Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2021; 27(27): 4322-4341
Published online Jul 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i27.4322
Published online Jul 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i27.4322
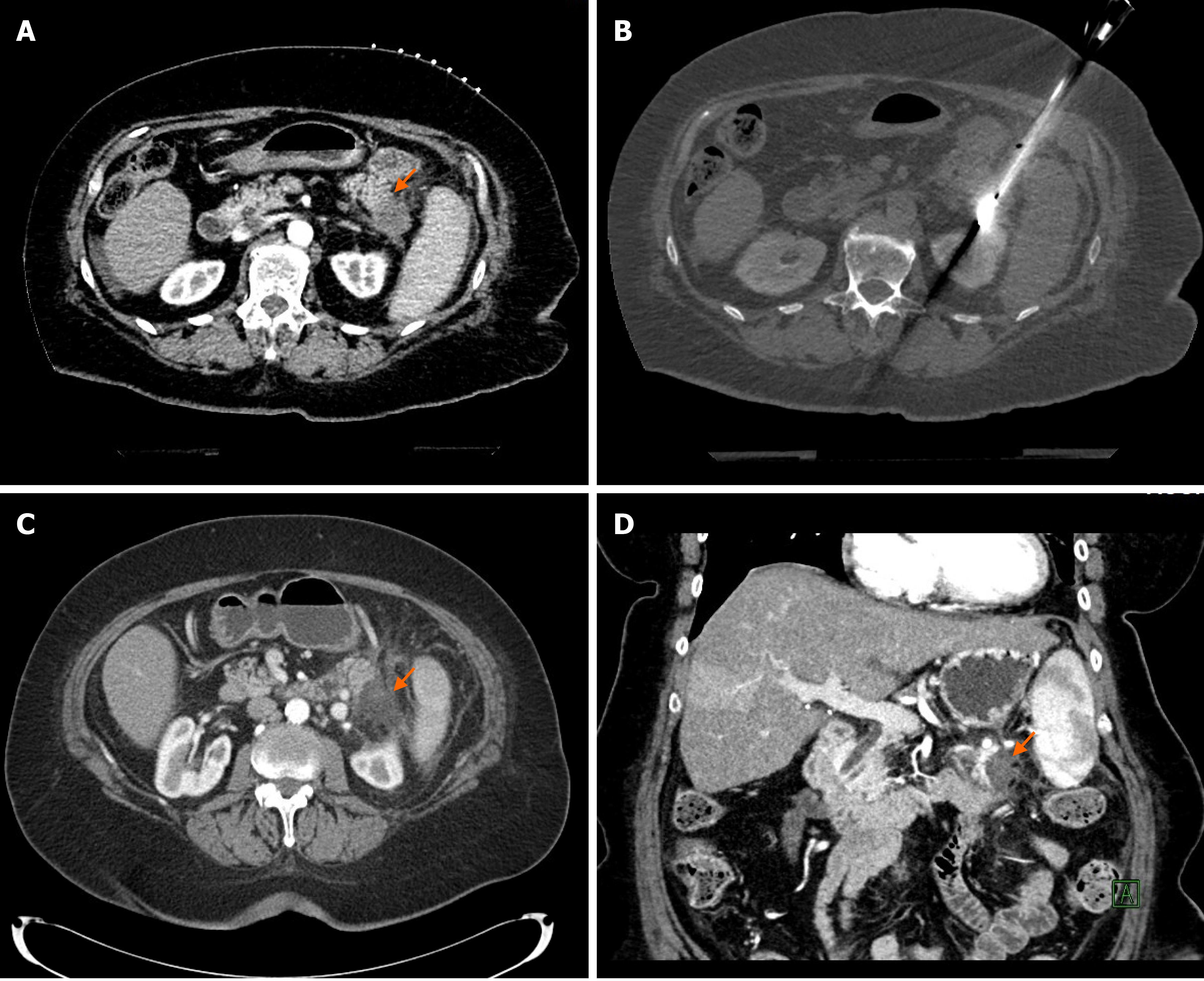
Figure 1 Percutaneous computed tomography-guided microwave ablation of a pancreatic tail adenocarcinoma.
A: 72-year-old patient presented with a 1.9 cm biopsy-proven pancreatic adenocarcinoma in the tail of the pancreas as it shown on this contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) image (orange arrow); B: The patient was not surgical candidate due to comorbidities and underwent percutaneous CT-guided microwave ablation (MWA) of the pancreatic tumor. CT image shows the microwave antenna in place in the pancreatic tail tumor; C and D: Axial and coronal contrast-enhanced CT images 6 wk after the MWA show good radiological response with an avascular area in the tail of the pancreas corresponding to the ablation zone (orange arrows). Patient developed peritoneal metastases 4 mo later and died 13 mo after the MWA treatment.
- Citation: Bibok A, Kim DW, Malafa M, Kis B. Minimally invasive image-guided therapy of primary and metastatic pancreatic cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(27): 4322-4341
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i27/4322.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i27.4322