Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 21, 2021; 27(3): 294-304
Published online Jan 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i3.294
Published online Jan 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i3.294
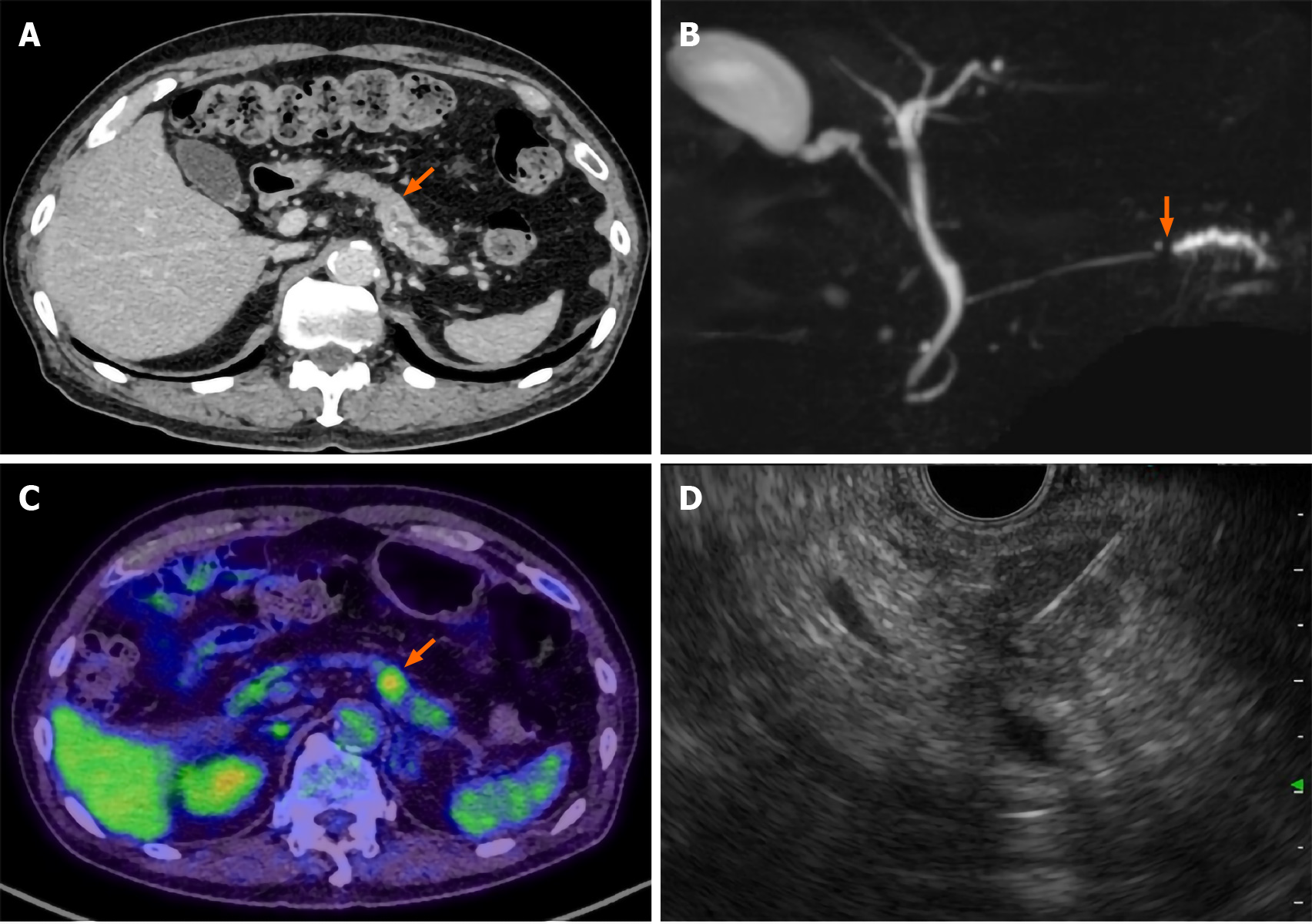
Figure 1 Pre-operative imaging findings.
A: Contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) scan showing a hypodense mass lesion (arrow) in the pancreatic tail region as well as dilation of the main pancreatic duct; B: Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography showing obstruction (arrow) and dilation of the main pancreatic duct; C: Positron emission tomography-CT scan showing the high uptake (arrow) of fluorodeoxyglucose by the pancreatic tail mass; D: Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration performed using a 22-gauge needle through the posterior gastric wall.
- Citation: Kojima H, Kitago M, Iwasaki E, Masugi Y, Matsusaka Y, Yagi H, Abe Y, Hasegawa Y, Hori S, Tanaka M, Nakano Y, Takemura Y, Fukuhara S, Ohara Y, Sakamoto M, Okuda S, Kitagawa Y. Peritoneal dissemination of pancreatic cancer caused by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration: A case report and literature review. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(3): 294-304
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i3/294.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i3.294