Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2021; 27(22): 2994-3009
Published online Jun 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i22.2994
Published online Jun 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i22.2994
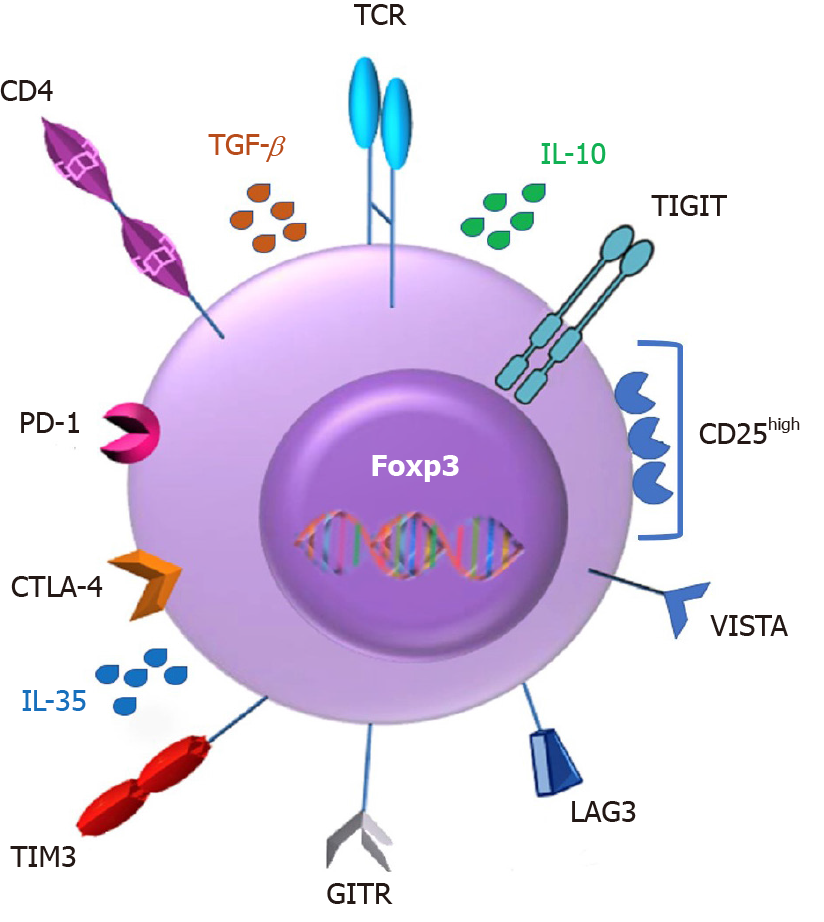
Figure 2 Regulatory T cells are recognized as CD4+CD25high positive and Foxp3+ expressing cells.
They feature a range of other phenotypic markers such as T-cell immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domains, glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor-related protein, cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4, programmed cell-death 1 receptor, V-domain Ig suppressor of T cell activation, lymphocyte activation gene-3, T cell immunoglobulin mucin 3. Upon activation, Tregs release the inhibitory cytokines interleukin (IL)-10, transforming growth factor β and IL-35. TCR: T-cell receptor; IL: Interleukin; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor β; TIGIT: T-cell immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domains; VISTA: V-domain Ig suppressor of T cell activation; LAG3: Lymphocyte activation gene-3; GITR: Glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor-related protein; TIM3: T cell immunoglobulin mucin 3; CTLA-4: Cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4; PD-1: Programmed cell-death 1 receptor.
- Citation: Granito A, Muratori L, Lalanne C, Quarneti C, Ferri S, Guidi M, Lenzi M, Muratori P. Hepatocellular carcinoma in viral and autoimmune liver diseases: Role of CD4+ CD25+ Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in the immune microenvironment. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(22): 2994-3009
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i22/2994.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i22.2994