Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2021; 27(30): 5019-5036
Published online Aug 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i30.5019
Published online Aug 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i30.5019
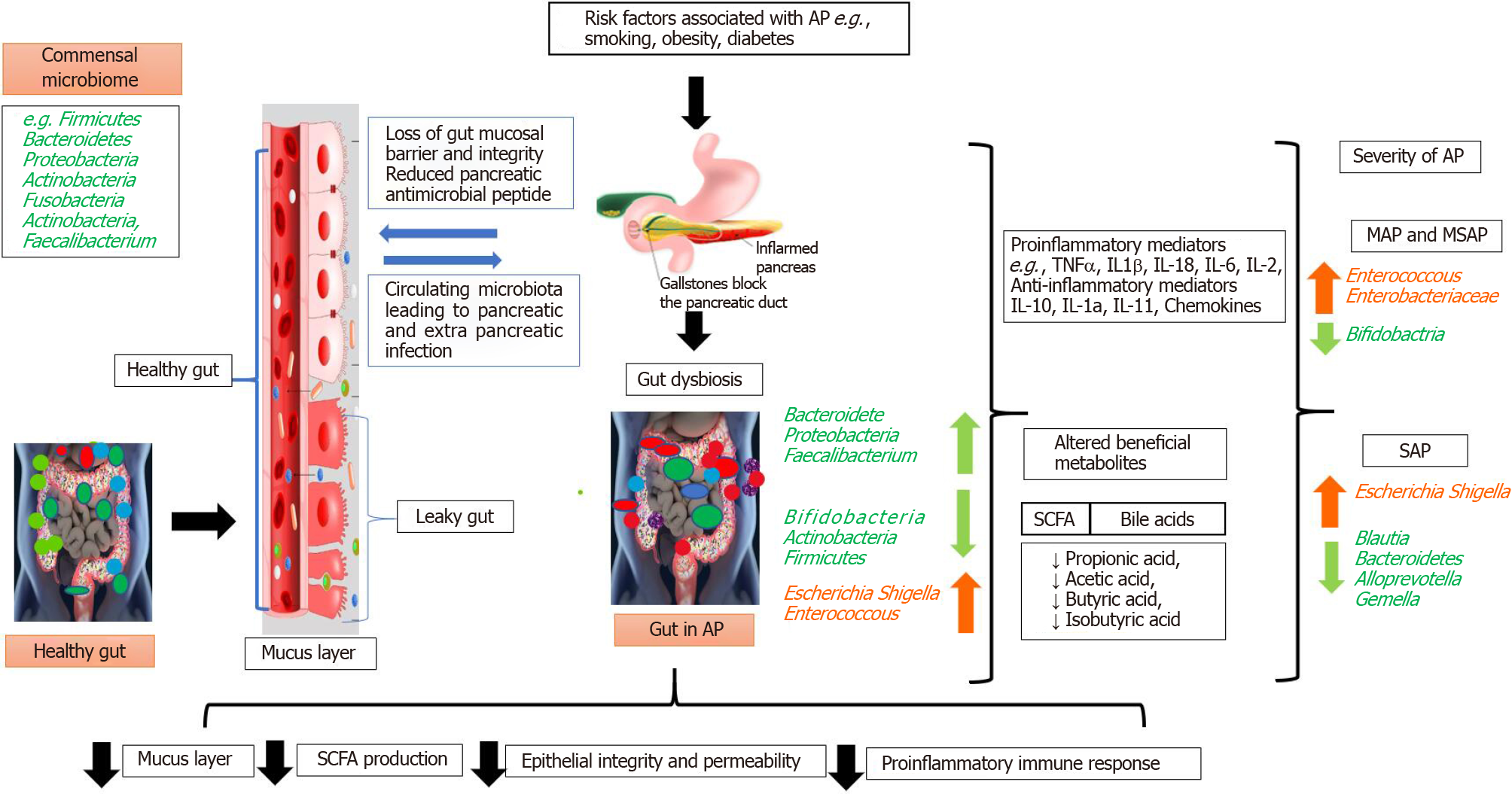
Figure 2 Role of the gut microbiota in inflammation of the pancreas and acute pancreatitis.
Breakdown of the relationship between physiologic and pathogenic bacteria, the immune system, and the intestinal epithelial barrier leads to gut dysbiosis. Inflammation and gut dysbiosis causes the translocation of microbes to the pancreas. The translocation of bacteria results in pancreatic inflammation due to toxin diffusion and complications like fibrosis, digestive and absorption disorders, diabetes, and other metabolic disorders. AP: Acute pancreatitis; MAP: Mild acute pancreatitis; MSAP: Moderate severe acute pancreatitis; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; IL: Interleukin; SAP: Severe acute pancreatitis; SCFA: Short-chain fatty acids.
- Citation: Patel BK, Patel KH, Bhatia M, Iyer SG, Madhavan K, Moochhala SM. Gut microbiome in acute pancreatitis: A review based on current literature. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(30): 5019-5036
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i30/5019.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i30.5019