Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2021; 27(25): 3851-3862
Published online Jul 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i25.3851
Published online Jul 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i25.3851
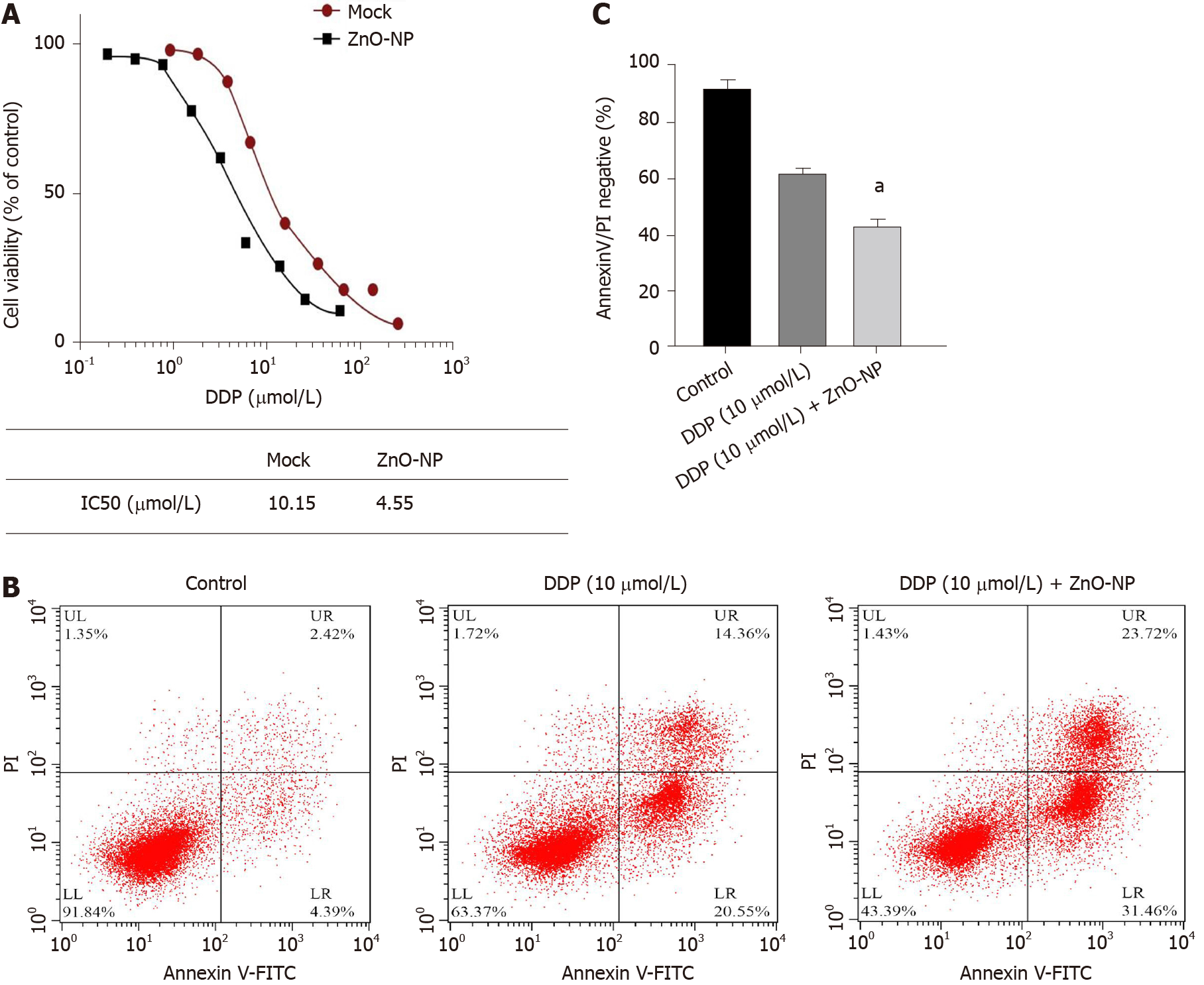
Figure 3 Zinc oxide nanoparticle attenuates the chemotherapy drug resistance of gastric cancer cells.
A: SGC7901/cisplatin (DDP) cells were treated with DDP at the indicated doses and treated with zinc oxide nanoparticle (ZnO-NP, 5 μg/mL) or an equal volume of saline. Cell viability was measured by the MTT assay; B and C: SGC7901/DDP cells were treated with DDP or co-treated with DDP and ZnO-NP (5 μg/mL). Cell apoptosis was assessed by flow cytometry. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. Statistically significant differences are indicated: ns, no significance, aP < 0.05. FITC: Fluorescein isothiocyanate.
- Citation: Miao YH, Mao LP, Cai XJ, Mo XY, Zhu QQ, Yang FT, Wang MH. Zinc oxide nanoparticles reduce the chemoresistance of gastric cancer by inhibiting autophagy. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(25): 3851-3862
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i25/3851.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i25.3851