Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2021; 27(28): 4504-4535
Published online Jul 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i28.4504
Published online Jul 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i28.4504
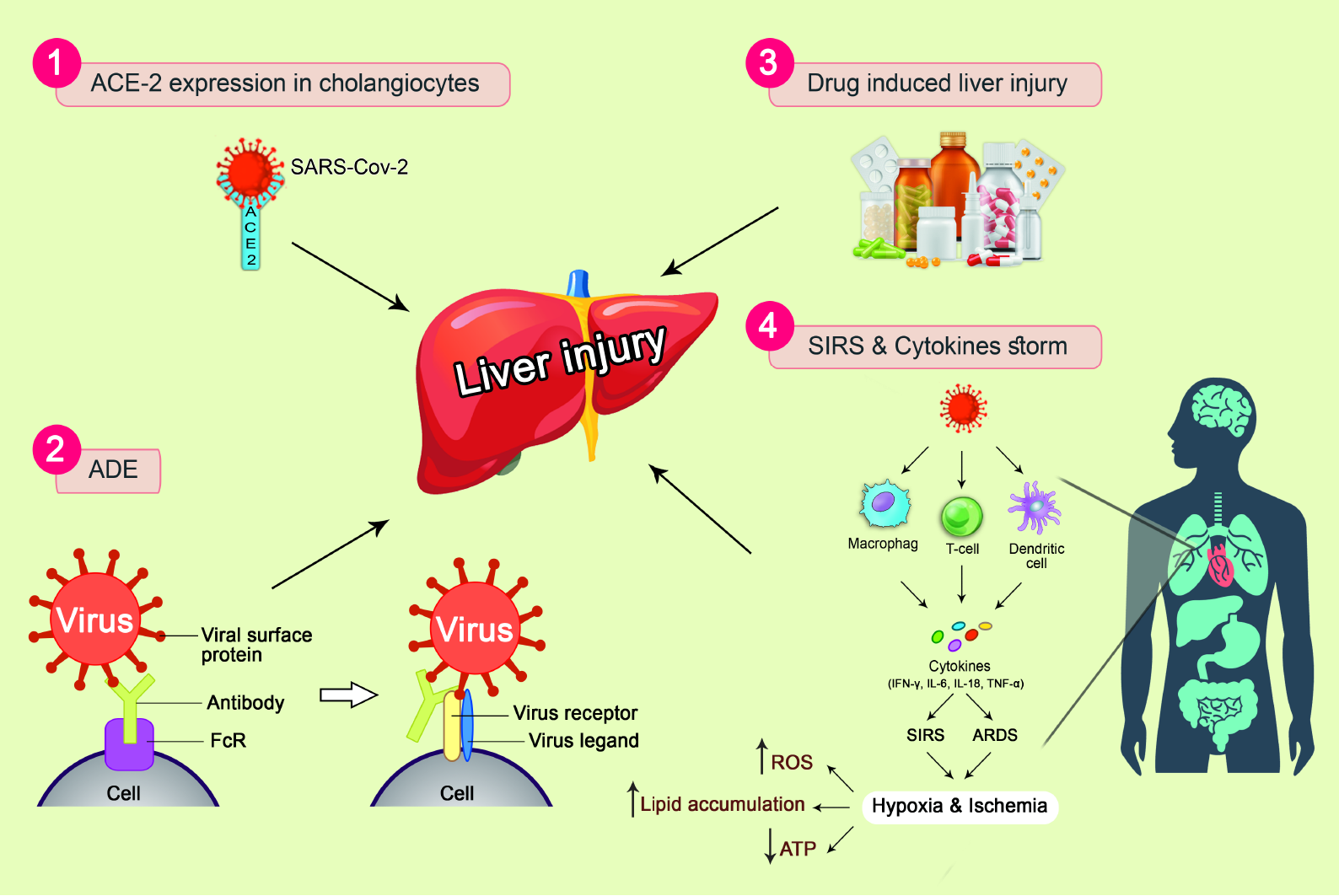
Figure 5 Mechanisms of liver injury in patients with coronavirus disease 2019.
(1) Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2-mediated targeting of cholangiocytes; (2) Antibody-dependent enhancement of infection; (3) Systemic inflammatory response syndrome and cytokine storms; and (4) Drug-induced liver injury. SARS-CoV-2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; ACE2: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; ADE: Antibody-dependent enhancement of infection; SIRS: Systemic inflammatory response syndrome; ARDS: Acute respiratory distress syndrome; IFN-γ: Interferon-γ; IL-6: Interleukin-6; IL-18: Interleukin-18; TNF-α; Tumor necrosis factor-α; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; ATP: Adenosine triphosphate.
- Citation: Mohamed DZ, Ghoneim MES, Abu-Risha SES, Abdelsalam RA, Farag MA. Gastrointestinal and hepatic diseases during the COVID-19 pandemic: Manifestations, mechanism and management. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(28): 4504-4535
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i28/4504.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i28.4504