Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2021; 27(37): 6248-6261
Published online Oct 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i37.6248
Published online Oct 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i37.6248
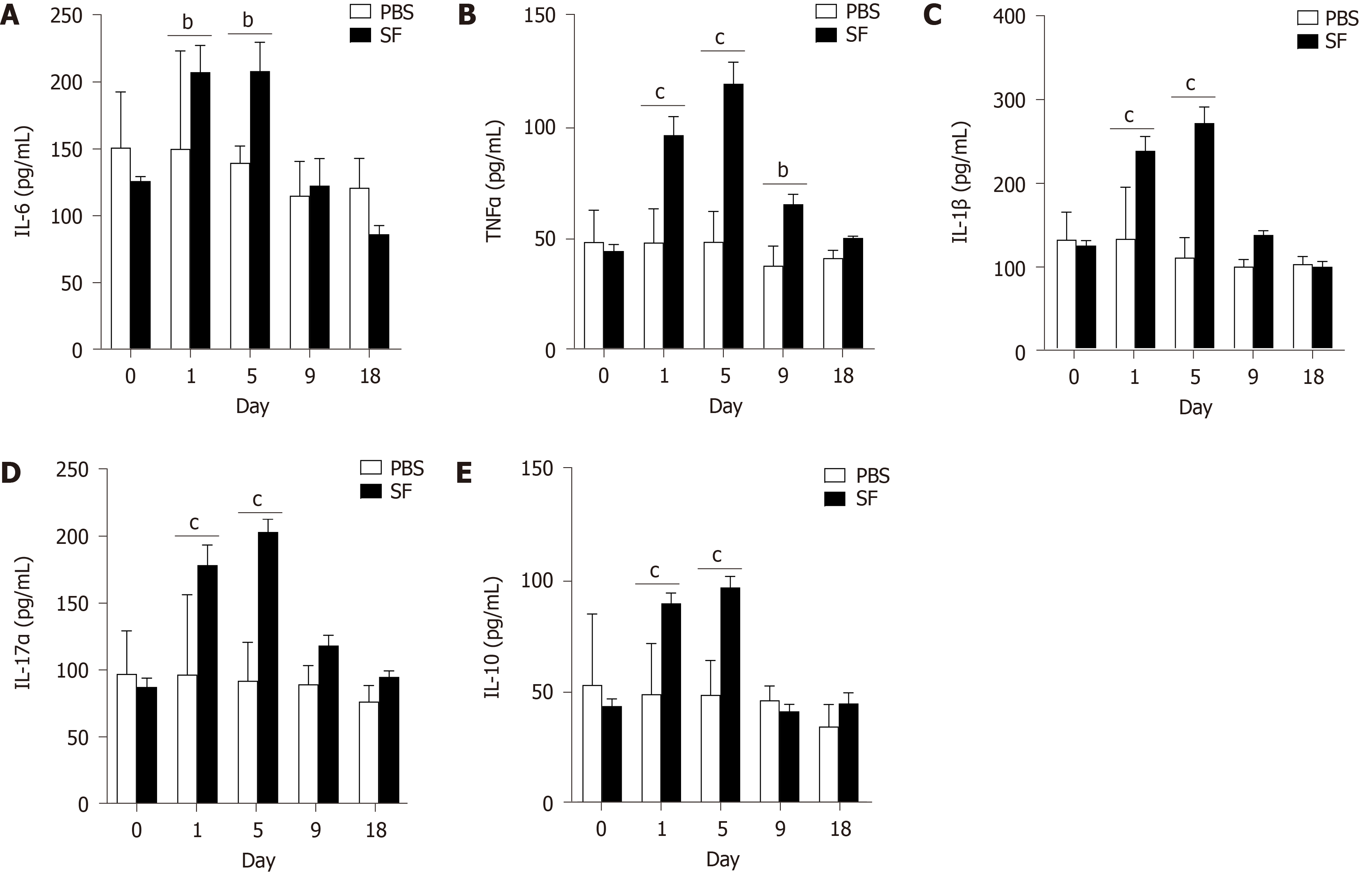
Figure 2 Inflammatory cytokines interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-1β, interleukin-17α, and interleukin-10 detected in serum samples of Shigellaflexneri infected rats.
A: Interleukin (IL)-6; B: Tumor necrosis factor-α; C: IL-1β; D: IL-17α; E: IL-10. 0: Before infection. 1-18: The number of days after the establishment of the Shigella flexneri infection model. n = 12 per group on day 0 and day 1; n = 9 per group on day 5; n = 6 per group on day 9; n = 3 per group on day 18. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; and cP < 0.001 (two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test). PBS: Phosphate-buffered saline; IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor.
- Citation: Nie JJ, Pian YY, Hu JH, Fan GQ, Zeng LT, Ouyang QG, Gao ZX, Liu Z, Wang CC, Liu Q, Cai JP. Increased systemic RNA oxidative damage and diagnostic value of RNA oxidative metabolites during Shigella flexneri-induced intestinal infection. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(37): 6248-6261
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i37/6248.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i37.6248