Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2021; 27(42): 7247-7270
Published online Nov 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i42.7247
Published online Nov 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i42.7247
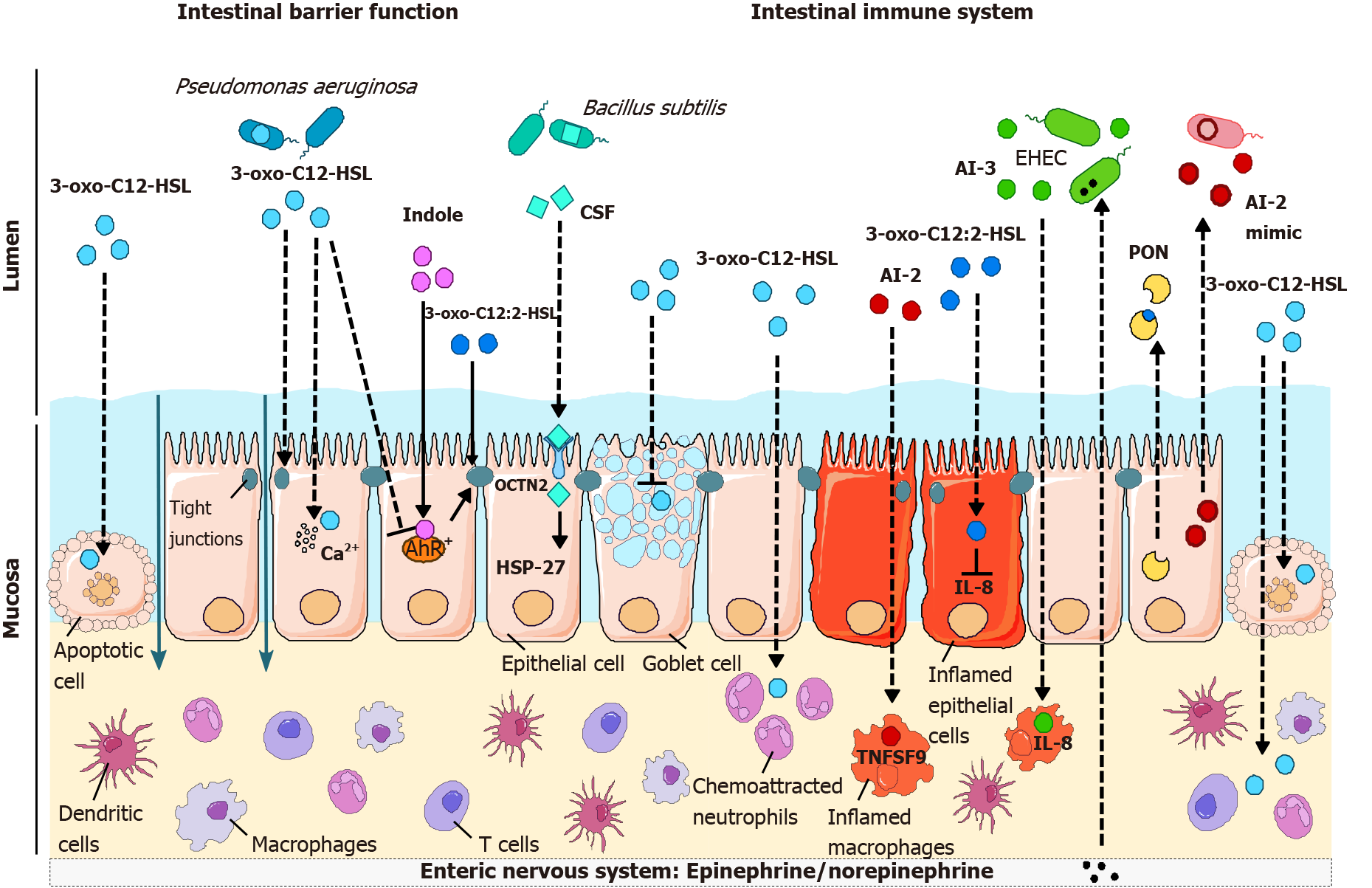
Figure 3 Effects of quorum sensing molecules on intestinal barrier function (see Table 2) and on the immune response (see Table 3).
The Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing (QS) molecule 3-oxo-C12-HSL induces apoptosis in various cell types, including epithelial cells, promoting a breach in the intestinal barrier. In addition, 3-oxo-C12-HSL disrupts tight junctions, thus leading to increased paracellular permeability, and affects mucin production. Conversely, intestinal acyl-homoserine lactone 3-oxo-C12:2-HSL and the tryptophan metabolite indole protect tight junctions. Bacillus subtilis CSF, which binds to OCTN2, also promotes intestinal barrier integrity by reducing cell death through activation of HSP27 signaling. While 3-oxo-C12-HSL stimulates chemoattraction and phagocytosis in neutrophils and induces cell death, its pro- or anti-inflammatory effects on immune cells are more complex (see Table 3). Autoinducers (AI)-2 and AI-3 both exert proinflammatory effects on macrophages by inducing the expression of the immune mediators TNSF9 and interleukin (IL)-8, respectively, whereas 3-oxo-C12:2-HSL reduces IL-8 production by epithelial cells. It remains to be clarified how all these QS molecules could cross the intestinal barrier and/or reach immune cells in vivo in a physiological context, as illustrated by dotted lines. Last, just as QS molecules can impact eukaryotic cells, the host can interfere with QS: the hormones epinephrine/norepinephrine bind to the AI-3 receptor in EHEC; intestinal epithelial cells secrete an AI-2 mimic in addition to paraoxonase (PON) enzymes degrading homoserine lactones. CSF: Competence and sporulation factor; AI: Autoinducer; PON: Paraoxonase; AhR: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor; IL: Interleukin.
- Citation: Coquant G, Aguanno D, Pham S, Grellier N, Thenet S, Carrière V, Grill JP, Seksik P. Gossip in the gut: Quorum sensing, a new player in the host-microbiota interactions. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(42): 7247-7270
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i42/7247.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i42.7247