Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2021; 27(24): 3581-3594
Published online Jun 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i24.3581
Published online Jun 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i24.3581
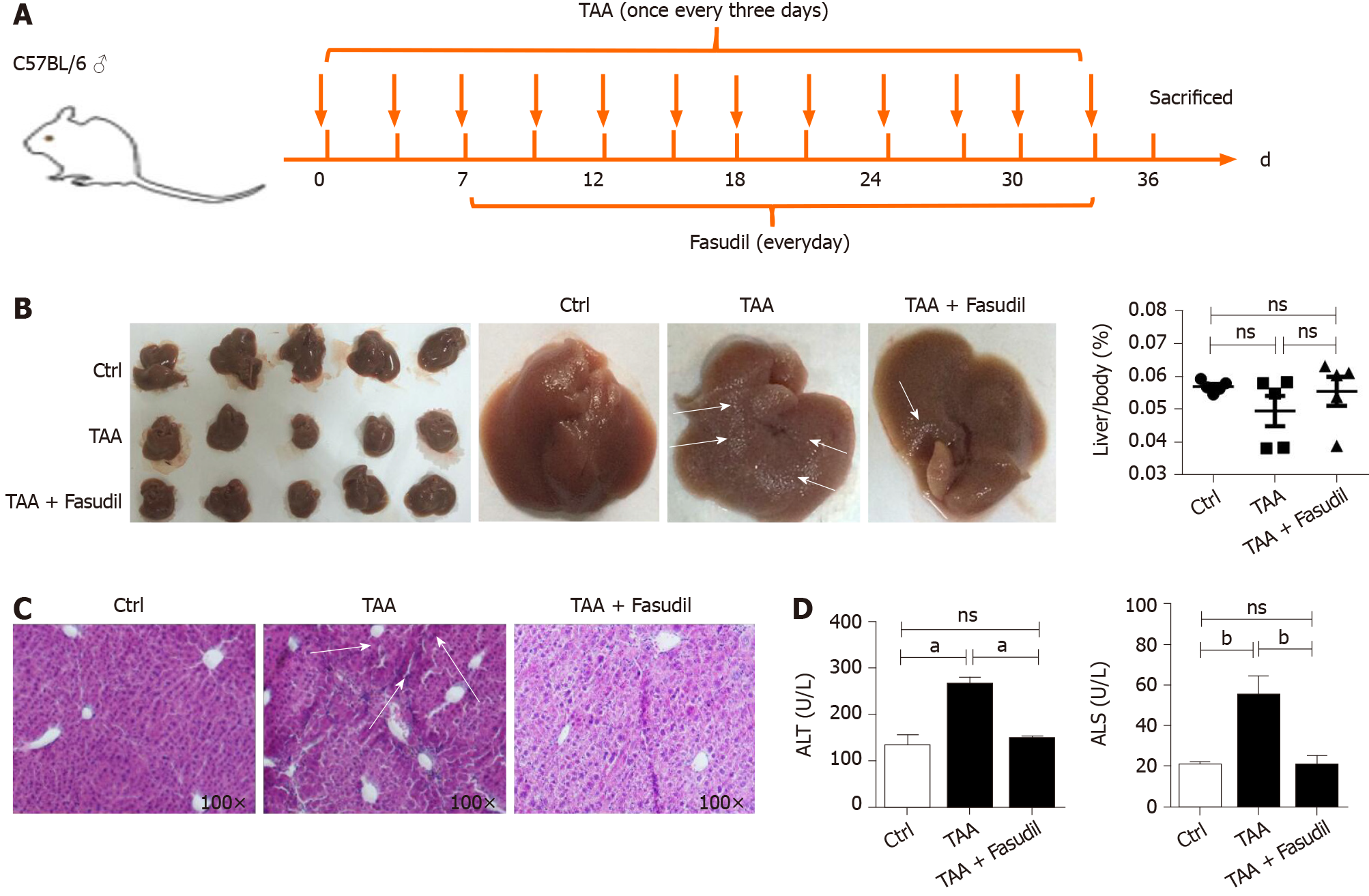
Figure 1 Fasudil protects thioacetamide-induced liver injury.
A: Establishment of a liver fibrosis mouse model; B: Representative detection of liver images is shown. Gross pathological examination of liver taken from normal control, thioacetamide (TAA)-treated, and TAA + Fasudil-treated groups, and the liver/body ratio was assayed among these three groups; C: Histological observation of liver fibrosis by hematoxylin and eosin staining under light-field microscope with × 100 magnification; D: Enzyme-linked immunoassay was used to assess the level of serum alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase. Data represent the mean ± SD from at least three independent experiments (n = 5/group). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01.
- Citation: Han QJ, Mu YL, Zhao HJ, Zhao RR, Guo QJ, Su YH, Zhang J. Fasudil prevents liver fibrosis via activating natural killer cells and suppressing hepatic stellate cells. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(24): 3581-3594
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i24/3581.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i24.3581