Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2021; 27(42): 7247-7270
Published online Nov 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i42.7247
Published online Nov 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i42.7247
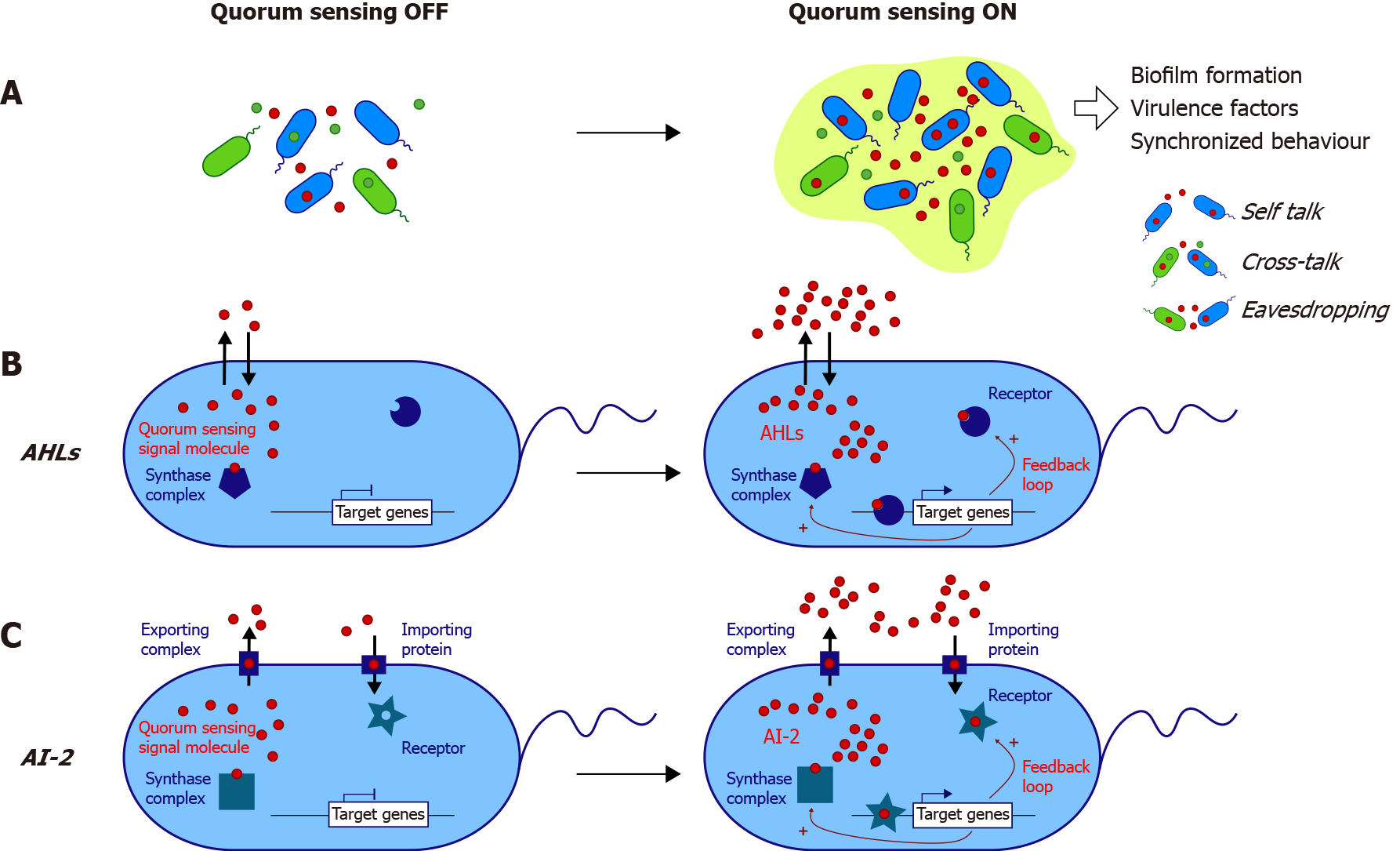
Figure 1 Main known mechanisms of quorum sensing activation in bacteria.
A: Quorum sensing (QS) signaling depends on the release of autoinducers (AIs) in the environment. Above a threshold concentration depending on bacterial density, QS is activated and triggers gene expression. QS can be classified into three categories: self-talk (i.e., one species “talking” to itself), crosstalk (i.e., different species communicating using common AI), and eavesdropping, which refers to “listening” by species unable to produce AI by itself; B: The acyl-homoserine lactone (AHL) used by Gram-negative bacteria is produced by the synthase complex, and AHL can freely diffuse through the membrane. AHL is recognized by its intracellular receptor, and the complex binds to target gene regulatory elements; C: The AI-2 system is used by both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. AI-2 needs a transporter protein to exit and enter the cell. For both AHLs and AI-2, there is a positive feedback loop, allowing the expression of the synthase complex and receptor of AIs. AHL: Acyl-homoserine lactone; AI: Autoinducer.
- Citation: Coquant G, Aguanno D, Pham S, Grellier N, Thenet S, Carrière V, Grill JP, Seksik P. Gossip in the gut: Quorum sensing, a new player in the host-microbiota interactions. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(42): 7247-7270
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i42/7247.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i42.7247