Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2021; 27(21): 2850-2870
Published online Jun 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i21.2850
Published online Jun 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i21.2850
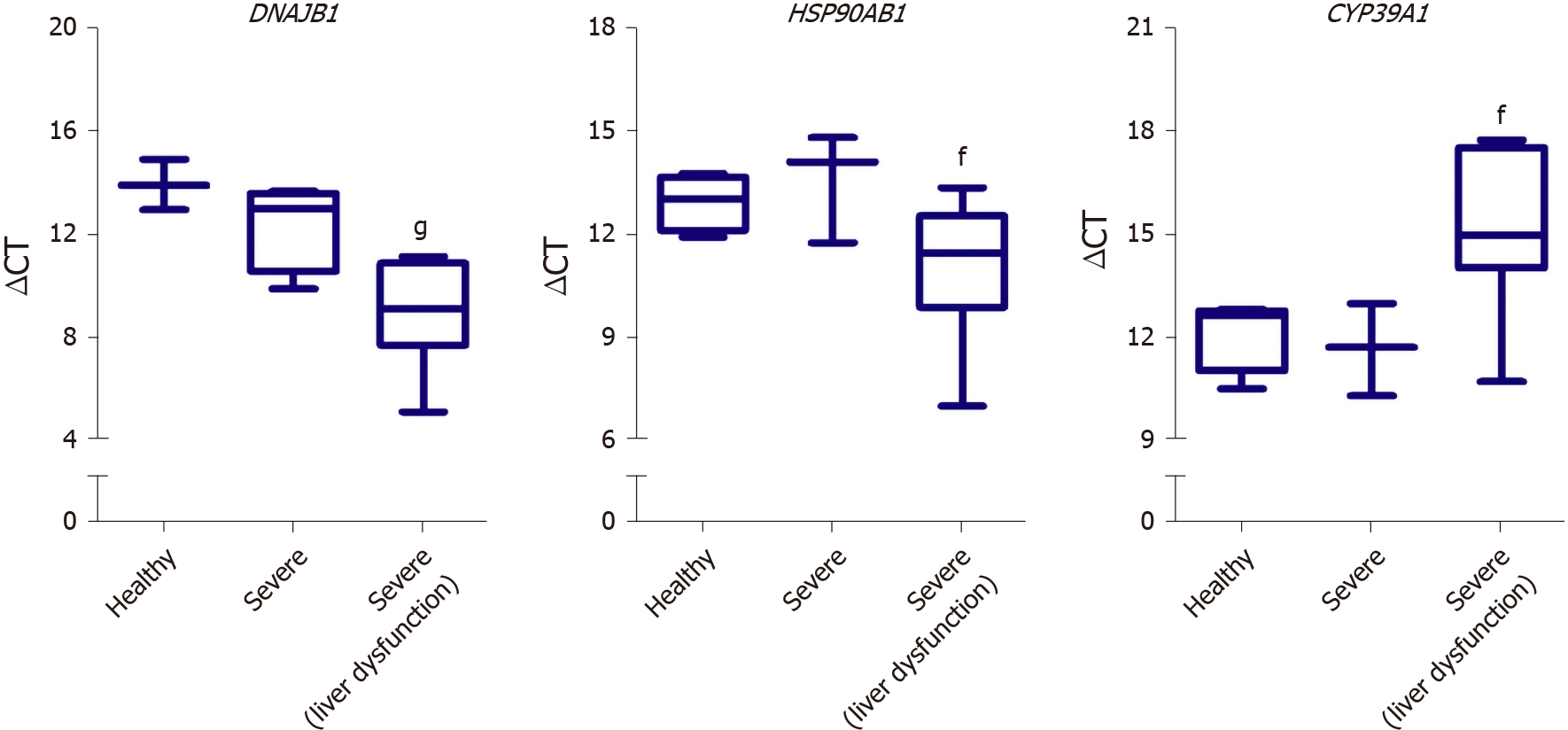
Figure 8 Validation of differentially expressed genes identified from the RNA-seq analysis of the severe coronavirus disease 2019 patients liver samples using blood plasma samples of severe coronavirus disease 2019 patients.
Box plot representation of the gene expression of DNAJB1, HSP90AB1, and CYP39A1 in the blood plasma of severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients without liver dysfunction (Severe) or with liver dysfunction (Severe (liver dysfunction)) in comparison to non-COVID-19 controls (Healthy); The expression was detected in 4 healthy samples (DNAJB1 expression was only detected in 3 samples), 4 severe COVID-19 samples, and 9 severe COVID-19 samples with liver dysfunction (CYP39A1 expression was only detected in 8 samples); Data presented as mean ± SE; fP < 0.05, gP < 0.001 Severe with liver dysfunction vs Healthy. DNAJB1: DnaJ heat shock protein family (Hsp40) member B1; HSP90AB1: Heat shock protein 90 alpha family class B member 1; CYP39A1: Cytochrome P450 family 39 subfamily A member 1.
- Citation: Hammoudeh SM, Hammoudeh AM, Bhamidimarri PM, Mahboub B, Halwani R, Hamid Q, Rahmani M, Hamoudi R. Insight into molecular mechanisms underlying hepatic dysfunction in severe COVID-19 patients using systems biology. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(21): 2850-2870
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i21/2850.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i21.2850