Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2021; 27(33): 5555-5565
Published online Sep 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i33.5555
Published online Sep 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i33.5555
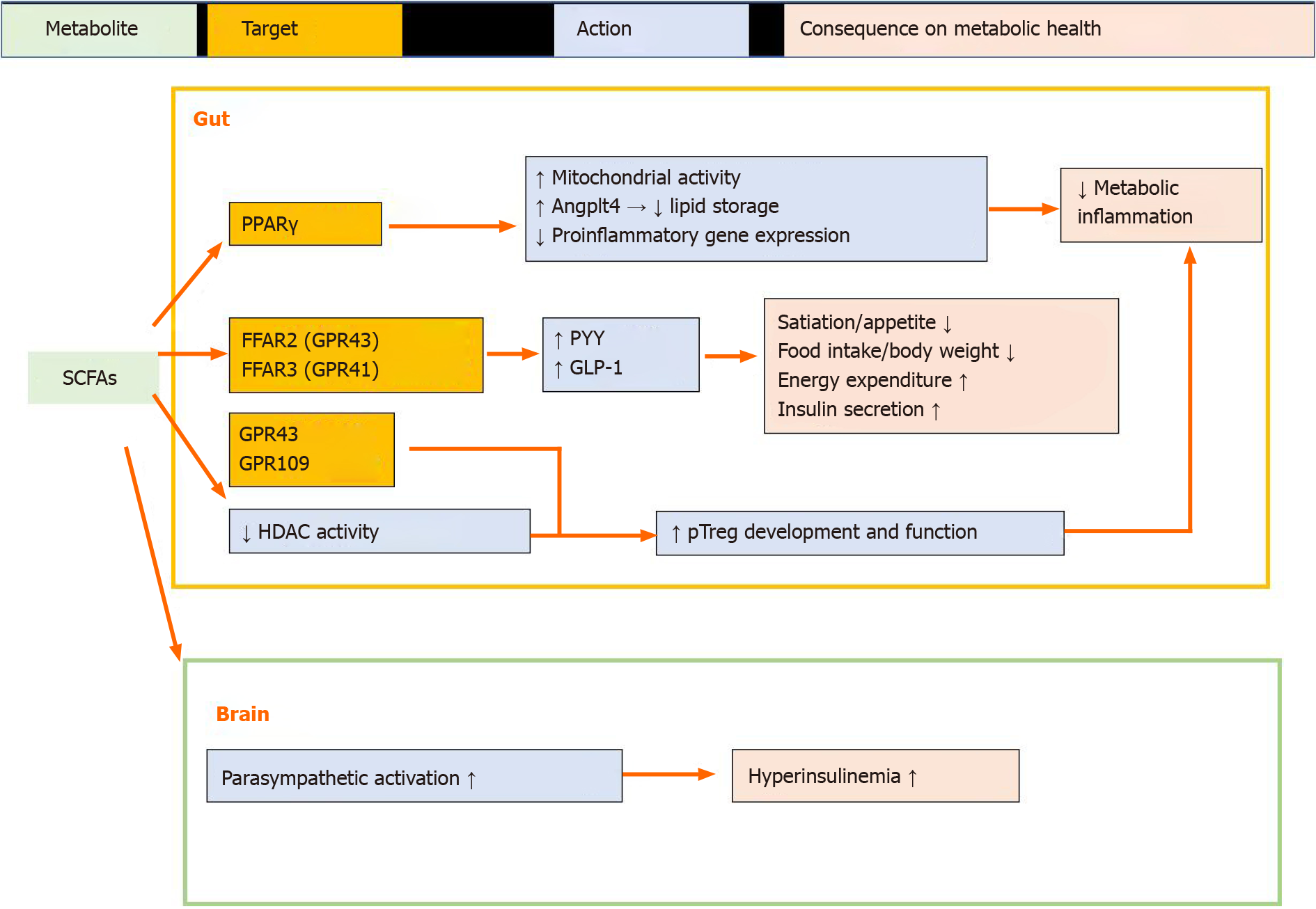
Figure 1 The roles of short-chain fatty acids in mucosal homeostasis and metabolic health.
Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) can engage various molecular targets in the gut, and play positive roles in maintaining mucosal barrier integrity and systemic metabolic health via regulating gut epithelial cell metabolic programming by activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma signals, maintaining immune homeostasis by promoting peripheral regulatory T helper cell development and functions, and stimulating energy expenditure and insulin secretion by releasing the gut hormones peptide tyrosine and glucagon-like peptide-1. SCFAs also exert some negative influences on host metabolic health via the gut–brain axis. Angplt4: Angiopoietin-like protein 4; FFAR: Free fatty acid receptor; GLP-1: Glucagon-like peptide-1; GPR: G-coupled receptor; HDAC: Histone deacetylase; PPAR: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; pTreg: Peripheral regulatory T helper cell; PYY: Peptide tyrosine.
- Citation: Wei YX, Zheng KY, Wang YG. Gut microbiota-derived metabolites as key mucosal barrier modulators in obesity. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(33): 5555-5565
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i33/5555.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i33.5555