Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2021; 27(48): 8302-8322
Published online Dec 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i48.8302
Published online Dec 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i48.8302
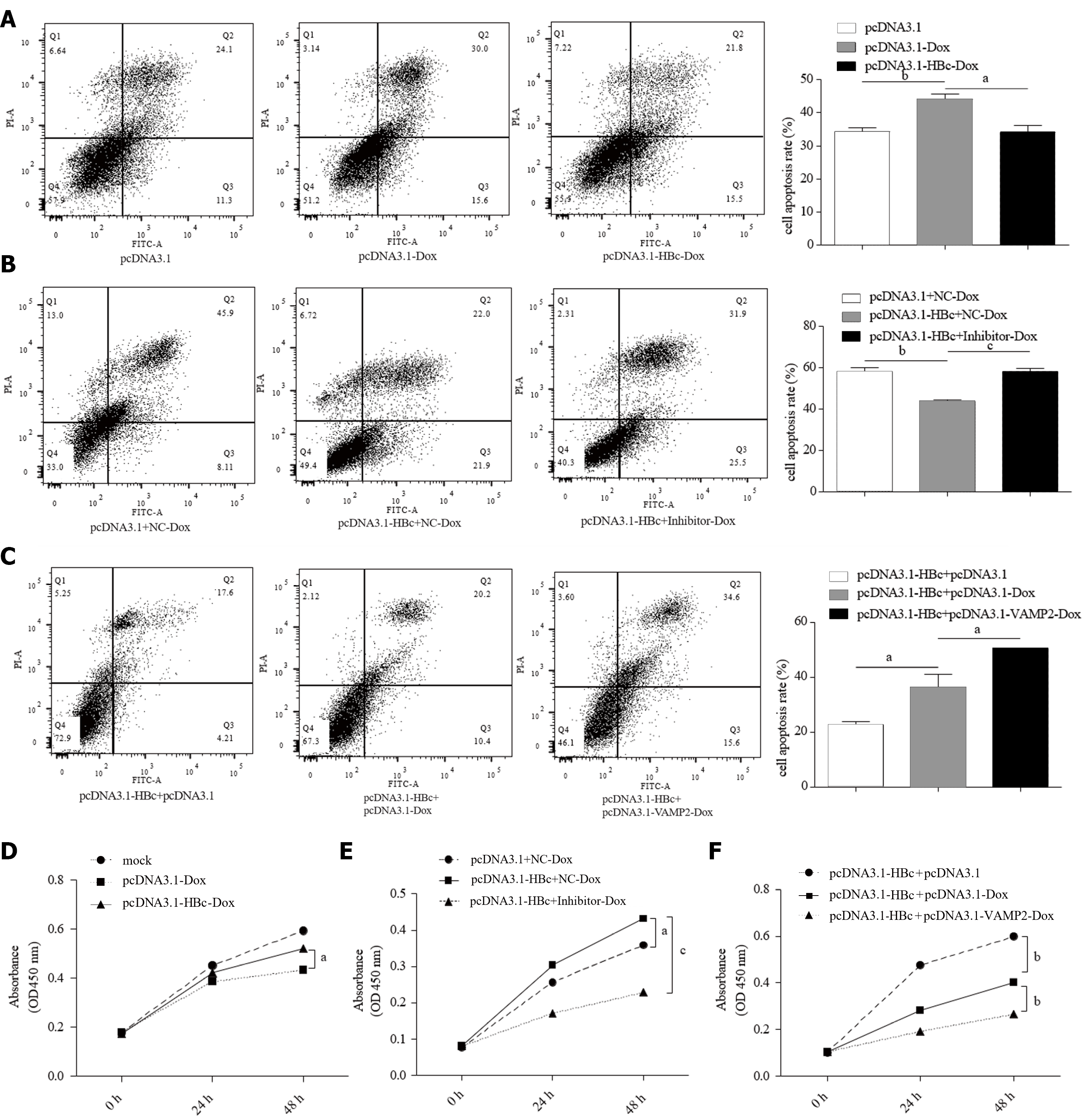
Figure 7 Hepatitis B core antigen mediated resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to Doxorubicin hydrochloride via miR-135a-5p/vesicle-associated membrane protein 2.
A: HepG2 cells were transfected with pcDNA3.1-hepatitis B core antigen (HBc) plasmids, flow cytometry was used to determine the rate of Doxorubicin hydrochloride (Dox)-induced apoptosis; B and C: Cell apoptosis rate was measured in HepG2 cells treated with Dox by flow cytometry after transfection with the indicated plasmid; D: Cell counting assay was performed to determine the proliferation of HepG2 cells transfected with pcDNA3.1-HBc plasmids after treatment with Dox; E: Cell proliferation in HepG2 cells co-transfected with pcDNA3.1-HBc plasmids and miR-135a-5p inhibitors assessed by the cell counting kit 8 assay; F: Cell counting assay used to determine the proliferation of HepG2 cells co-transfected with pcDNA3.1-HBc and pcDNA3.1-vesicle-associated membrane protein 2 plasmids after treatment with Dox. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001. HBc: Hepatitis B core antigen; VAMP2: Vesicle-associated membrane protein 2; Dox: Doxorubicin hydrochloride.
- Citation: Wei XC, Xia YR, Zhou P, Xue X, Ding S, Liu LJ, Zhu F. Hepatitis B core antigen modulates exosomal miR-135a to target vesicle-associated membrane protein 2 promoting chemoresistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(48): 8302-8322
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i48/8302.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i48.8302