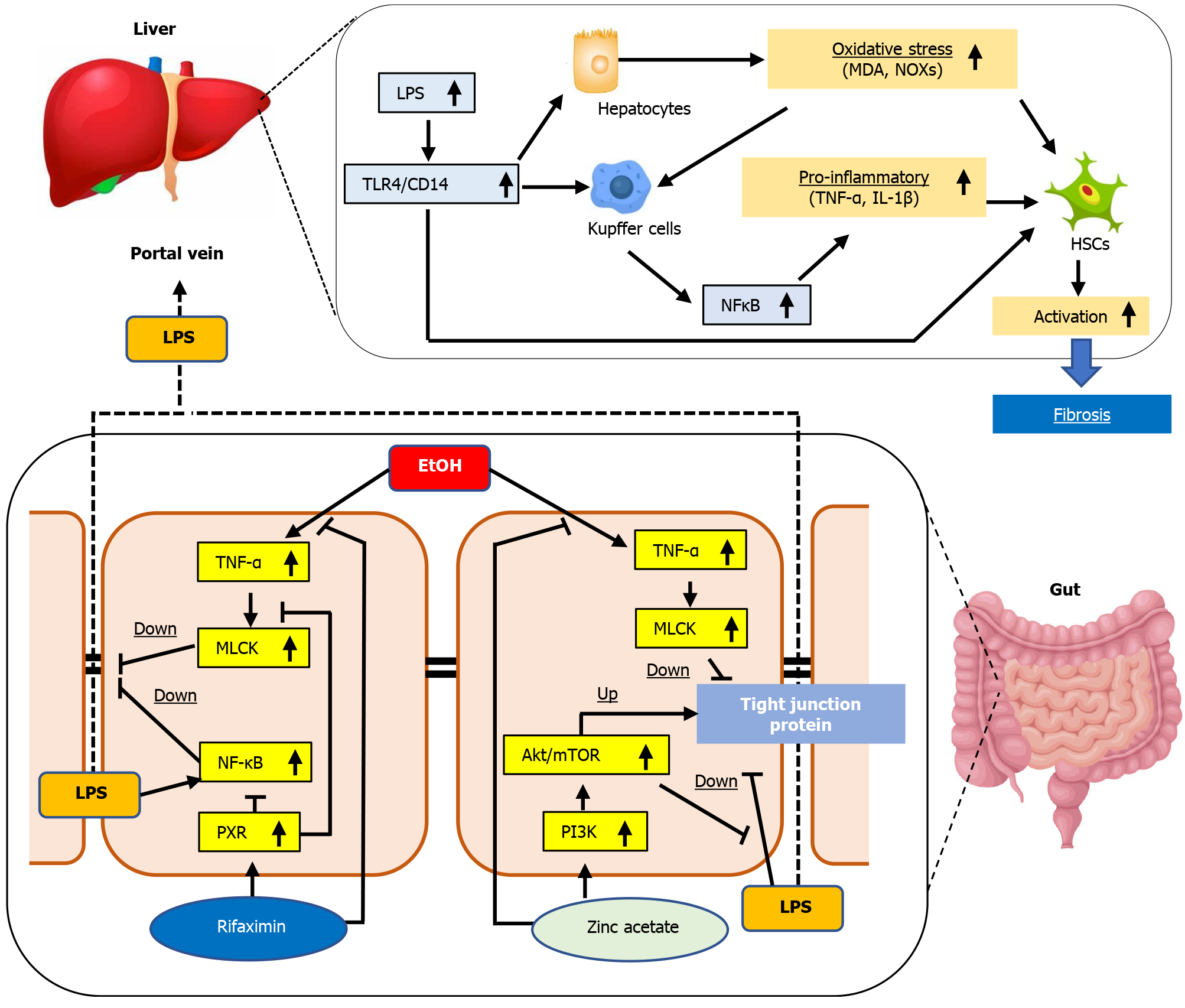
Figure 7 Graphic summary of the effect of zinc acetate and rifaximin on the alcoholic liver disease-related liver fibrosis.
ALD: Alcoholic liver disease; TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4; MDA: Malondialdehyde; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; HSC: Hepatic stellate cell; TNFα: Tumor necrosis factor α; MLCK: Myosin light chain kinase; NF-kB: Nuclear factor kB; PXR: Pregnane X receptor.
- Citation: Fujimoto Y, Kaji K, Nishimura N, Enomoto M, Murata K, Takeda S, Takaya H, Kawaratani H, Moriya K, Namisaki T, Akahane T, Yoshiji H. Dual therapy with zinc acetate and rifaximin prevents from ethanol-induced liver fibrosis by maintaining intestinal barrier integrity. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(48): 8323-8342
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i48/8323.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i48.8323