Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2021; 27(39): 6590-6600
Published online Oct 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i39.6590
Published online Oct 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i39.6590
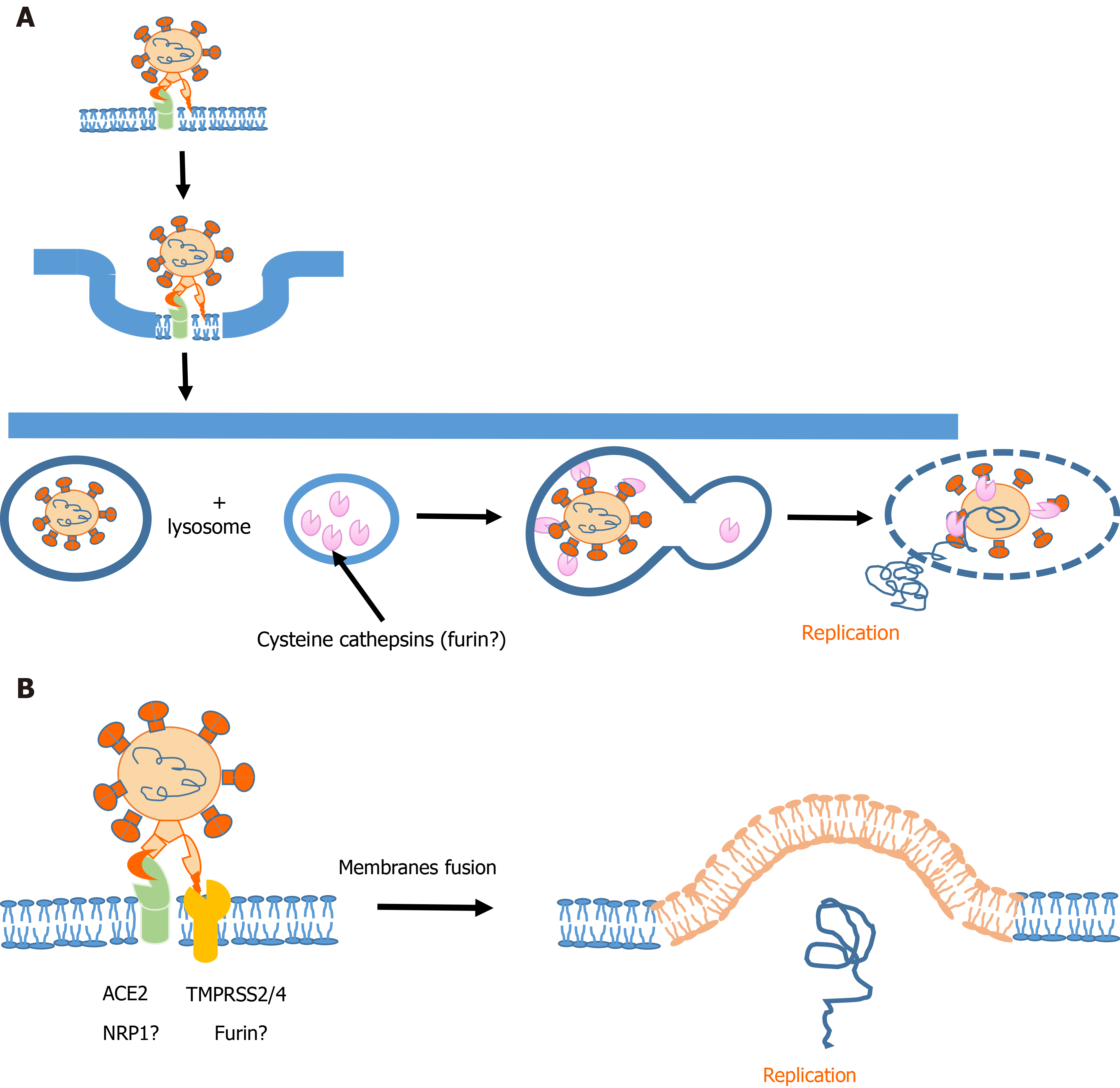
Figure 2 Two modes of virus entry.
A: Receptor-mediated endocytosis of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2. After binding to ACE2 and formation of endosome, lysosomal cathepsins activate spike protein, which leads to the release of the viral RNA into host cell. B: Membrane fusion mechanism - priming of the spike proteins is mediated by transmembrane peptidase/serine subfamily member 2/4, which leads to fusion of viral and host membranes and release of the viral RNA into host cell.
- Citation: Berdowska I, Matusiewicz M. Cathepsin L, transmembrane peptidase/serine subfamily member 2/4, and other host proteases in COVID-19 pathogenesis – with impact on gastrointestinal tract. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(39): 6590-6600
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i39/6590.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i39.6590