Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2021; 27(42): 7311-7323
Published online Nov 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i42.7311
Published online Nov 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i42.7311
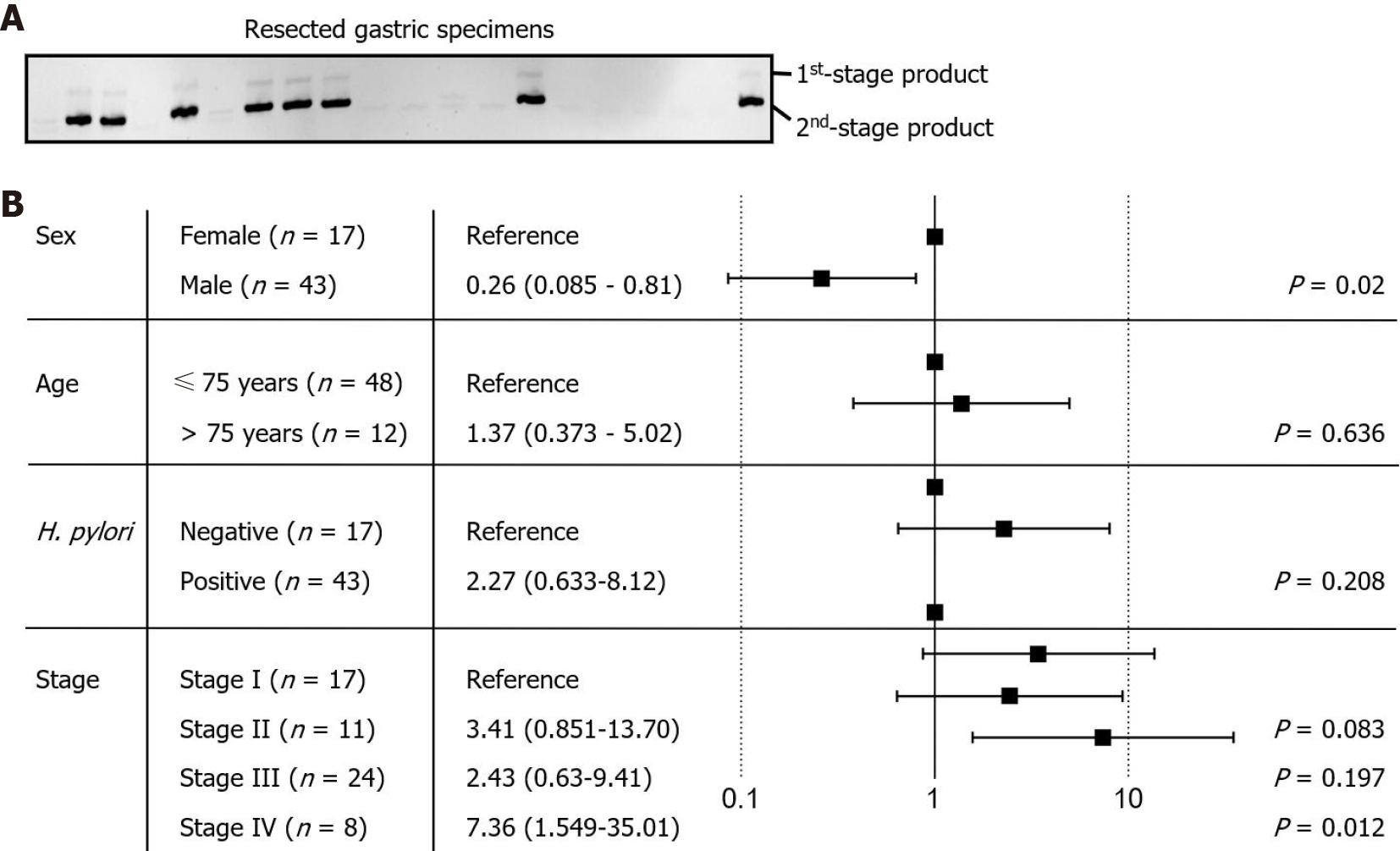
Figure 3 Identification of Fusobacterium nucleatum in the resected gastric cancer tissues.
A: Fusobacterium nucleatum (F. nucleatum) was detected by amplification of the conserved NusG gene sequence using nested polymerase chain reaction method. The end point product was analyzed using 6% nondenaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis; B: The relative risk of F. nucleatum colonization was analyzed against the sex, age, status of Helicobacter pylori colonization, and cancer stage. Data analysis is shown as Forest plot.
- Citation: Hsieh YY, Tung SY, Pan HY, Chang TS, Wei KL, Chen WM, Deng YF, Lu CK, Lai YH, Wu CS, Li C. Fusobacterium nucleatum colonization is associated with decreased survival of helicobacter pylori-positive gastric cancer patients. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(42): 7311-7323
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i42/7311.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i42.7311