Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2021; 27(23): 3208-3222
Published online Jun 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i23.3208
Published online Jun 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i23.3208
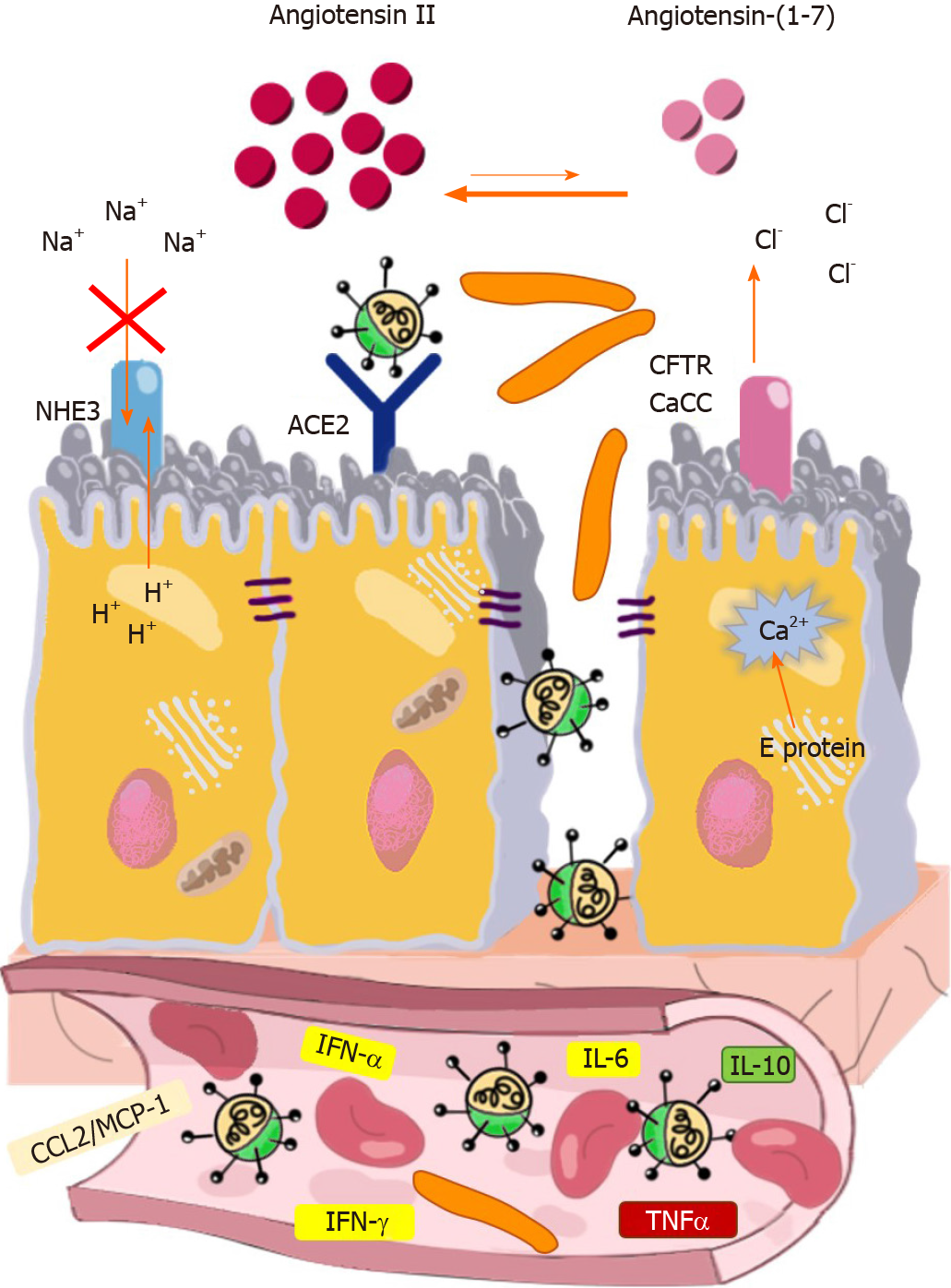
Figure 1 Mechanism involved in coronavirus disease 2019-associated diarrhea.
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) binds to its corresponding cell-surface receptor, angiotensin-converting enzyme type 2. In the intestines, SARS-CoV-2 viroporins, E protein, dysregulation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system triggering ionic imbalance, disruption of barrier integrity and inflammation play important roles in the development of coronavirus disease 2019-associated secretory diarrhea and leaky gut. ACE: Angiotensin-converting enzyme; IFN: Interferon; IL: Interleukin; TNFα: tumor necrosis factor alpha; CFTR: CF transmembrane conductance regulator; CaCC: Ca2+-activated Cl- channel; NHE3: Na+-H+ exchanger 3.
- Citation: Megyeri K, Dernovics Á, Al-Luhaibi ZII, Rosztóczy A. COVID-19-associated diarrhea. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(23): 3208-3222
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i23/3208.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i23.3208