Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2021; 27(23): 3327-3341
Published online Jun 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i23.3327
Published online Jun 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i23.3327
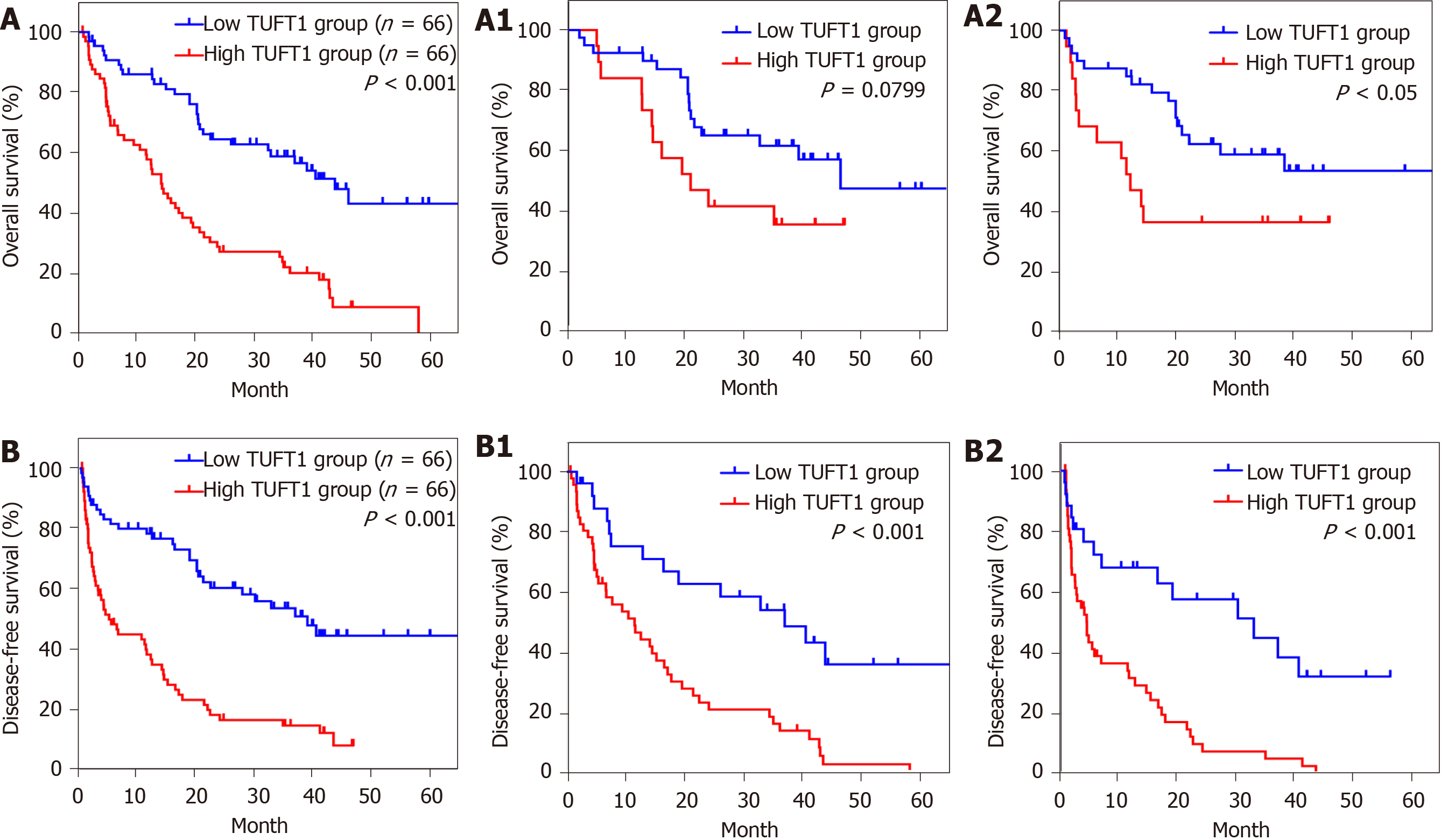
Figure 3 Relationship between tuftelin 1 expression and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma.
A: Kaplan-Meier analysis was performed to compare the overall survival (OS) between hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with high (n = 66) and low (n = 66) TUFT1; A1: The high (n = 19) and low (n = 40) tuftelin 1 (TUFT1) with OS at early HCC; A2: The high (n = 47) and low (n = 26) TUFT1 with OS at advanced HCC; B: Kaplan-Meier analysis was performed to compare the disease-free survival (DFS) between HCC with high (n = 66) and low (n = 66) TUFT1; B1: The high (n = 19) and low (n = 40) TUFT1 with DFS at early HCC; B2: The high (n = 47) and low (n = 26) TUFT1 with DFS at advanced HCC.
- Citation: Wu MN, Zheng WJ, Ye WX, Wang L, Chen Y, Yang J, Yao DF, Yao M. Oncogenic tuftelin 1 as a potential molecular-targeted for inhibiting hepatocellular carcinoma growth. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(23): 3327-3341
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i23/3327.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i23.3327