Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2021; 27(40): 6908-6926
Published online Oct 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i40.6908
Published online Oct 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i40.6908
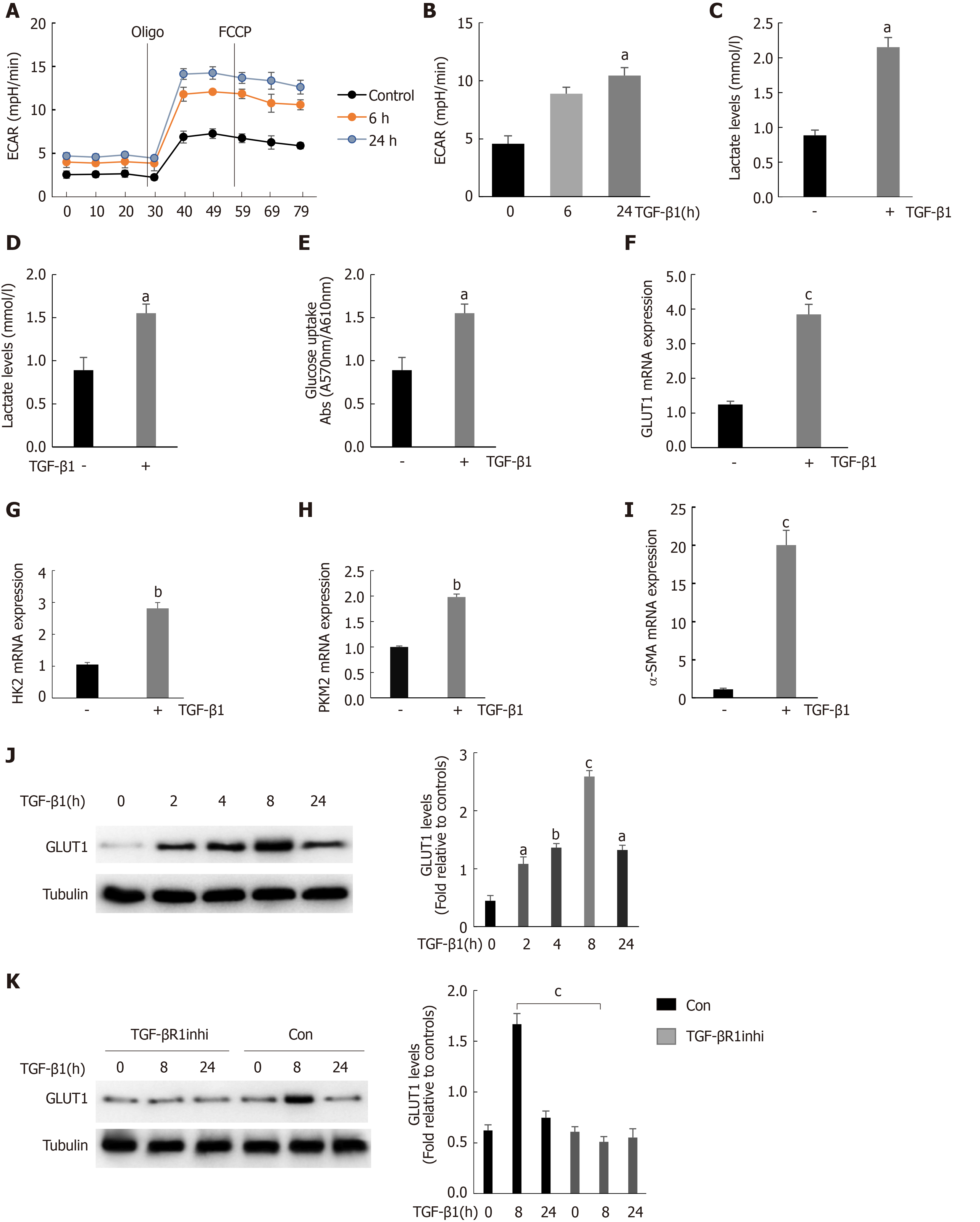
Figure 2 Stimulation of hepatic stellate cells with transforming growth factor-β1 induces glucose transporter 1 expression and promotes glycolysis.
A: Serum-starved (for 20 h) primary mouse hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) were seeded into Seahorse XF-24 cell culture microplates (5 × 104 cells/well). The cells were first treated with transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) (3 ng/mL) for 0, 6 or 24 h, followed by sequential treatment with oligomycin (Oligo) and carbonyl cyanide 4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenylhydrazone (FCCP). The extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) was recorded in real time; B: The basic ECAR. n = 6; the mean ± SE; aP < 0.05 compared to the level before TGF-β1 treatment (0 h); unpaired t test; C and D: Mouse HSCs were treated with or without TGF-β1 (3 ng/mL) for 24 h. The cells were then lysed, and the lactic acid contents in the cell lysate (C) and the culture medium (D) were examined; E: Determination of glucose consumption in the culture medium; F-I: Mouse HSCs were treated with or without TGF-β1 (3 ng/mL) for 24 h. RNA was purified, and RT-PCR was performed to examine the expression levels of glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) (F), HK-2 (G), PKM-2 (H) and α-SMA (I), n = 5, the mean ± SE; aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 and cP < 0.001 compared with those at 0 h or those in the TGF-β1-untreated group; one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA); J: Western blot analysis of the expression levels of GLUT1 and tubulin at various time points after HSCs were treated with TGF-β1 (3 ng/mL); K: Examination of the changes in GLUT1 and tubulin levels after sequential treatment with a type 1 TGF-β receptor inhibitor (LY2109761, 2 μm) for 1 h and then with TGF-β1 (3 ng/mL) for 0, 8 or 24 h. All experiments shown in A-E and F-I were performed 2-3 times. Inhi: Inhibitor; Con: Control; FCCP: Carbonyl cyanide 4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenylhydrazone; ECAR: Extracellular acidification rate; GLUT1: Glucose transporter 1; TGF-β1: Transforming growth factor-β1.
- Citation: Zhou MY, Cheng ML, Huang T, Hu RH, Zou GL, Li H, Zhang BF, Zhu JJ, Liu YM, Liu Y, Zhao XK. Transforming growth factor beta-1 upregulates glucose transporter 1 and glycolysis through canonical and noncanonical pathways in hepatic stellate cells. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(40): 6908-6926
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i40/6908.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i40.6908