Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2021; 27(24): 3483-3501
Published online Jun 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i24.3483
Published online Jun 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i24.3483
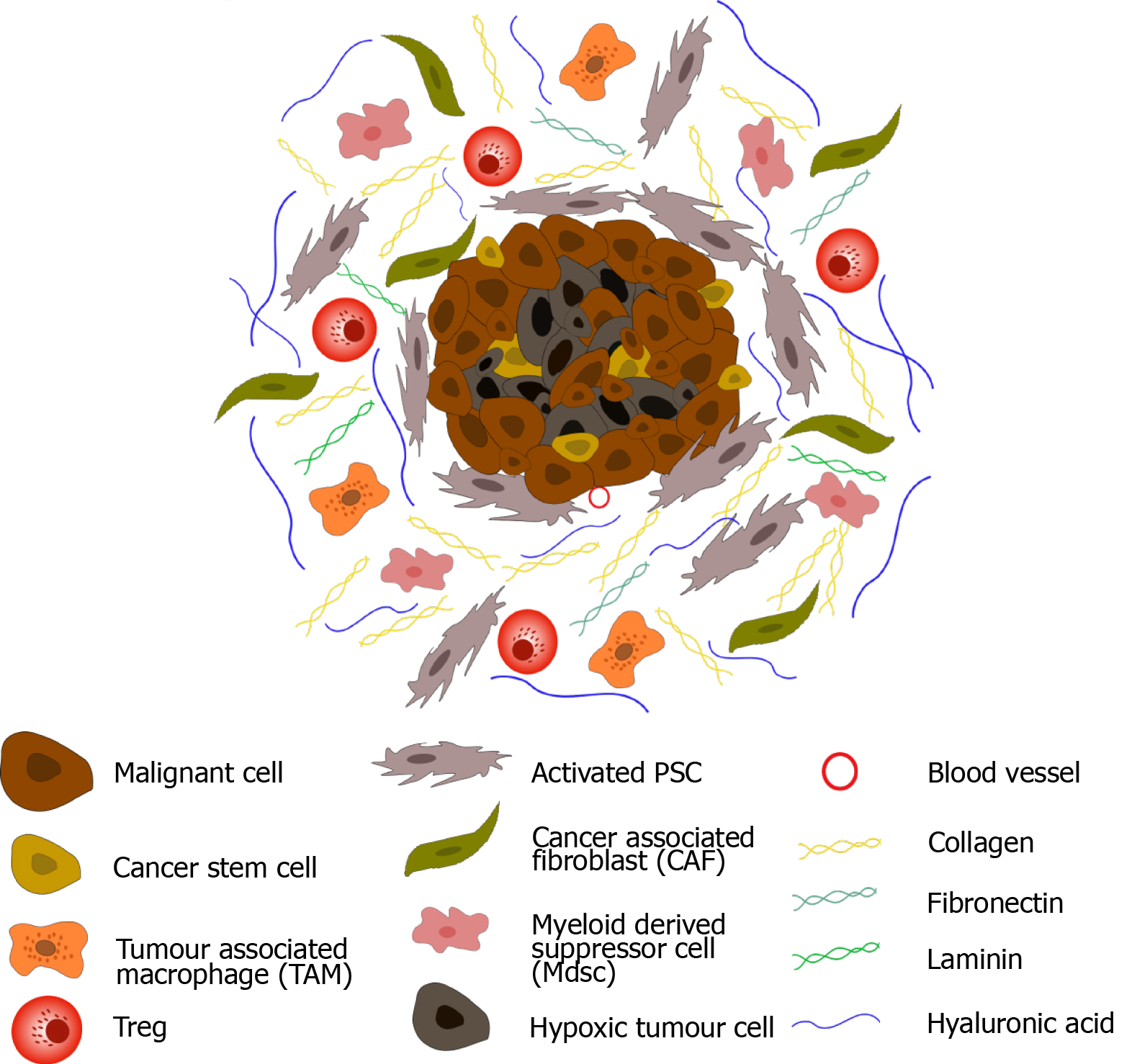
Figure 1 Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma tumour microenvironment.
Upon activation, pancreatic stellate cells secrete an abundance of extracellular matrix proteins including collagen, fibronectin, laminin, and hyaluronic acid, leading to dense desmoplasia. In addition, fibroblastic cells (CAFs) become active, and immune suppressive cells (myeloid-derived suppressor cells, regulatory T-cells and tumour associated macrophages) are sequestered to the tumour microenvironment (TME). Secretion of anti-angiogenic factors, in addition to dense desmoplasia, results in the development of a hypoxic TME. Cancer stem cells are also observed in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
- Citation: Fincham REA, Delvecchio FR, Goulart MR, Yeong JPS, Kocher HM. Natural killer cells in pancreatic cancer stroma. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(24): 3483-3501
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i24/3483.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i24.3483