Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2021; 27(24): 3581-3594
Published online Jun 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i24.3581
Published online Jun 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i24.3581
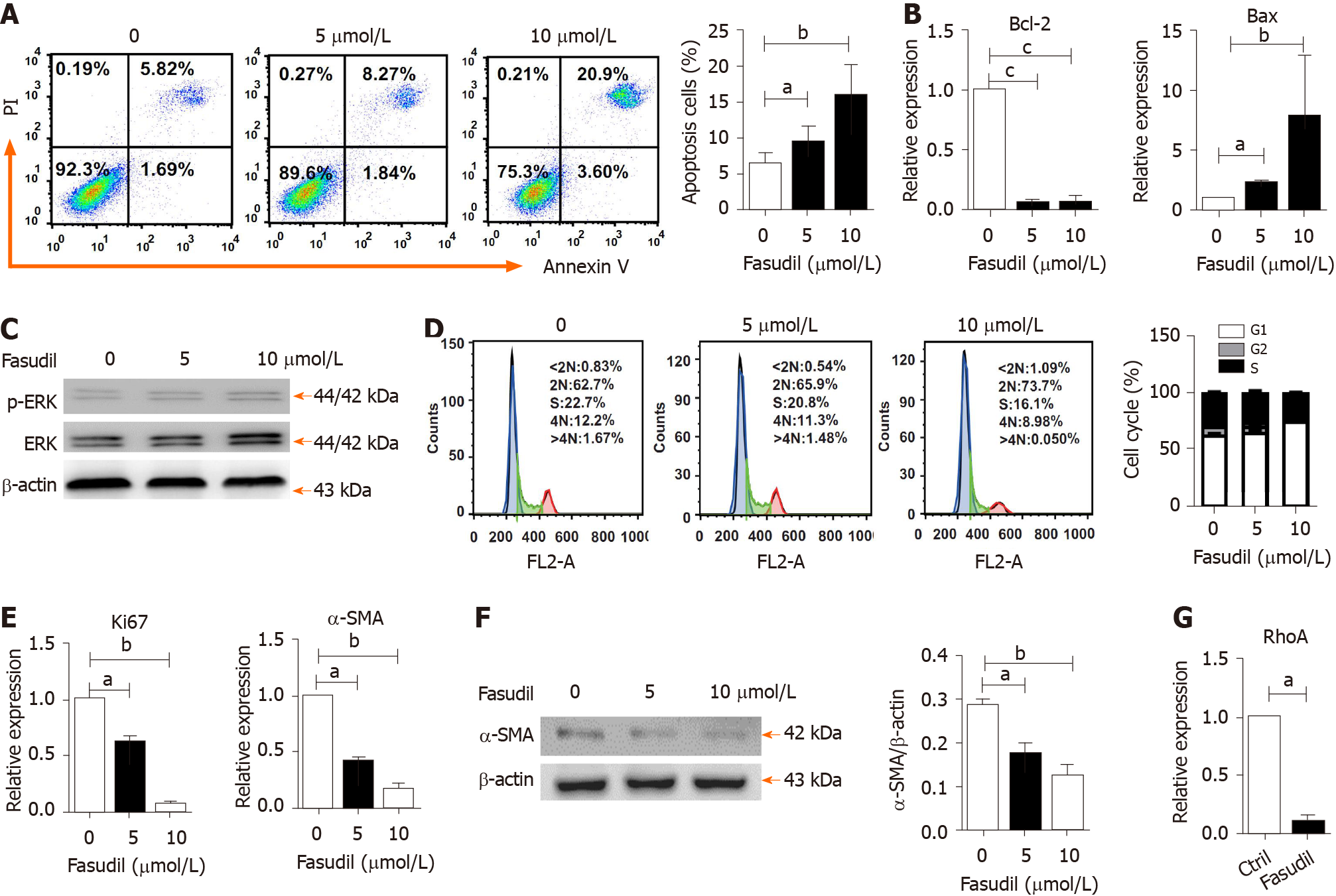
Figure 5 Fasudil inhibits the proliferation but promotes the apoptosis of hepatic stellate cells.
A: LX2 cells were treated with different concentrations of Fasudil (5 mM, 10 mM) for 24 h in vitro; B: The apoptosis of LX2 cells was analyzed by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS). mRNA levels of B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) and Bcl-2-associated X protein (Bax) in LX2 cells were detected by quantitative real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR); C: The phosphorylated extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK)/ERK levels in LX2 cells were detected by western blotting. The cell cycle of LX2 cells was analyzed by FACS; D: Left panel shows the representative FACS plots of cell cycle, and right panel shows the quantification of percentage of cells in G1, S and G2 phase; E: Relative expression level of Ki67 and alpha smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) mRNA in LX2 cells was analyzed by qRT-PCR; F: α-SMA level in LX2 cells was analyzed by western blotting; G: mRNA levels of Ras homology family member A in LX2 cells were analyzed by qRT-PCR. Data represent the mean ± SD from at least three independent experiments. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001.
- Citation: Han QJ, Mu YL, Zhao HJ, Zhao RR, Guo QJ, Su YH, Zhang J. Fasudil prevents liver fibrosis via activating natural killer cells and suppressing hepatic stellate cells. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(24): 3581-3594
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i24/3581.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i24.3581