Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2021; 27(33): 5575-5594
Published online Sep 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i33.5575
Published online Sep 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i33.5575
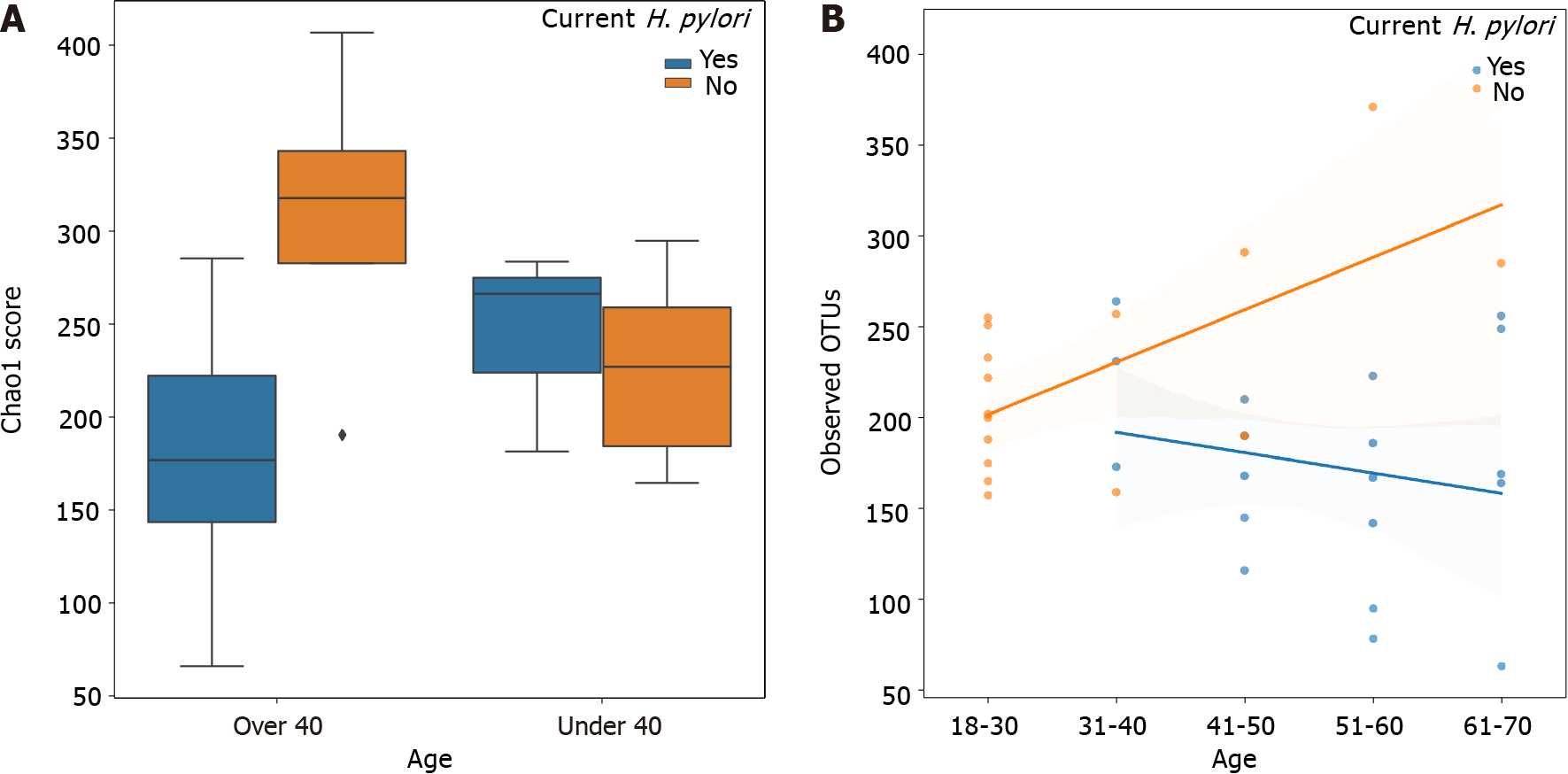
Figure 1 Chao1 index alpha diversity and observed operational taxonomic units by Helicobacter pylori status stratified by age.
A: Chao1 index alpha diversity is compared between Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) patients (blue) and control subjects (orange), subgrouped by age. H. pylori patients over 40 years old (n = 16) had significantly lower Chao1 scores compared to control subjects over 40 (n = 4) (Kruskal-Wallis H = 6.036, P = 0.014). Boxes represent 1st and 3rd quartiles, and central lines represent median values. Whiskers represent non-outlier high and low values. Points show outliers, which were determined by having a distance from the 1st or 3rd quartile greater than 1.5 times the interquartile range; B: Observed operational taxonomic units (operational taxonomic units) are compared between H. pylori patients (blue, n = 19) and control subjects (orange, n = 16), as a function of age. Shading around the regression lines indicates 95% confidence intervals. OTU: Operational taxonomic units; H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori.
- Citation: White B, Sterrett JD, Grigoryan Z, Lally L, Heinze JD, Alikhan H, Lowry CA, Perez LJ, DeSipio J, Phadtare S. Characterization of gut microbiome and metabolome in Helicobacter pylori patients in an underprivileged community in the United States. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(33): 5575-5594
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i33/5575.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i33.5575