Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2021; 27(48): 8323-8342
Published online Dec 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i48.8323
Published online Dec 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i48.8323
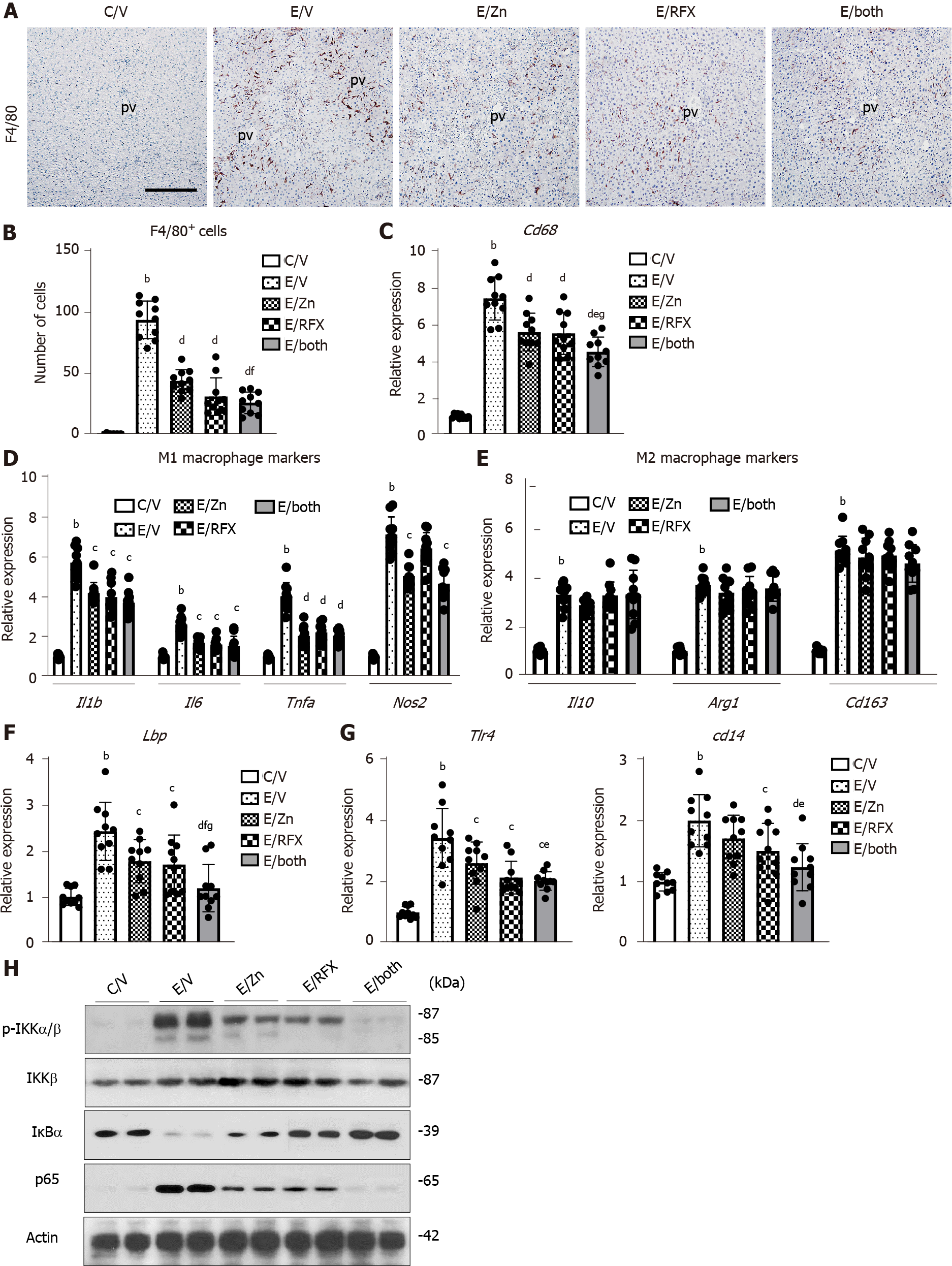
Figure 3 Zinc acetate and rifaximin against toll-like receptor 4-mediated pro-inflammatory response in alcoholic liver disease mice.
A: Representative microphotographs of liver sections stained with F4/80. Scale bar: 50 μm. B: Semi-quantitation of F4/80 immuno-positive Kupffer cells in high-power field by NIH imageJ software. Histochemical quantitative analyses included five fields per section; C-G: Relative mRNA expression level of Cd68 (C), M1-polarized macrophage-related genes (Il1b, Il6, Tnfa and Nos2) (D), M2-polarized macrophage-related genes (Il10, Arg1 and Cd163) (E), Lbp (F), Tlr4 and Cd14 (G) in the liver of experimental mice. The mRNA expression levels were measured by RT-qPCR, and Gapdh was used as internal control. Quantitative values are indicated as fold changes to the values of C/V group; H: Western blots for p-IKKα/β, IKKβ, IkBα and NF-kB p65 in the liver of experimental mice. Actin was used as internal control. Data are mean ± SD (B-G; n = 10), aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01 vs C/V group; cP < 0.05 and dP < 0.01 vs E/V group; eP < 0.05 and fP < 0.01 vs E/Zn group; gP < 0.05 and hP < 0.01 vs E/RFX group. pv: Portal vein.
- Citation: Fujimoto Y, Kaji K, Nishimura N, Enomoto M, Murata K, Takeda S, Takaya H, Kawaratani H, Moriya K, Namisaki T, Akahane T, Yoshiji H. Dual therapy with zinc acetate and rifaximin prevents from ethanol-induced liver fibrosis by maintaining intestinal barrier integrity. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(48): 8323-8342
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i48/8323.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i48.8323