Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2021; 27(48): 8227-8241
Published online Dec 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i48.8227
Published online Dec 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i48.8227
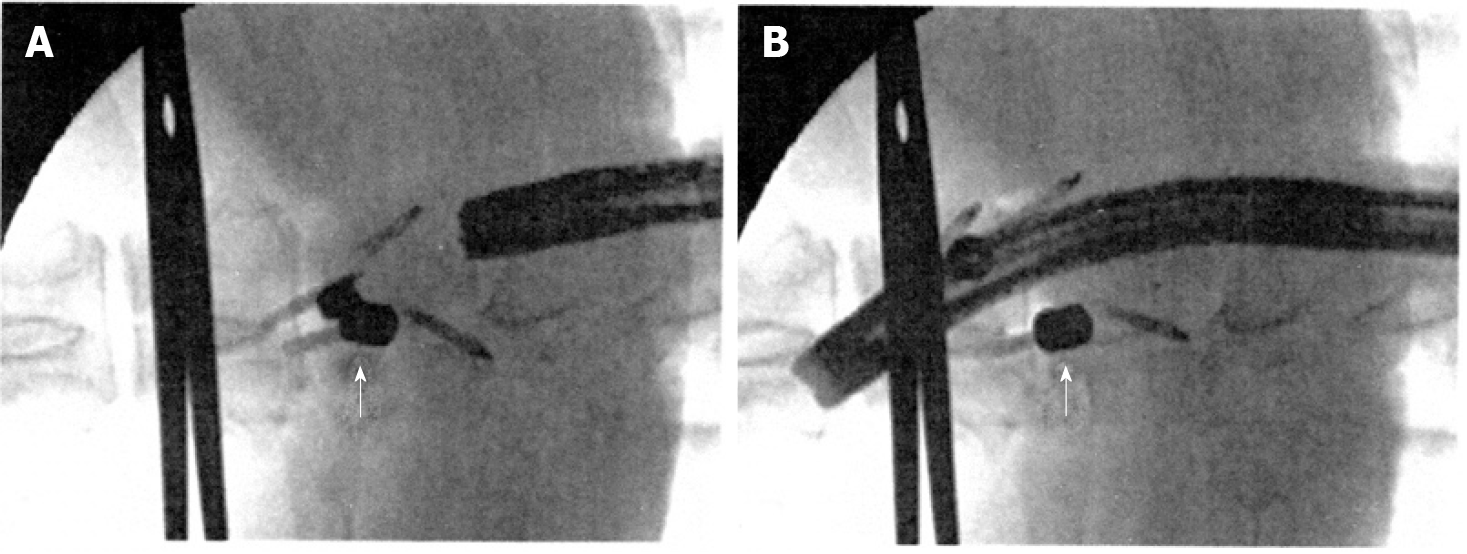
Figure 5 Fluoroscopic view after insertion of the magnets.
A: Magnets in the sub-adventitial space opposing the respective esophageal walls. A surgical clamp indicates the level of the esophago-gastric junction and the arrow indicates the magnets attracted to one another and closing the lumen; B: Magnets separated by the passage of the endoscope. The arrow indicates one of the magnets separated from the other. A-B: Citation: Modified from: Dobashi A, Wu SW, Deters JL, Miller CA, Knipschield MA, Cameron GP, Lu L, Rajan E, Gostout CJ. Endoscopic magnet placement into subadventitial tunnels for augmenting the lower esophageal sphincter using submucosal endoscopy: ex vivo and in vivo study in a porcine model (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 2019; 89: 422-428. Copyright© The Authors 2020. Published by Elsevier. The authors obtained permission for use of the figure from Elsevier (Supplementary material).
- Citation: Bortolotti M. Magnetic challenge against gastroesophageal reflux . World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(48): 8227-8241
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i48/8227.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i48.8227