Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2021; 27(37): 6277-6289
Published online Oct 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i37.6277
Published online Oct 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i37.6277
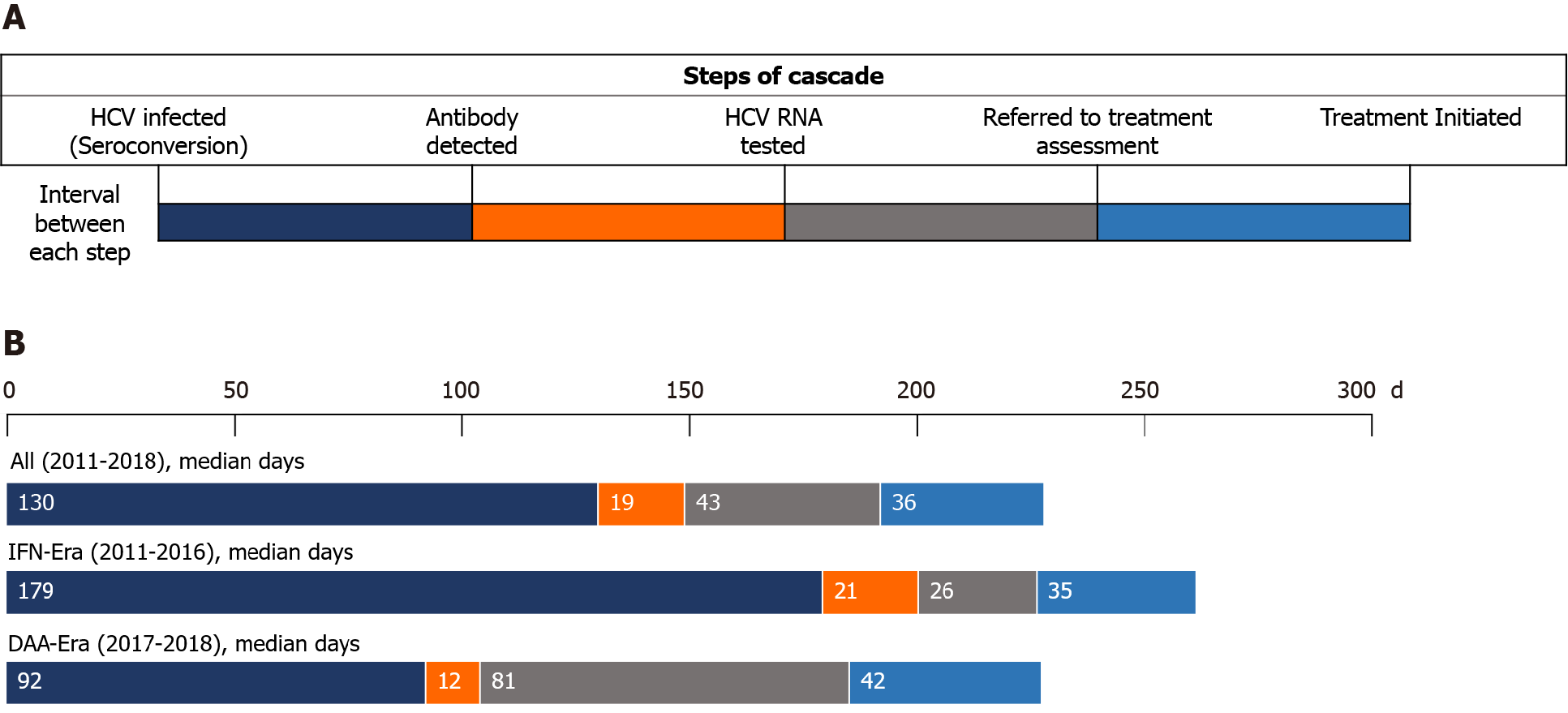
Figure 3 Intervals between steps of the care cascade of incident hepatitis C virus infections.
A: Demonstration of the intervals between each step of the care cascade; B: In all included people living with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) (PLWH), the median interval from seroconversion to detection of hepatitis C virus (HCV) seropositivity by HIV-treating physicians was 130 days, which was significantly shorter in the direct-acting antiviral (DAA) era (median 92 d) than that in the interferon (IFN) era (median 179 d) (P < 0.001). In the IFN era, the median interval from detection of HCV seropositivity to HCV RNA testing was 21 d, that from RNA testing to referral to treatment assessment was 26 d, and that from assessment to treatment initiation was 35 d. In the DAA era, the median interval from detection of HCV seropositivity to HCV RNA testing was 12 d, that from RNA testing to referral to treatment assessment was 81 d, and that from assessment to treatment initiation was 42 d. The differences in the intervals after antibody diagnosis were not statistically significant between PLWH included in the IFN era and those in the DAA era. HCV: Hepatitis C virus; IFN: Interferon; DAA: Direct-acting antiviral.
- Citation: Huang MH, Sun HY, Ho SY, Chang SY, Hsieh SM, Sheng WH, Chuang YC, Huang YS, Su LH, Liu WC, Su YC, Hung CC. Recently acquired hepatitis C virus infection among people living with human immunodeficiency virus at a university hospital in Taiwan. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(37): 6277-6289
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i37/6277.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i37.6277