Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2021; 27(40): 6908-6926
Published online Oct 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i40.6908
Published online Oct 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i40.6908
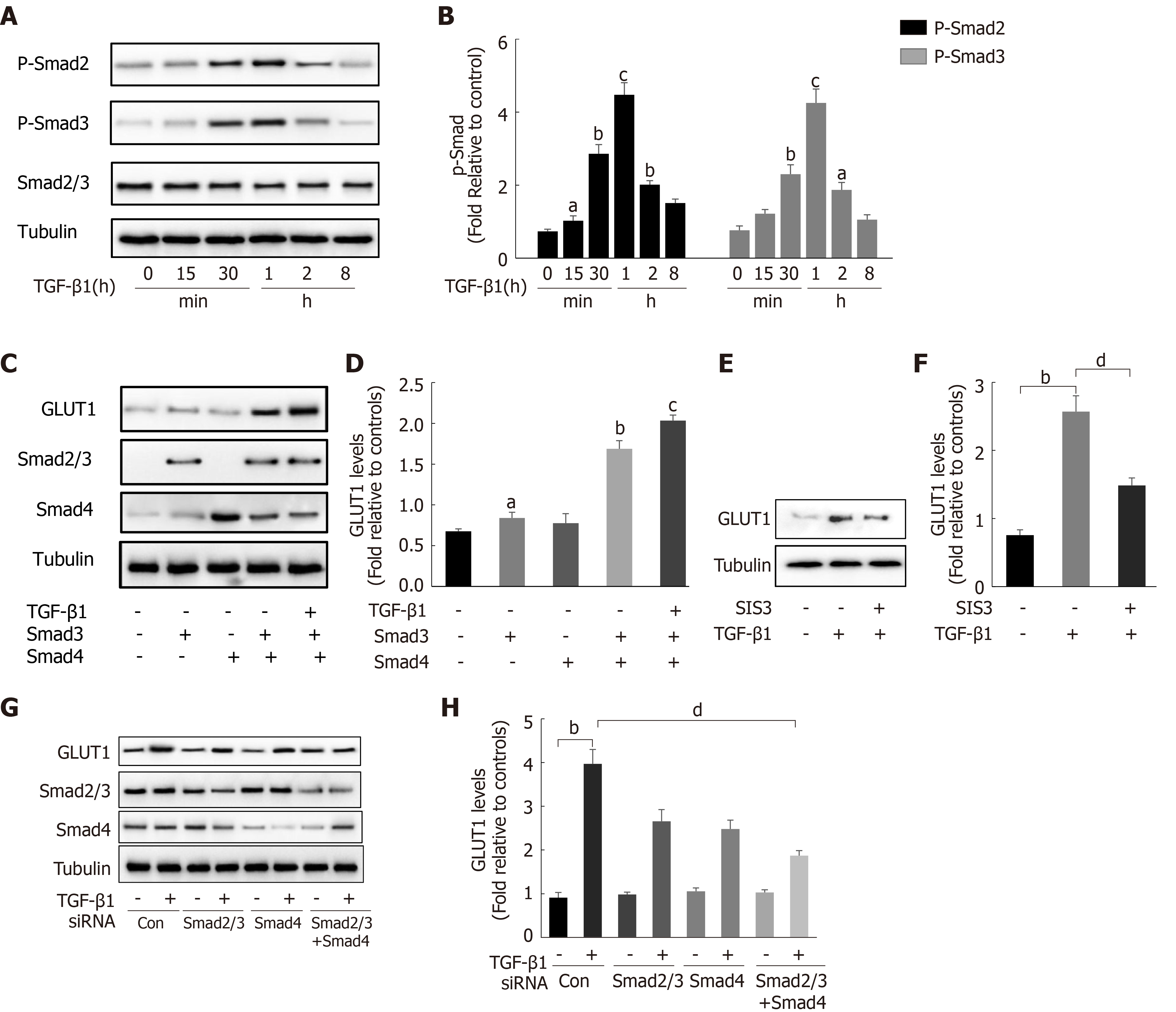
Figure 3 Transforming growth factor-β1 induces glucose transporter 1 expression through the Smad pathway.
A and B: Serum-starved (for 20 h) primary mouse hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) were treated with transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) (3 ng/mL) and examined at various time points. Western blot analysis using specific antibodies (A). Quantitative analysis of the levels of the p-Smad2 and p-Smad3 proteins in five independent experiments (B); C and D: After transiently transfecting HSCs with 2 μg of Smad3 and/or Smad4 expression plasmids, the cells were cultured in serum-free medium for 48 h and then treated with TGF-β1 (3 ng/mL) for 4 h. Green fluorescent protein (GFP) was used as a transfection control. Western blot analysis using specific antibodies (C). Quantitative analysis of glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) protein expression in five independent experiments (D); E and F: HSCs were first pretreated with a Smad3 inhibitor (SIS3, 20 μm) for 1 h and then treated with TGF-β1 (3 ng/mL) for 4 h. Western blot analysis using specific antibodies (E). Quantitative analysis of the GLUT1 protein level in five independent experiments (F); G and H: Mouse primary HSCs were transfected with 20 μmol/L control small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) or siRNAs targeting Smad2/3 and Smad4. After transfection in serum-free medium for 48 h, the cells were treated with TGF-β1 (3 ng/mL) for 4 h. Western blot analysis using specific antibodies (G). Quantitative analysis of the GLUT1 protein level in five independent experiments (H) (the mean ± SE; aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 and cP < 0.001 compared with that in the group of cells without TGF-β1; dP < 0.05 for the comparison of the groups treated with TGF-β1 and the groups treated with TGF-β1 and different additional reagents; Student’s t test). GLUT1: Glucose transporter 1; TGF-β1: Transforming growth factor-β1; Con: Control; siRNAs: Small interfering RNAs.
- Citation: Zhou MY, Cheng ML, Huang T, Hu RH, Zou GL, Li H, Zhang BF, Zhu JJ, Liu YM, Liu Y, Zhao XK. Transforming growth factor beta-1 upregulates glucose transporter 1 and glycolysis through canonical and noncanonical pathways in hepatic stellate cells. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(40): 6908-6926
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i40/6908.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i40.6908