Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2021; 27(37): 6277-6289
Published online Oct 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i37.6277
Published online Oct 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i37.6277
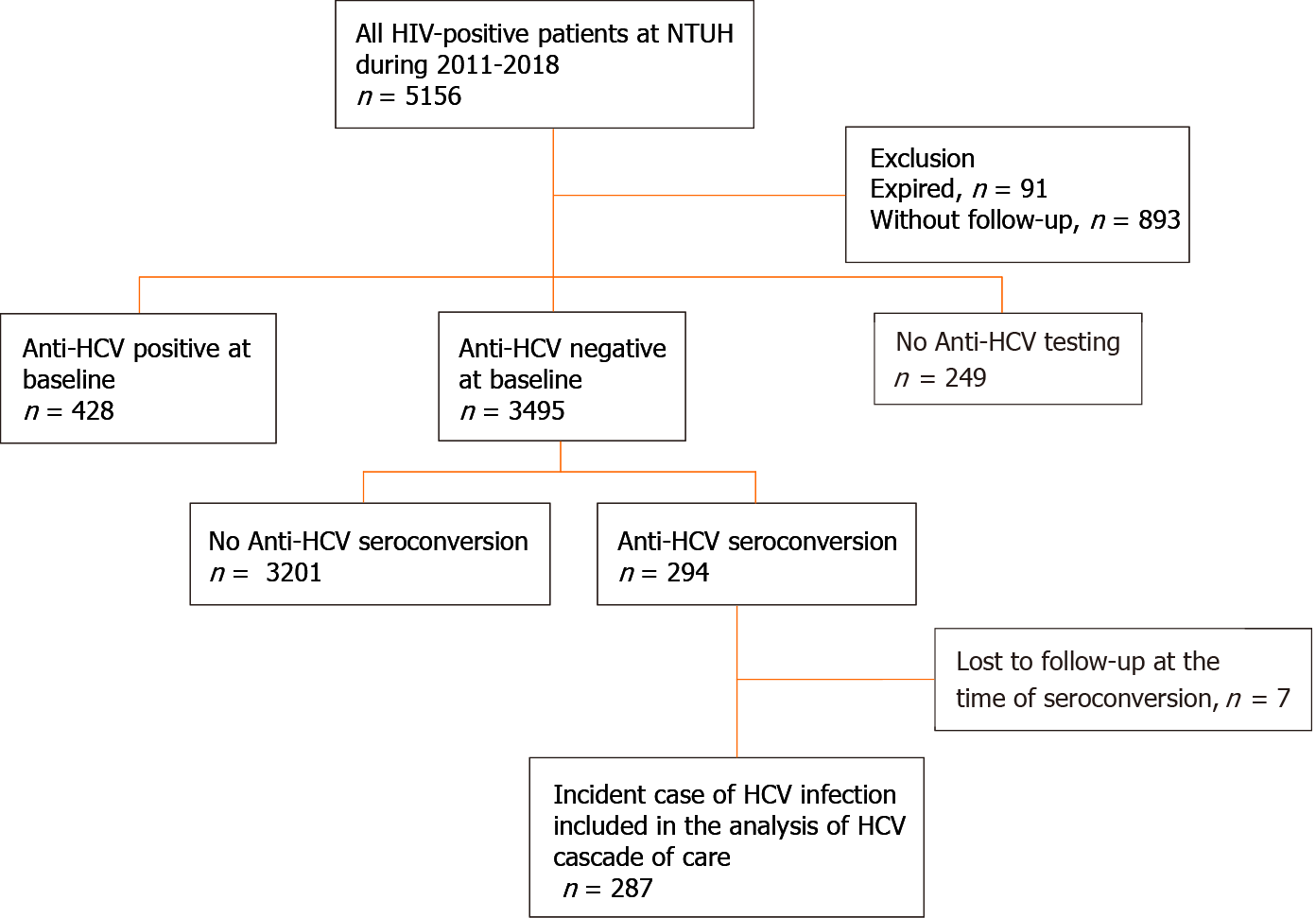
Figure 1 Patient flow.
Between 2011 and 2018, 3495 people living with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) (PLWH) had negative anti-hepatitis C virus (HCV) antibody tests at baseline and HCV seroconversion was detected in 294 (8.4%) PLWH. After excluding 7 PLWH who were lost to follow-up when HCV seroconversion occurred, a total of 287 PLWH were included in the analysis of the care cascade of incident HCV infections. HIV: Human immunodeficiency virus; NTUH: National Taiwan University Hospital; HCV: Hepatitis C virus.
- Citation: Huang MH, Sun HY, Ho SY, Chang SY, Hsieh SM, Sheng WH, Chuang YC, Huang YS, Su LH, Liu WC, Su YC, Hung CC. Recently acquired hepatitis C virus infection among people living with human immunodeficiency virus at a university hospital in Taiwan. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(37): 6277-6289
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i37/6277.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i37.6277