Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2021; 27(24): 3581-3594
Published online Jun 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i24.3581
Published online Jun 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i24.3581
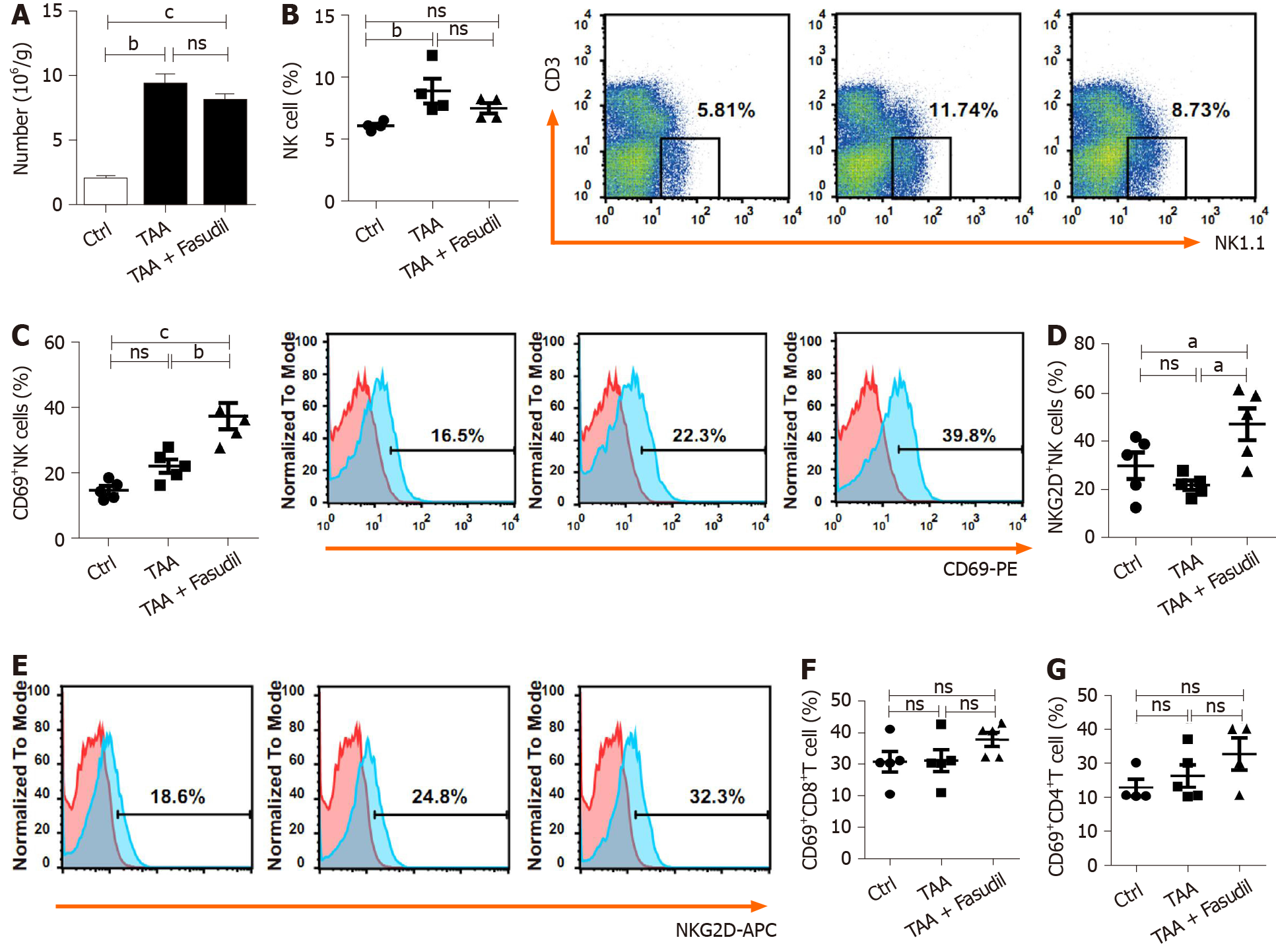
Figure 3 Natural killer cells are activated in a Fasudil-treated liver fibrotic mouse model.
After the last treatment, the mice were sacrificed and the intrahepatic lymphocytes were isolated. A: Absolute number of mononuclear cells in the liver from the normal control, thioacetamide (TAA)-induced, and TAA + Fasudil groups was assessed; B-G: Then the percentages and representative fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) plots of natural killer (NK) cells among lymphocytes (B), CD69+ NK cells and representative FACS plots (C), quantification of NKG2D+ NK cells (D), representative FACS plots of NKG2D on NK cells (E), CD69+CD8+ T cells (F) and CD69+CD4+ T cells (G) in liver from the above three groups were analyzed by FACS. Data represent the mean ± SD from at least three independent experiments (n = 5/group). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001.
- Citation: Han QJ, Mu YL, Zhao HJ, Zhao RR, Guo QJ, Su YH, Zhang J. Fasudil prevents liver fibrosis via activating natural killer cells and suppressing hepatic stellate cells. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(24): 3581-3594
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i24/3581.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i24.3581