Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 21, 2021; 27(3): 281-293
Published online Jan 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i3.281
Published online Jan 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i3.281
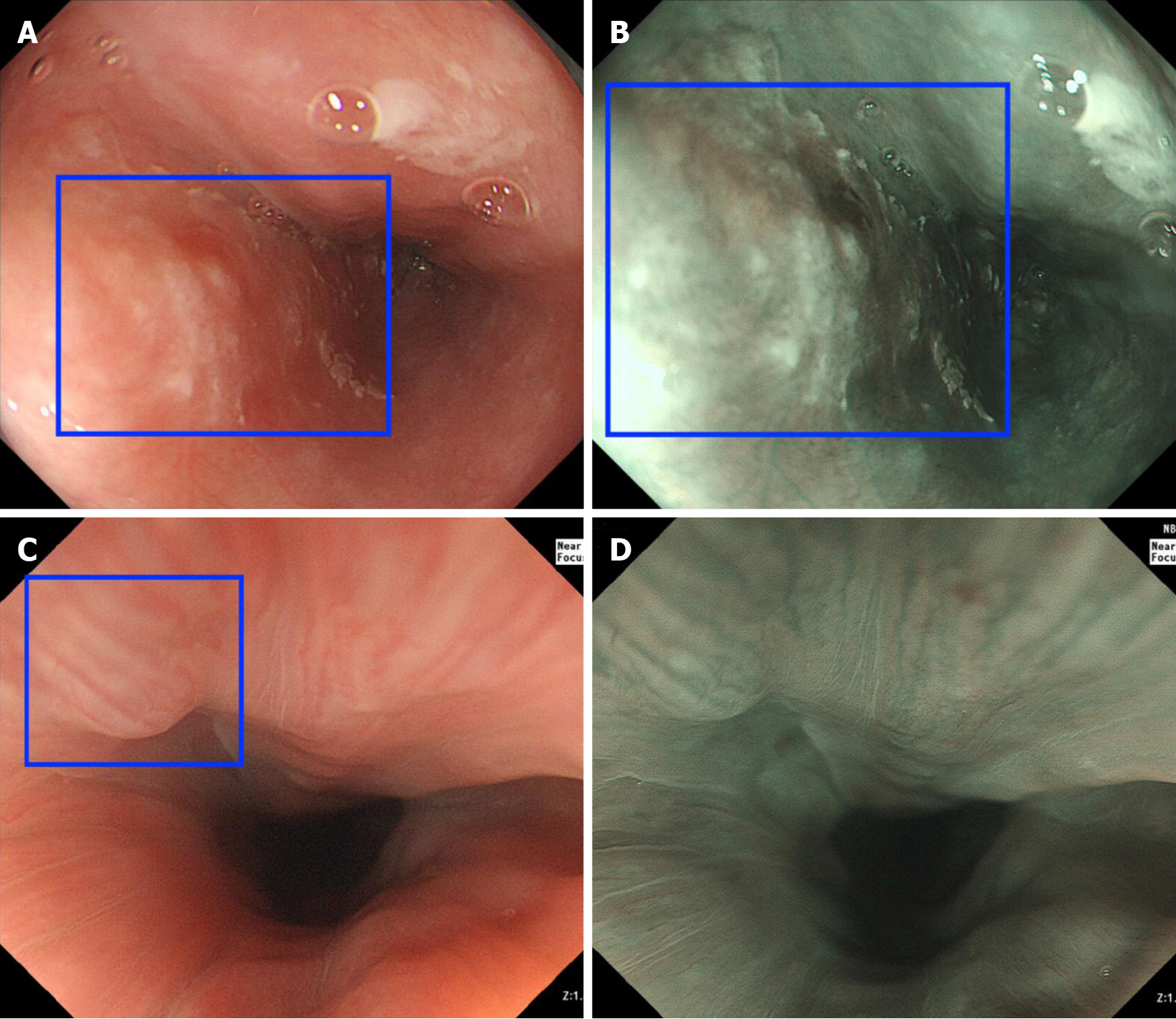
Figure 4 Examples of computer-assisted detection system-diagnosed images.
A and B: under white-light imaging (WLI) and narrow-band imaging (NBI), computer-assisted detection (CAD)-WLI and CAD-NBI recognized the esophageal cancer lesion (blue square); C and D: CAD-WLI mistakenly identified the normal mucosa as a lesion (blue square) in WLI, while CAD-NBI corrected it in NBI.
- Citation: Li B, Cai SL, Tan WM, Li JC, Yalikong A, Feng XS, Yu HH, Lu PX, Feng Z, Yao LQ, Zhou PH, Yan B, Zhong YS. Comparative study on artificial intelligence systems for detecting early esophageal squamous cell carcinoma between narrow-band and white-light imaging. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(3): 281-293
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i3/281.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i3.281