Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2021; 27(42): 7340-7349
Published online Nov 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i42.7340
Published online Nov 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i42.7340
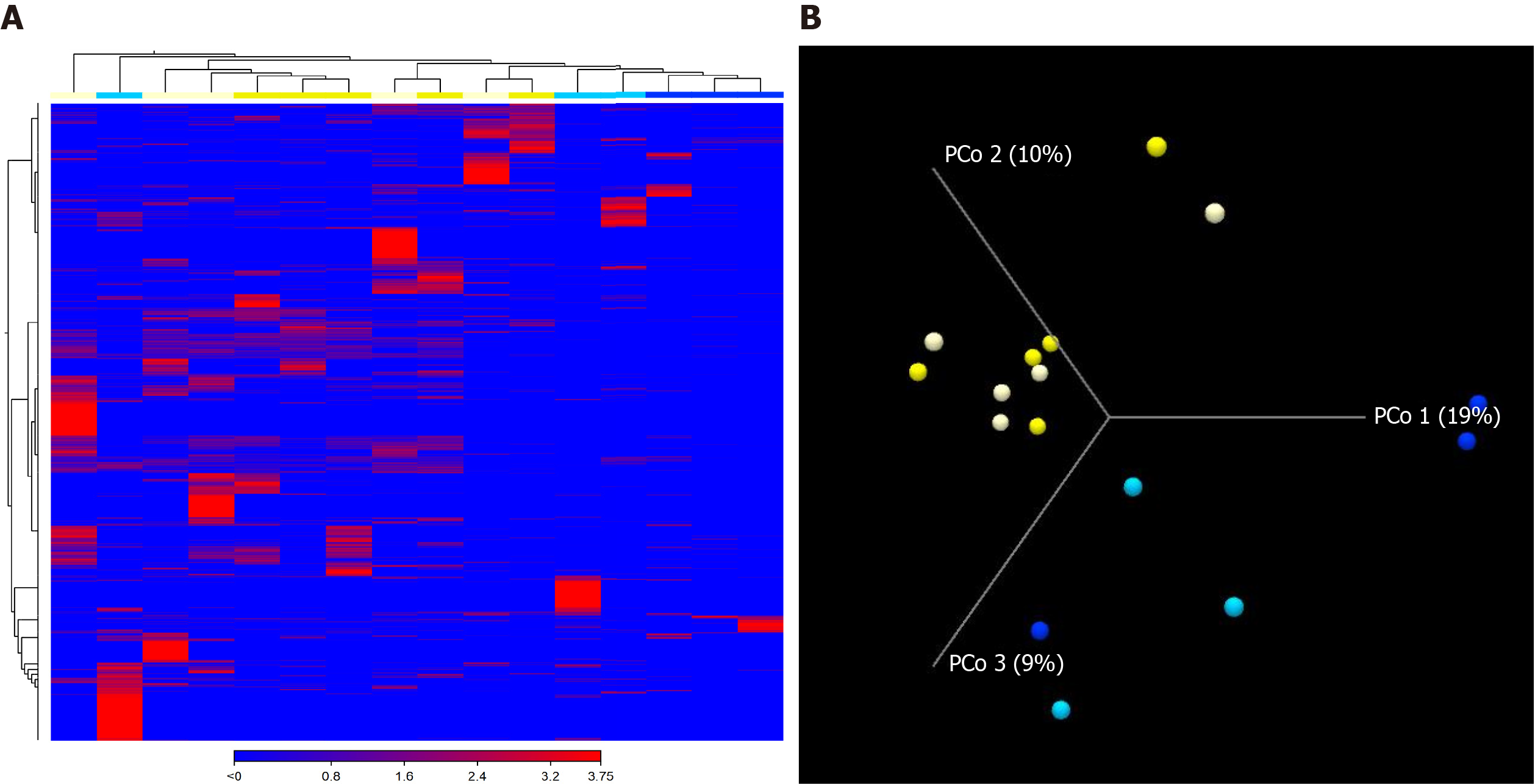
Figure 2 Composition of the gut microbiome in hepatocellular carcinoma patients is associated with the response to nivolumab.
A: Heatmap showing the abundance of operational taxonomic units in responders (yellow) and non-responders (blue). The original comprehensive figure, including the names of bacterial taxa, is presented as Supplemental Figure 1; B: Unweighted beta diversity analysis showed that the overall bacterial community structure and phylogenetic diversity at T0 (light yellow and light blue) and T1 (yellow and blue) were similar; distinct clusters were not observed for responders (yellow) and non-responders (blue). Statistical values obtained by the PERMANOVA test are presented in Supplemental Table 2.
- Citation: Chung MW, Kim MJ, Won EJ, Lee YJ, Yun YW, Cho SB, Joo YE, Hwang JE, Bae WK, Chung IJ, Shin MG, Shin JH. Gut microbiome composition can predict the response to nivolumab in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma patients. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(42): 7340-7349
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i42/7340.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i42.7340